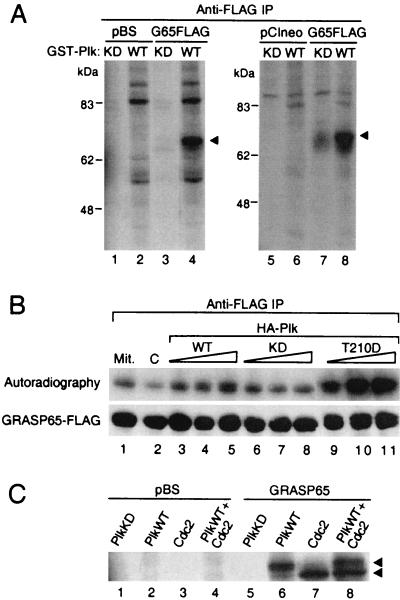
Figure 4.
Plk and Cdc2 are GRASP65 kinases. (A) Plk is a GRASP65 kinase. GRASP65-FLAG immunoprecipitated from in vitro expression reactions (lanes 1–4) or from transfected Cos-7 cells (lanes 5–8) was incubated with soluble GST-Plk (KD or WT) in kinase reaction buffer. A 0.5 μg sample of either vector (pBS) or GRASP65-FLAG constructs was used in each expression reaction. Equal aliquots of immunoprecipitates from transfected cells were used in each kinase reaction. (B) Expression of Plk enhances in vivo phosphorylation of GRASP65. Cos-7 cells were cotransfected with pCIneo vector (lanes 1 and 2) or HA-Plk WT (lanes 3–5), KD (lanes 6–8) or T210D (lanes 9–11), and GRASP65-FLAG. In each cotransfection experiment, 2.5, 5, or 7.5 μg of Plk constructs was used. Vector-only controls (lanes 1 and 2) were either treated with nocodazole (Mit.) or left untreated (C) to determine basal levels of GRASP65 phosphorylation. Transfected cells were incubated with [32P]orthophosphate for 3 h in phosphate-free medium, and GRASP65 was isolated by anti-FLAG immunoprecipitations (IP) and resolved by SDS/PAGE. Phosphorylated GRASP65 was detected by autoradiography (Upper), and the amount of GRASP65 in the immunocomplex was determined by Western analysis with anti-FLAG antibody (Lower). (C) GRASP65 is also phosphorylated by Cdc2. GRASP65-FLAG immunoprecipitated from in vitro expression reactions was incubated with soluble GST-Plk (KD or WT) or GST-cyclin B-Cdc2 in kinase reaction buffer.