Figure 4.
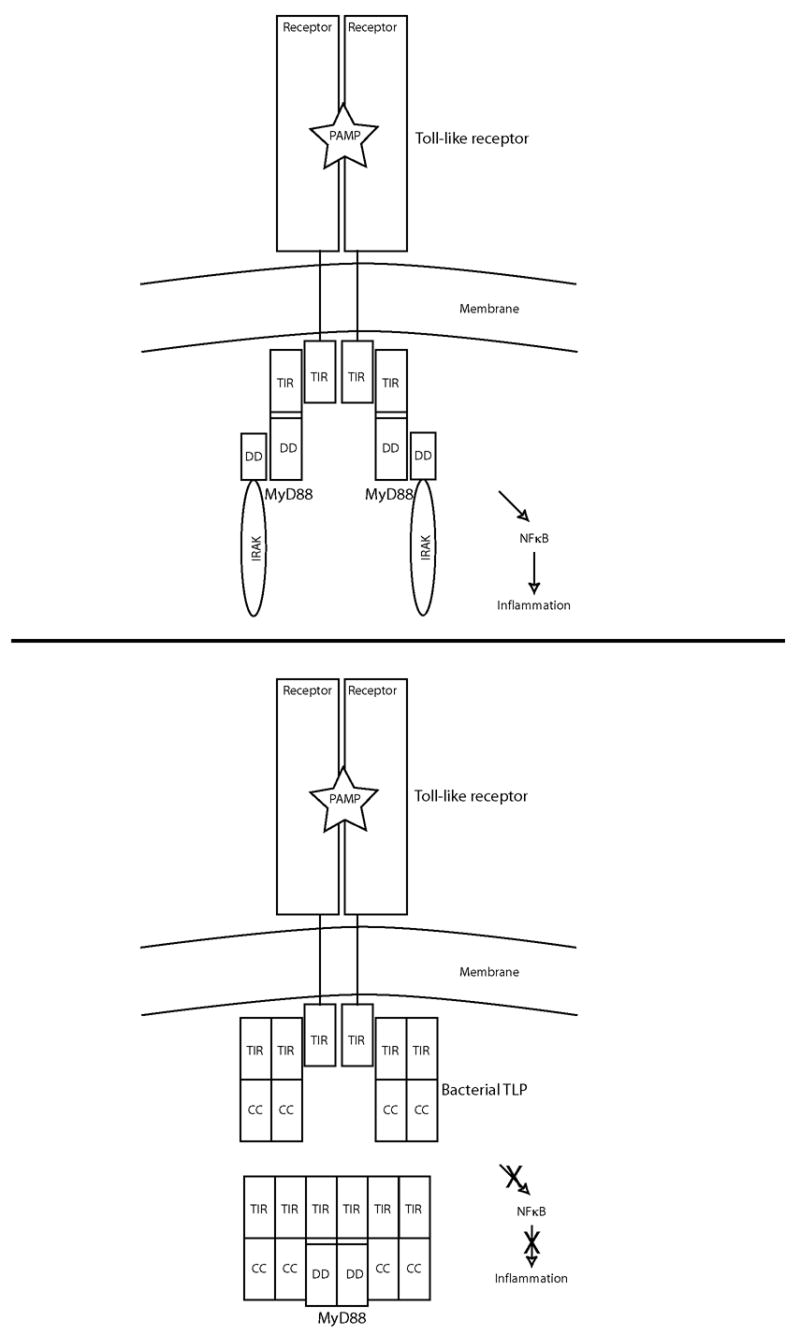
A model of how bacterial pathogens may use the TIR-like proteins to inhibit NFκB signaling in infected cells. Top panel: a simplified depiction of the Toll-like receptor signaling pathway with a productive receptor-adaptor TIR-TIR interaction. Bottom panel: the presence of bacterial TLPs, prevents the inflammatory signal to proceed by the formation of a bacterial-host TIR-TIR interaction. Legend: PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; TIR, Toll/IL-1 receptor/plant Resistance domain; DD, death domain; CC, coiled-coil.
