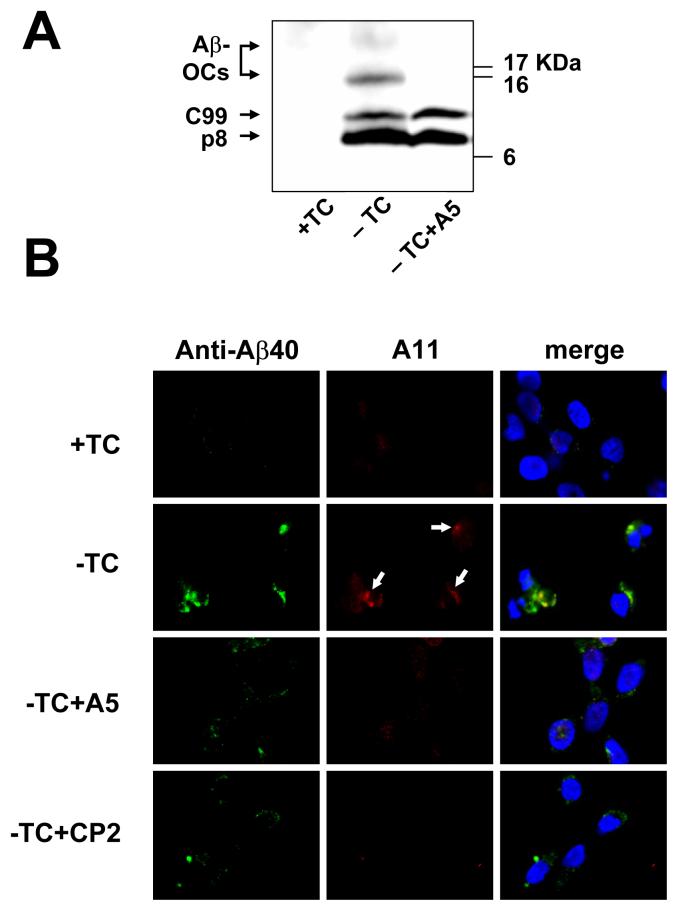
Fig. 4.
Effect of A5 on intacellular Aβ oligomers. In panel A, the Western blot of MC65 cell extracts shows that A5 treatment resulted in a significant reduction of Aβ-OCs. The cytotoxicity program of MC65 cells was initiated by removal of TC in the presence or absence of A5 (1 μM). After 48 hrs, cells were homogenized. Cellular proteins (20 μg protein each) were subjected to Tris/Tricine SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis with antibody 6E10 (for Aβ1-17). –TC MC65 cells expressed APP-C99, p8 (possibly containing CTFΔ31 and Aβ dimers, see Maezawa et al., 2006), and two major Aβ-OCs of MW 16.5 and 25 kDa, the locations of which are indicated. By contrast, cells cultured in the presence of TC (+TC) showed no expression of Aβ containing proteins derived from APP-C99. Panel B shows that A11, a specific amyloid oligomer antibody, stained a portion of Aβ40-immunoreactive intracellular deposits (arrows) and that these deposits were diminished by A5 and CP2 treatment. MC65 cells, treated as indicated (the concentration of A5 or CP2 was 1 μM) for 36 hrs, were co-stained with Aβ40 specific antibody (green fluorescence) and A11 (red fluorescence). The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue fluorescence). Representative photomicrographs are shown.