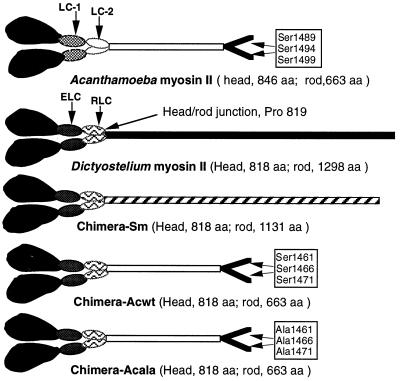
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the structures of the heavy chains of Acanthamoeba, Dictyostelium, and chimeric myosins. The 1,298-residue tail, beginning at Pro-819, of wild-type Dictyostelium myosin II heavy chain was replaced by the 1,131-residue and 663-residue tails of chicken gizzard smooth muscle and Acanthamoeba myosin II in chimera-Sm and chimera-Acwt heavy chains, respectively. The three serines whose phosphorylation inactivates the actin-dependent MgATPase of Acanthamoeba myosin II, and which were replaced by alanines in chimera-Acala, are numbered differently in the chimeras and wild-type heavy chains because the head/neck domain of Dictyostelium myosin II is 28 residues shorter than the head/neck domain of Acanthamoeba myosin II.