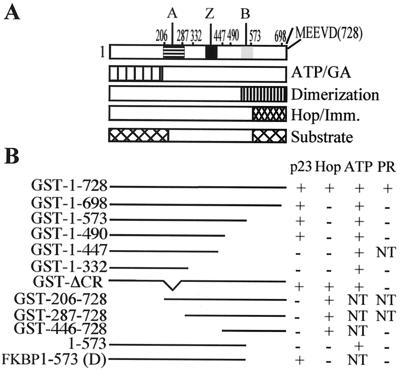
Figure 1.
Mutations and structural domains of hsp90. (A) The location of two highly charged regions (A, 206–287 and B, 548–563), a potential leucine zipper region (Z, 378–429), and the conserved MEEVD at the C terminus of hsp90. Regions that bind ATP/geldanamycin (GA) (12–14) or co-chaperones (8–11) plus two domains that have been proposed for substrate binding (29, 30) are also indicated. (B) The hsp90 constructs used in this study are illustrated plus a summary of their activities for binding p23, Hop, and, ATP or for chaperoning PR as active (+), not active (−) or not tested (NT).