Abstract
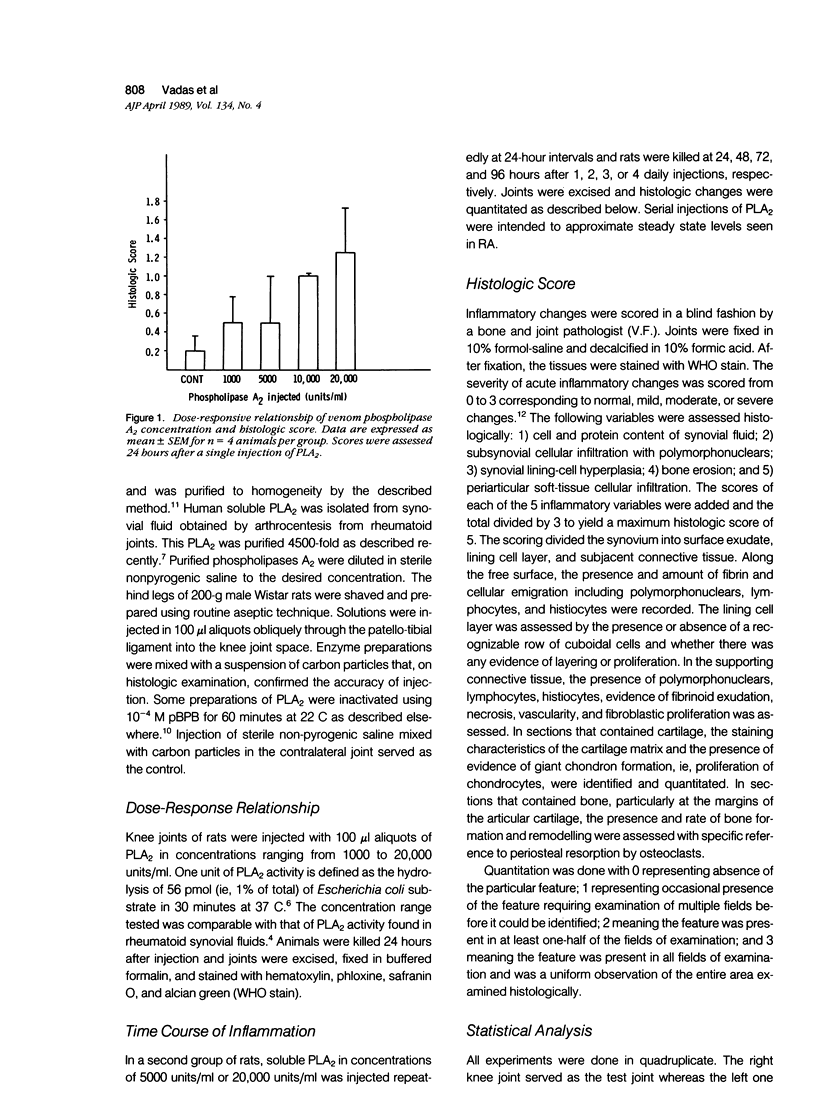
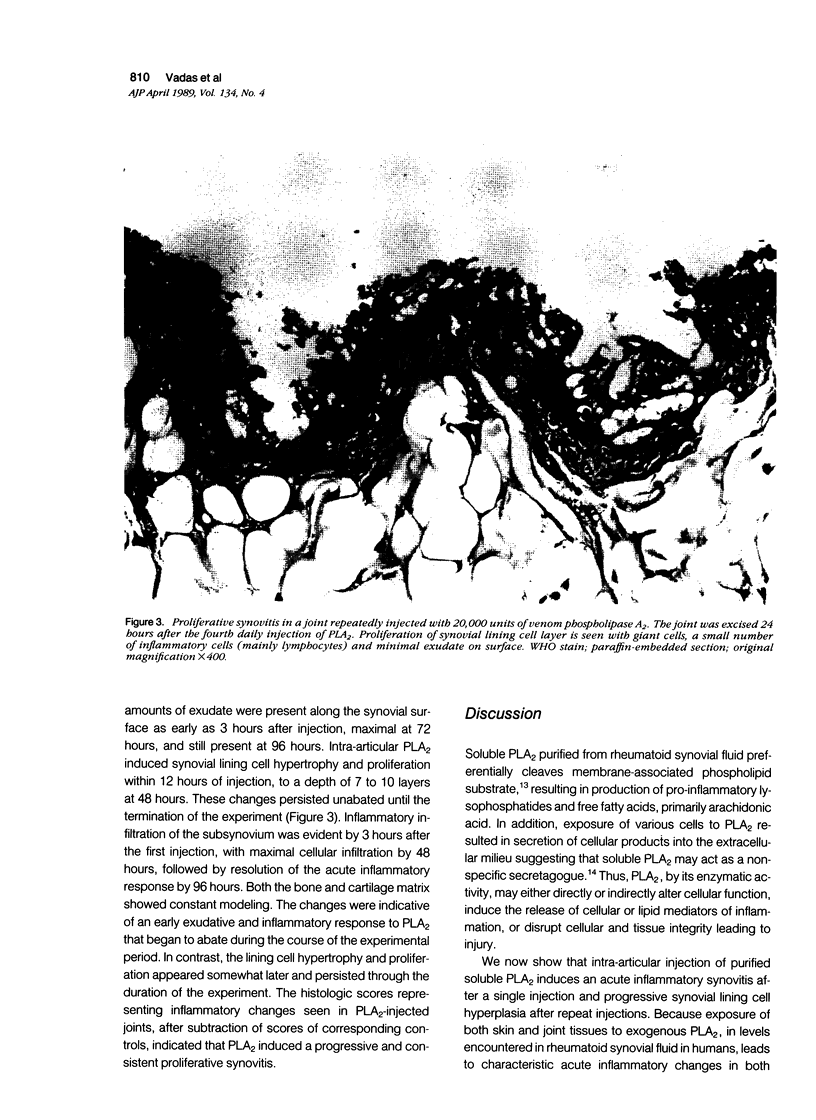
The proinflammatory effects of intra-articular injection of purified phospholipase A2 from snake venom and rheumatoid synovial fluid were studied in rats. Purified soluble phospholipase A2 (PLA2) in concentrations ranging from 1000 to 20,000 units/ml, was injected intra-articularly. Histologic parameters examined were cell and protein content of synovial fluid, subsynovial cellular infiltration, synovial lining cell hyperplasia, bone erosion, and peri-articular soft tissue infiltration. Single intra-articular injections of PLA2 resulted in an acute inflammatory infiltrate of the subsynovium with maximal changes seen 2 to 6 hours after injection. Acute inflammatory changes were dose-dependent. Joints injected repeatedly at 24-hour intervals showed prominent synovial lining cell hyperplasia, maximal at 96 hours. Human synovial and snake venom PLA2s were equipotent at inducing both the acute and chronic articular changes. These changes were not seen in joints injected with inactivated PLA2. It is concluded that soluble PLA2 causes time- and dose-dependent acute inflammatory changes after a single intra-articular injection and synovial lining cell hyperplasia in response to repeated exposure to PLA2. The experimental proliferative synovitis in this model may correlate with features of acutely inflammed joints bathed in synovial fluids containing high levels of PLA2 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang J., Gilman S. C., Lewis A. J. Interleukin 1 activates phospholipase A2 in rabbit chondrocytes: a possible signal for IL 1 action. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1283–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Cassell G. H. Mycoplasma infections as models of chronic joint inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Dec;22(12):1375–1381. doi: 10.1002/art.1780221209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deems R. A., Dennis E. A. Phospholipase A2 from cobra venom (Naja naja naja). Methods Enzymol. 1981;71(Pt 100):703–710. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)71083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KULKA J. P., BOCKING D., ROPES M. W., BAUER W. Early joint lesions of rheumatoid arthritis; report of eight cases, with knee biopsies of lesions of less than one year's duration. AMA Arch Pathol. 1955 Feb;59(2):129–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keystone E. C., Taylor-Robinson D., Metcalfe A., Ling L., Fornasier V., Pope C. Role of viable mycoplasmas in the pathogenesis of arthritis induced by M. pulmonis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Aug;62(4):350–356. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Vadas P., Fornasier V. Inflammatory effect of intradermal administration of soluble phospholipase A2 in rabbits. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Apr;86(4):380–383. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12285639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruzanski W., Vadas P., Stefanski E., Urowitz M. B. Phospholipase A2 activity in sera and synovial fluids in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Its possible role as a proinflammatory enzyme. J Rheumatol. 1985 Apr;12(2):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santer V., Sriratana A., Lowther D. A. Carrageenin-induced arthritis: V. A morphologic study of the development of inflammation in acute arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Nov;13(2):160–168. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(83)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Kitridou R. C. Synovitis of recent onset. A clinicopathologic study during the first month of disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 Sep-Oct;15(5):465–485. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanski E., Pruzanski W., Sternby B., Vadas P. Purification of a soluble phospholipase A2 from synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis. J Biochem. 1986 Nov;100(5):1297–1303. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Pruzanski W. Role of secretory phospholipases A2 in the pathobiology of disease. Lab Invest. 1986 Oct;55(4):391–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Stefanski E., Pruzanski W. Characterization of extracellular phospholipase A2 in rheumatoid synovial fluid. Life Sci. 1985 Feb 11;36(6):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90640-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Stefanski E., Pruzanski W. Influence of plasma proteins on activity of proinflammatory enzyme phospholipase A2. Inflammation. 1986 Jun;10(2):183–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00916000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]