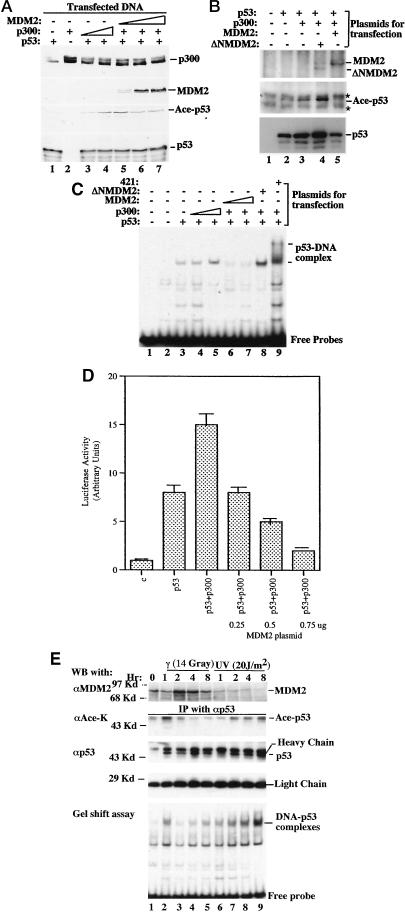
Figure 4.
MDM2 inhibits p53 acetylation and activation by p300 in vivo. (A) MDM2 reduces p300-mediated p53 acetylation in cells. H1299 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding p53 (0.3 μg), p300 (0.5 μg), and/or MDM2 (0.5, 1, or 2 μg) as indicated on top. MG132 (5 μM) was added into media 12 h before harvesting. Cell lysates were prepared 36 h posttransfection for WB analysis; 400 μg of proteins were loaded onto a 10% SDS gel. (B) Wild-type but not N-terminally deleted MDM2 reduces p53 acetylation and level. The same transfection as that in A was conducted except the N-terminally deleted MDM2 (ΔNMDM2; 2 μg) was used without MG132 in this experiment. Asterisks indicate nonspecific signals. (C) MDM2 reduces the sequence-specific DNA-binding activity of p53 in cells. The exact same transfection as that in A was carried out. Nuclear extracts were prepared for EMSA analysis. Proteins (15 μg) were used for each reaction except lane 1; 1 μg of 421 was used in lane 9. (D) MDM2 reverses the enhancement of p53-dependent transcription by p300 in cells. As indicated, plasmids encoding no protein as a control (1 μg; C), p53 (50 ng) alone, or with p300 (0.15 μg) or with MDM2, and with a luciferase reporter gene (0.2 μg) driven by the p53RE motif derived from the MDM2 promoter (35), as well as a β-galactosidase reporter plasmid (0.1 μg) as an internal control, were introduced into H1299 cells (5 × 104 cells per 35 mm dish) by using Lipofectamine (GIBCO/BRL). Posttransfection (48 h) and 12 h after MG132 treatment (5 μM), cells were harvested for luciferase assays. Each column represents the mean data of three experiments. The bars denote that deviation of errors. (E) UV and γ irradiation differentially regulate p53 acetylation and DNA-binding activity, which are reciprocal to the MDM2 level. Tera-2 cells were irradiated with UV or γ ray, as indicated on top and harvested at different time points postirradiation for immunoprecipitation-WB. Proteins (300 μg) of the cell lysates from each time point were used for immunoprecipitation-WB by using antibodies as indicated (two middle panels). Nuclear extracts with 150 μg of proteins were directly loaded onto a 10% SDS gel for WB by using an anti-MDM2 antibody (Upper). EMSA (Lower) was carried out by using 15 μg of proteins in nuclear extracts and the 32P-labeled p53RE-containing DNA probes as described in Materials and Methods. αAce-K denotes the antibody specifically against the acetylated Lys. Similar results to that of E were also obtained by using F9 cells. All of these experiments were reproducible.