Figure 1.
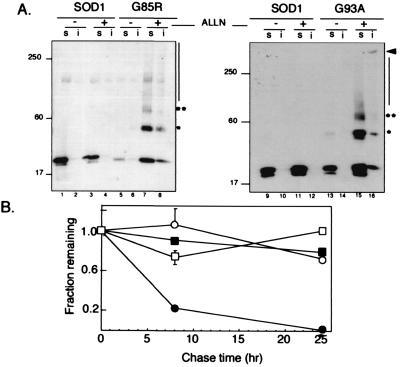
IPC formation by mutant SOD. (A) Effect of proteasome inhibition on electrophoretic mobility and detergent solubility of SOD. HEK cells transiently expressing wild-type SOD (lanes 1–4 and 9–12), G85R (lanes 5–8), or G93A (lanes 13–16) mutant SOD were treated overnight with proteasome inhibitor (ALLN, 10 μg/ml), lysed, and separated into nonionic detergent soluble (s) and insoluble (i) fractions and analyzed on immunoblots probed with a mAb to the HA epitope tag. Mobility of molecular weight markers in kDa is indicated at Left. Asterisks denote positions of high molecular SOD at ×2 and ×3 the apparent molecular weight of monomeric SOD. (B) Decreased stability of mutant SOD. HEK cells transiently expressing wild-type (○ and □) or G85R (● and ■) SOD were pulse-labeled with [35S]Cys for 45 min and chased for the times indicated in the presence (□ and ■) or absence (○ and ●) of the proteasome inhibitor lactacystin (5 μM). Data are mean ± SEM from 4–6 independent experiments. Similar data were obtained for the G93A mutant.