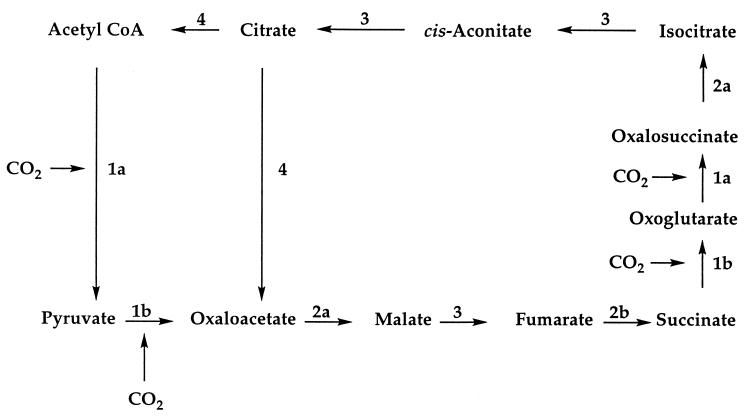
Figure 1.
The reductive (reverse) citric acid cycle adapted from the scheme in Morowitz et al. (13). The nature of the chemical steps is indicated as follows: 1a, introduction of CO2 and reduction to give an α-ketoacid; 1b, introduction of CO2 to give a β-ketoacid; 2a, reduction of a carbonyl group; 2b, reduction of a double bond; 3, reversible hydration/dehydration; and 4, cleavage of citrate to acetate and oxaloacetate.