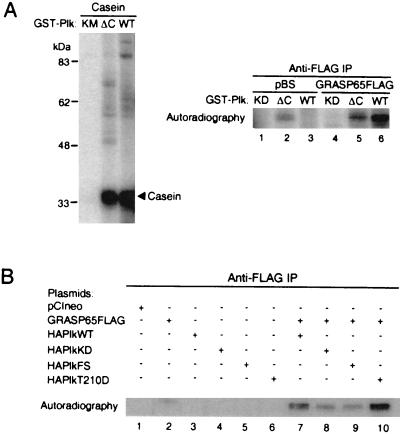
Figure 6.
The conserved C-terminal domain of Plk is important for GRASP65 phosphorylation. (A) Deletion of conserved Plk C terminus (amino acids 356–603 deleted) diminishes GRASP65 phosphorylation (lane 5). Comparable casein kinase activity was present in the WT or ΔC reactions (Left). GRASP65-FLAG expressed in vitro was immunoprecipitated and incubated in kinase reaction buffer with purified GST-PlkKD, WT, or ΔC. (B) HA-Plk polo-box 1 FS mutant coimmunoprecipitates with GRASP65-FLAG but does not efficiently phosphorylate it in an immunocomplex kinase assay (lane 9). The immunocomplexes were denatured after the kinase reaction was terminated, and GRASP65-FLAG was immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG antibodies and subjected to autoradiography. The background kinase activity observed in KD (lane 8) and FS immunocomplexes is partly due to coimmunoprecipitating endogenous kinases (see GRASP65-FLAG-only control, lane 2).