Abstract
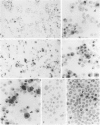
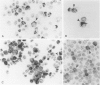
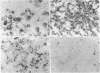
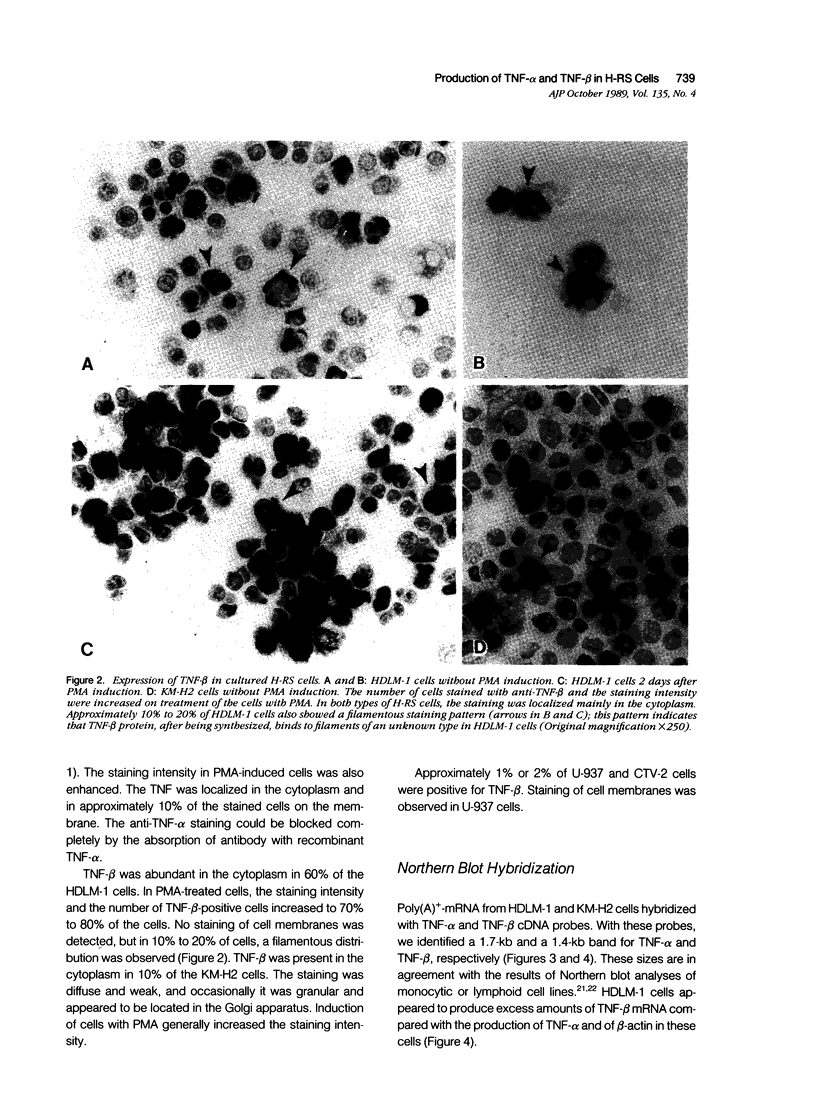
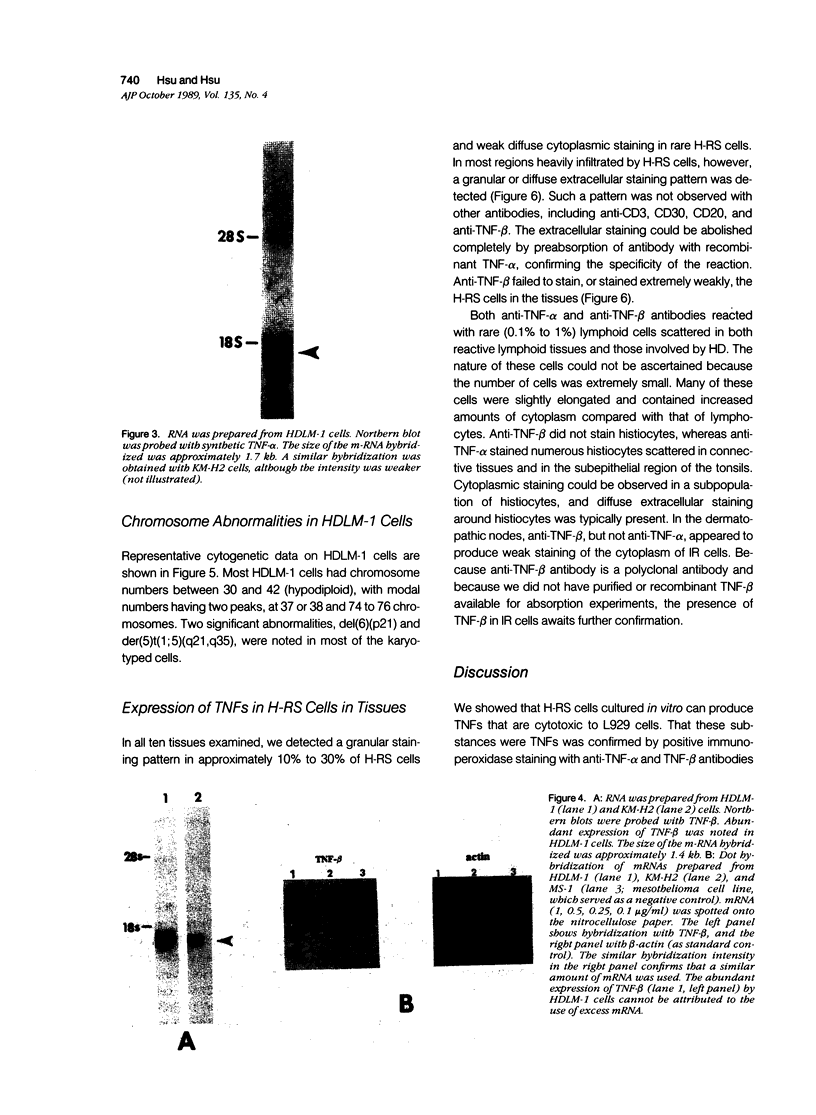
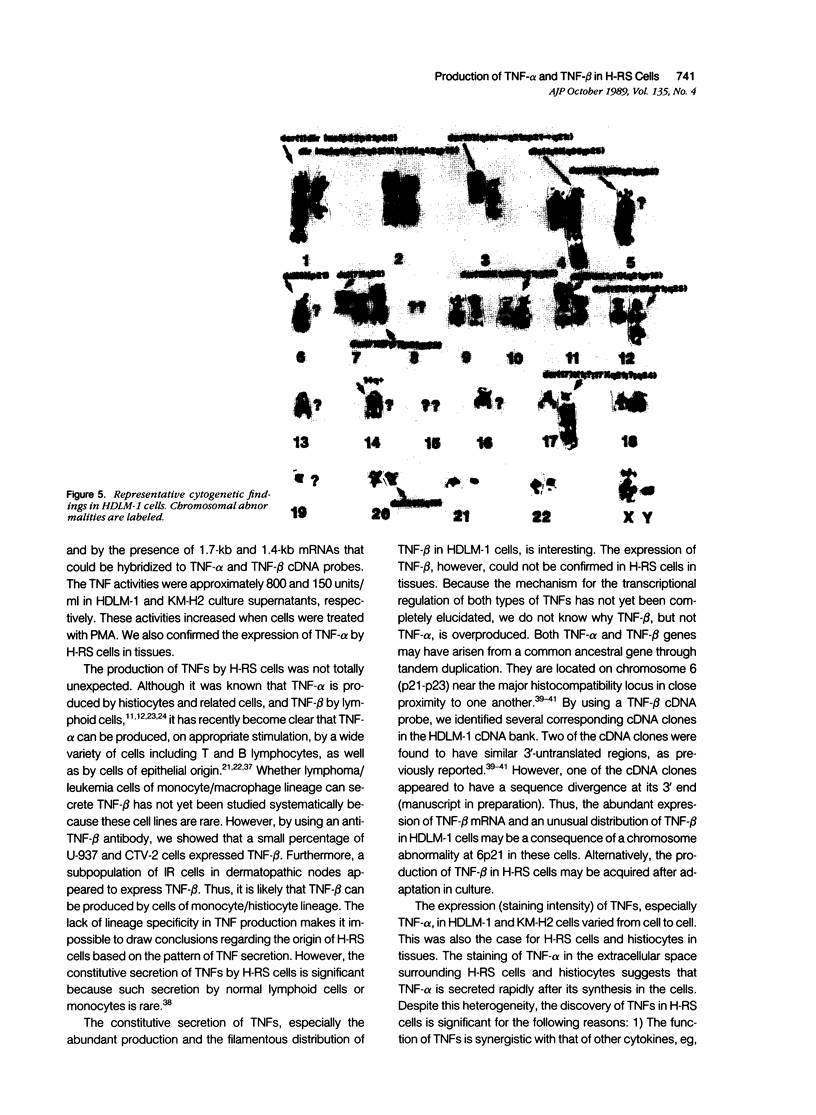
The production of tumor necrosis factors (TNF) from cells of two Hodgkin's Reed-Sternberg (H-RS) lines, HDLM-1 and KM-H2 was examined. The culture supernatant from these two types of H-RS cells exerts a cytotoxic effect on L929 cells. Both tumor necrosis factor (TNF-alpha) and lymphotoxin (TNF-beta) are responsible for this activity. This was confirmed by the presence in the cells of proteins and m-RNAs of TNF-alpha and TNF-beta, as determined with immunoperoxidase staining and Northern blot hybridization. Approximately 20% of HDLM cells and 5% of KM-H2 cells were positively stained by a monoclonal anti-TNF-alpha antibody, and this staining was inhibited by preabsorption of the antibody with recombinant TNF-alpha. Staining with anti-TNF-beta, however, showed an intense reaction in more than 60% of HDLM-1 cells, but only in 5% to 10% of KM-H2 cells. The abundant expression of TNF-beta in HDLM-1 cells is consistent with approximately 10 times the TNF activity in HDLM-1-conditioned medium as compared with that of KM-H2. The rich secretion of TNF-beta in HDLM-1 cells was also validated by the inhibition of most of the TNF activity in HDLM-1-conditioned medium with anti-TNF-beta antibody, and by the presence of abundant TNF-beta mRNA in HDLM-1 cells. The reason for the abundant production of TNF-beta in HDLM-1 cells is not yet known, but may be attributable to a chromosomal abnormality in the 6p21 region. The expression of TNF-alpha, but not TNF-beta, by H-RS cells was demonstrated in lymph nodes from patients with Hodgkin's disease. The capacity of H-RS cells to secrete TNF as well as other cytokines, such as interleukin-1, colony-stimulating factors, and transforming growth factors, may contribute to the unique clinical and histopathologic alterations in patients with Hodgkin's disease.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal B. B., Henzel W. J., Moffat B., Kohr W. J., Harkins R. N. Primary structure of human lymphotoxin derived from 1788 lymphoblastoid cell line. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2334–2344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beran M., McCredie K. B., Keating M. J., Gutterman J. U. Antileukemic effect of recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha in vitro and its modulation by alpha and gamma interferons. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):728–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch D. R., Turner A. R., Guilbert L. J. Synergistic stimulation of macrophage proliferation by the monokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha and colony-stimulating factor 1. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):307–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrichter H., Heit W., Schaadt M., Kirchner H., Diehl V. Production of colony-stimulating factors by Hodgkin cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1983 Mar 15;31(3):269–274. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne P. V., Heit W. F., March C. J. Human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor purified from a Hodgkin's tumor cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 12;874(3):266–273. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):2163–2168. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drexler H. G., Gaedicke G., Lok M. S., Diehl V., Minowada J. Hodgkin's disease derived cell lines HDLM-2 and L-428: comparison of morphology, immunological and isoenzyme profiles. Leuk Res. 1986;10(5):487–500. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(86)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrke M. J., Ho R. L., Hori K. Species-specific TNF induction of thymocyte proliferation. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1988;27(2):103–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00200012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J. Mechanism of in vitro antitumor effects of interleukin 1 (IL 1). Immunobiology. 1986 Sep;172(3-5):316–322. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(86)80113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esparza I., Männel D., Ruppel A., Falk W., Krammer P. H. Interferon gamma and lymphotoxin or tumor necrosis factor act synergistically to induce macrophage killing of tumor cells and schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):589–594. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Nandoskar M., Walz A., Goh D. H., Kowanko I. C. Effects of tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1 alpha and beta on human neutrophil migration, respiratory burst and degranulation. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1988;86(1):82–91. doi: 10.1159/000234610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Aggarwal B. B., Benton C. V., Bringman T. S., Henzel W. J., Jarrett J. A., Leung D. W., Moffat B., Ng P., Svedersky L. P. Cloning and expression of cDNA for human lymphotoxin, a lymphokine with tumour necrosis activity. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):721–724. doi: 10.1038/312721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensel G., Männel D. N., Pfizenmaier K., Krönke M. Autocrine stimulation of TNF-alpha mRNA expression in HL-60 cells. Lymphokine Res. 1987 Spring;6(2):119–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofsli E., Lamvik J., Nissen-Meyer J. Evidence that tumour necrosis factor (TNF) is not constitutively present in vivo. The association of TNF with freshly isolated monocytes reflects a rapid in vitro production. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Oct;28(4):435–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb01473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Ho Y. S., Li P. J., Monheit J., Ree H. J., Sheibani K., Winberg C. D. L&H variants of Reed-Sternberg cells express sialylated Leu M1 antigen. Am J Pathol. 1986 Feb;122(2):199–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Hsu P. L. Aberrant expression of T cell and B cell markers in myelocyte/monocyte/histiocyte-derived lymphoma and leukemia cells. Is the infrequent expression of T/B cell markers sufficient to establish a lymphoid origin for Hodgkin's Reed-Sternberg cells? Am J Pathol. 1989 Jan;134(1):203–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Hsu P. L., Lo S. S., Wu K. K. Expression of prostaglandin H synthase (cyclooxygenase) in Hodgkin's mononuclear and Reed-Sternberg cells. Functional resemblance between H-RS cells and histiocytes or interdigitating reticulum cells. Am J Pathol. 1988 Oct;133(1):5–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Hsu P. L. Phenotypes and phorbol ester-induced differentiation of human histiocytic lymphoma cell lines (U-937 and SU-DHL-1) and Reed-Sternberg cells. Am J Pathol. 1986 Feb;122(2):223–230. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Huang L. C., Hsu P. L., Ge Z. H., Ho Y. S., Cuttita F., Mulshine J. Biochemical and ultrastructural study of Leu M1 antigen in Reed-Sternberg cells: comparison with granulocytes and interdigitating reticulum cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Aug;77(2):363–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Jaffe E. S. Leu M1 and peanut agglutinin stain the neoplastic cells of Hodgkin's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jul;82(1):29–32. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Pescovitz M. D., Hsu P. L. Monoclonal antibodies against SU-DHL-1 cells stain the neoplastic cells in true histiocytic lymphoma, malignant histiocytosis, and Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):213–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Soban E. Color modification of diaminobenzidine (DAB) precipitation by metallic ions and its application for double immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Oct;30(10):1079–1082. doi: 10.1177/30.10.6182185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Yang K., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1985 Feb;118(2):209–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Zhao X., Chakraborty S., Liu Y. F., Whang-Peng J., Lok M. S., Fukuhara S. Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's cell lines HDLM, L-428, and KM-H2 are not actively replicating: lack of bromodeoxyuridine uptake by multinuclear cells in culture. Blood. 1988 May;71(5):1382–1389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Zhao X. Expression of interleukin-1 in Reed-Sternberg cells and neoplastic cells from true histiocytic malignancies. Am J Pathol. 1986 Nov;125(2):221–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahaleh M. B., Smith E. A., Soma Y., LeRoy E. C. Effect of lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor on endothelial and connective tissue cell growth and function. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Nov;49(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90116-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamesaki H., Fukuhara S., Tatsumi E., Uchino H., Yamabe H., Miwa H., Shirakawa S., Hatanaka M., Honjo T. Cytochemical, immunologic, chromosomal, and molecular genetic analysis of a novel cell line derived from Hodgkin's disease. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Alvarez-Mon M., Delsing G. A., Fauci A. S. Lymphotoxin is an important T cell-derived growth factor for human B cells. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1144–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.3500512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Hensel G., Schlüter C., Scheurich P., Schütze S., Pfizenmaier K. Tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin gene expression in human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988 Oct 1;48(19):5417–5421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Last-Barney K., Homon C. A., Faanes R. B., Merluzzi V. J. Synergistic and overlapping activities of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-1. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):527–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H., Seto Y., Motoyoshi S., Kadokawa T., Sunahara N. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor causes long-lasting and prostaglandin-mediated fever, with little tolerance, in rabbits. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Apr;245(1):336–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Bank I., Handley D., Cassimeris J., Chess L., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin interacts with endothelial cell receptors to induce release of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1363–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedospasov S. A., Turetskaya R. L., Shakhov A. N. Cloning and characterization of the rabbit lymphotoxin (TNF-beta) gene and its tight linkage to the gene coding for tumor necrosis factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):3112–3112. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.3112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcom S. R., O'Rourke L. Potentiation of fibroblast growth by nodular sclerosing Hodgkin's disease cell cultures. Blood. 1982 Jul;60(1):228–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF). Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.2413547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Scheurich P., Schlüter C., Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor enhances HLA-A,B,C and HLA-DR gene expression in human tumor cells. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):975–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed D., Moore F. D., Jr Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor increases granulocyte cell-surface complement receptor number. Arch Surg. 1988 Nov;123(11):1333–1336. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1988.01400350047006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin B. Y., Anderson S. L., Lunn R. M., Richardson N. K., Hellermann G. R., Smith L. J., Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor and IFN induce a common set of proteins. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1180–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Aggarwal B. B., Rinderknecht E., Svedersky L. P., Finkle B. S., Palladino M. A., Jr Activation of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factors. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):2069–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalaby M. R., Espevik T., Rice G. C., Ammann A. J., Figari I. S., Ranges G. E., Palladino M. A., Jr The involvement of human tumor necrosis factors-alpha and -beta in the mixed lymphocyte reaction. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):499–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spies T., Morton C. C., Nedospasov S. A., Fiers W., Pious D., Strominger J. L. Genes for the tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta are linked to the human major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8699–8702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. S., Bjorndahl J. M., Wang C. Y., Kao H. T., Fu S. M. Production of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin by human T cell lines and peripheral blood T lymphocytes stimulated by phorbol myristate acetate and anti-CD3 antibody. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):937–953. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. S., Jung L. K., Walters J. A., Chen W., Wang C. Y., Fu S. M. Production of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin by human B cell lines and tonsillar B cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1539–1551. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Iwamoto S., Sugimoto H., Takuma T., Kawatani N., Noda M., Masaki A., Morise H., Arimura H., Konno K. Identity of differentiation inducing factor and tumour necrosis factor. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):338–340. doi: 10.1038/323338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voth R., Rossol S., Gallati H., Pracht I., Laubenstein H. P., Hess G., Müller W. E., Schröder H. C., Jochum C., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. In vivo and in vitro induction of natural killer cells by cloned human tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1988;27(2):128–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00200016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. S., Starnes H. F., Jr, Alcock N., Calvano S., Brennan M. F. Hormonal and metabolic response to recombinant human tumor necrosis factor in rat: in vitro and in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 1):E206–E212. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.2.E206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. H., Lin J. X., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Enhancement of cAMP levels and of protein kinase activity by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 in human fibroblasts: role in the induction of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6802–6805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]