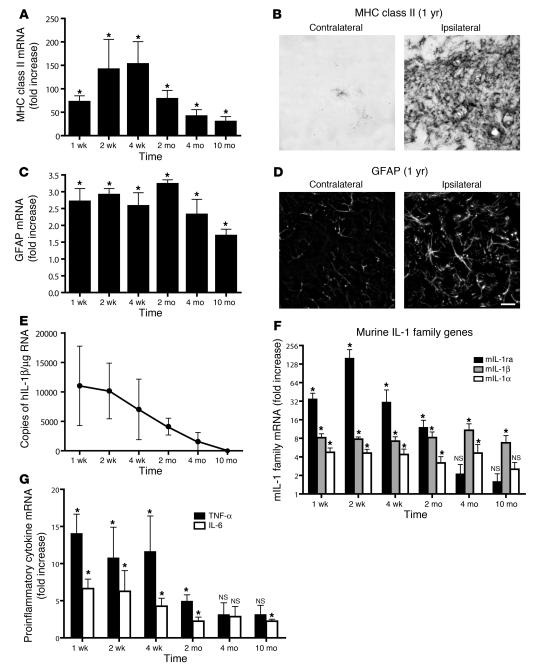
Figure 4. Transgene activation in the IL-1βXAT mouse elicits a chronic neuroinflammatory response.
IL-1βXAT B/b and WT control mice received intrahippocampal injections of FIV-Cre and were analyzed over a prolonged time course for neuroinflammatory indices. (A, C, F, and G) qRT-PCR generated a ratio of gene expression in the ipsilateral hippocampi of B/b compared with WT mice at the same time point, except for MHC class II analysis, in which the 4-week time point was used for all comparisons. (A) MHC class II expression was significantly upregulated at all time points assayed. (B) MHC class II staining in the dentate gyrus of a B/b mouse 1 year after FIV-Cre injection. (C) GFAP expression was also significantly upregulated at all time points examined. (D) GFAP expression in the dentate gyrus at 1 year. Scale bar: 20 μm. (E) GFAP and MHC class II upregulation coincided with prolonged expression of ssIL-1β. (F and G) In addition to glial activation markers, hIL-1β expression caused significant increases in qRT-PCR gene transcripts coding for all members of the mIL-1 family (F) and for proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α (G). n = 4–5 animals per group. Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 versus WT as described.