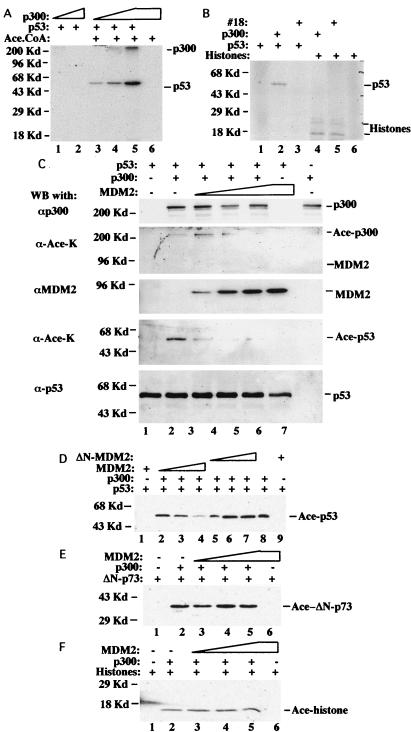
Figure 2.
Inhibition of p300-mediated p53 acetylation by MDM2 in vitro. (A) Establishment of p53 acetylation by p300 in vitro. Recombinant human p53 (50 ng) purified from bacteria and 250 nM acetyl CoA were used in the reaction as indicated; 100 ng (lanes 1 and 3), 200 ng (lanes 2 and 4), and 300 ng (lanes 5 and 6) of recombinant p300 purified from baculovirus-infected insect cells were used. Acetylated p53 was detected by WB by using antiacetylated Lys antibodies (Upstate Biotechnology). (B) Histone and p53 acetylation by recombinant p300 or the native p300 complex purified from HeLa nuclear extracts (fraction 18 of Fig. 1 A and B); 1 μl of 14C-labeled acetyl CoA instead of nonlabeled acetyl CoA was used in each reaction. Histones (100 ng; Sigma), 50 ng of p53, 100 ng of p300, or 200 ng of the p300-containing fraction 18 from Superdex 200 were used in this experiment as indicated. Protein acetylation was detected by autoradiography. (C) MDM2 inhibits p53 acetylation by p300. In the acetylation reaction, 75 ng of p53, 200 ng of p300, and 250 nM acetyl CoA were used in this reaction as indicated; 200, 400, and 600 ng of recombinant MDM2 purified from baculovirus were used in lanes 3–5, respectively, and 600 ng of MDM2 for lane 6. Acetylated p53 was detected by antiacetylated Lys antibodies. (D) N-terminally deleted mutant MDM2 does not inhibit p53 acetylation by p300. The same acetylation reaction was performed as that in C; 200, 400, and 600 ng of either MDM2 or its N-terminal truncated mutant (ΔN-MDM2) were used as indicated. (E) MDM2 does not affect acetylation of the p73 C-terminal domain by p300; 75 ng of the p73 C-terminal fragment purified from bacteria (X.Z. and H.L., unpublished data) was used as a substrate. The same amounts of p300 and MDM2 as those in C were used in this experiment. (F) MDM2 does not affect acetylation of histones by p300. The same assay was conducted as that in E except that 40 ng of histones (Sigma) was used in this assay.