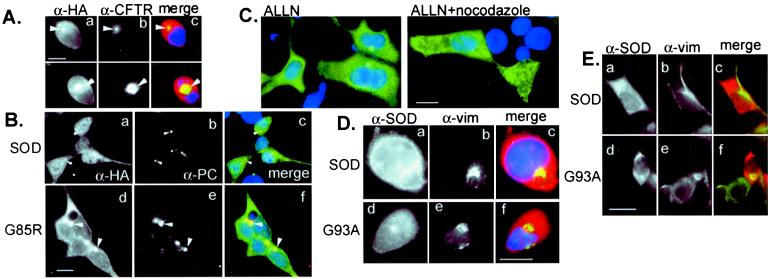
Figure 3.
Inclusion bodies containing mutant SOD are aggresomes. (A) Colocalization of G93A SOD with ΔF508 CFTR aggresomes. HEK cells were cotransfected with G93A and ΔF508 CFTR, treated with MG132 before examination by double indirect immunofluorescence for CFTR (α-CFTR; b) and HA epitope tag (α-HA; a). (B) Colocalization of SOD and pericentrin. HEK cells were transfected with wild-type (a–c) or G85R mutant (d–f) SOD, examined by double indirect immunofluorescence by using a polyclonal antibody to pericentrin (α-PC; b and e) and mAb to the HA epitope tag (α-HA; a and d). (C) Delivery of SOD to aggresomes requires an intact microtubule cytoskeleton. HEK cells expressing G85R SOD were exposed to proteasome inhibitor (ALLN, 10 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of nocodazole (10 μg/ml) as indicated. SOD immunolocalization was detected with α-HA mAb. (D) Vimentin colocalizes with mutant but not wild-type SOD. HEK cells expressing wild-type (a–c) or G93A (d–f) SOD were exposed overnight to the proteasome inhibitor MG132, examined by double indirect immunofluorescence by using a polyclonal antibody to SOD (α-SOD; a and c) and mAb to vimentin (α-vim; b and e). (Bar = 15 μm.) (E) Vimentin collapses around SOD aggresomes in the absence of proteasome inhibitor. HEK cells expressing wild-type (a–c) or G93A (d–f) SOD were examined by immunofluorescence with antibodies aginat SOD (a and c) and (b and e). (Bar = 15 μm.)