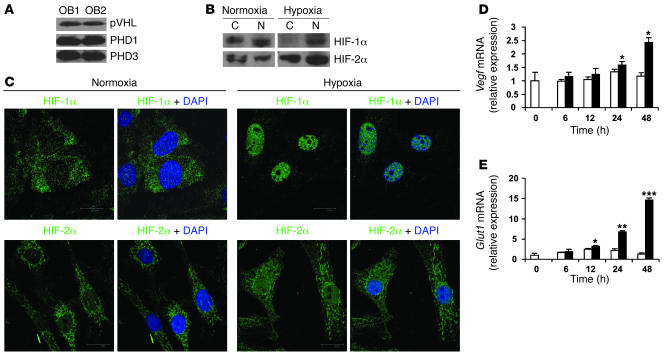
Figure 1. Primary mouse osteoblasts express components of the HIFα pathway.
(A) Calvarial primary osteoblasts were obtained from wild-type mice and cultured in α-MEM until confluent. Whole-cell lysate was analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies against pVHL (top), PHD1 (middle), and PHD3 (bottom) in experiments performed in duplicate. OB, osteoblast. (B and C) Confluent cell monolayers were exposed to 21% (normoxia) or 2% (hypoxia) O2 for 24 hours. (B) Proteins from cytoplasm (C) and nucleus (N) were extracted separately and analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against HIF-1α (top row) and HIF-2α (bottom row). (C) Nuclear translocation of HIF-1α (top row) and HIF-2α (bottom row) was assessed by confocal microscopy as described in Methods. DAPI was used to stain the nuclei. Original magnification, ×100. (D and E) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis was performed to determine Vegf and Glut1 mRNA expression after cell monolayers were exposed to normoxia (white bars) or hypoxia (black bars) for the indicated times. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.