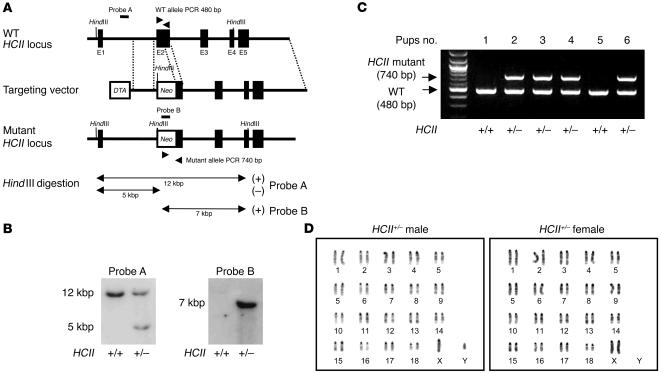
Figure 1. Targeted disruption of murine HCII gene, genotyping, and karyotypes of HCII-mutant mice.
(A) Genomic locus, targeting vector, and predicted targeting locus are illustrated. External (probe A) and internal (probe B) probes were used for Southern blot analysis. Two sets of PCR primers for detecting the 480-bp WT allele and 740-bp mutant allele were employed for genotyping. (B) Southern blot analysis of murine genomic DNA. A 5-kbp HindIII fragment denotes the homologous recombinant allele in probe A as an external probe, and a single 7-kbp HindIII fragment denotes the homologous recombinant allele without random integration in probe B as an internal probe. (C) Genotyping PCR. The mutant allele yielded a 740-bp band, and the WT allele yielded a 480-bp band. (D) Karyotype analysis of HCII+/– male and female mice. Chromosomes of splenic lymphocytes in both male and female HCII mutant mice showed normal karyotypes.