Abstract
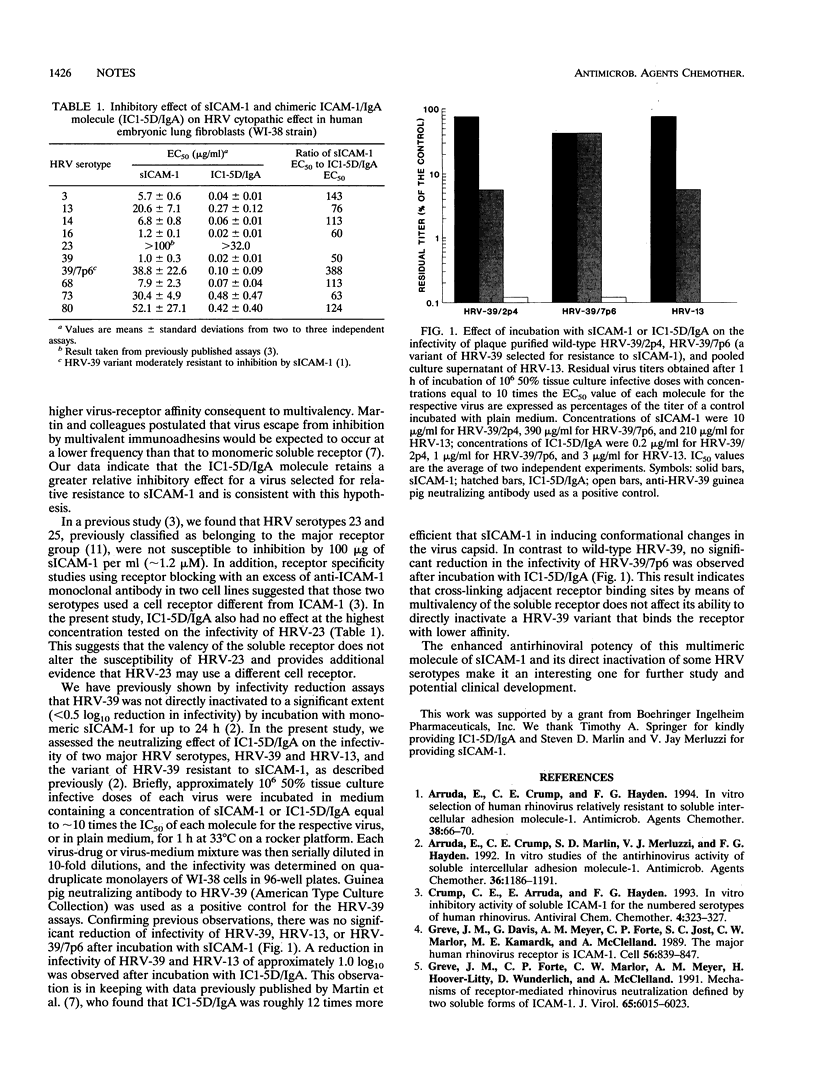
We conducted a comparative study of the antirhinovirus activities of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) and a chimeric ICAM-1/immunoglobulin A (IgA) molecule (ICI-5D/IgA) for nine major receptor group human rhinovirus (HRV) serotypes and for a variant of HRV-39 relatively resistant to inhibition by sICAM-1. ICI-5D/IgA inhibited the infectivity of eight of the nine wild-type HRVs and the resistant HRV-39 variant and was 60 to 170 times more potent than sICAM-1 on a molar basis. In contrast to sICAM-1, ICI-5D/IgA directly neutralized the infectivity of the representative HRVs by approximately 1 log10. These results expand on the antirhinovirus spectrum of ICI-5D/IgA, confirm that dimeric forms of sICAM-1 have a higher antirhinoviral potency than monomeric sICAM-1, and indicate that cross-linking of two adjacent receptor binding sites on the virus capsid by a divalent receptor enhances the direct inactivation of viral infectivity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arruda E., Crump C. E., Hayden F. G. In vitro selection of human rhinovirus relatively resistant to soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Jan;38(1):66–70. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arruda E., Crump C. E., Marlin S. D., Merluzzi V. J., Hayden F. G. In vitro studies of the antirhinovirus activity of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jun;36(6):1186–1191. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.6.1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. M., Davis G., Meyer A. M., Forte C. P., Yost S. C., Marlor C. W., Kamarck M. E., McClelland A. The major human rhinovirus receptor is ICAM-1. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90688-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greve J. M., Forte C. P., Marlor C. W., Meyer A. M., Hoover-Litty H., Wunderlich D., McClelland A. Mechanisms of receptor-mediated rhinovirus neutralization defined by two soluble forms of ICAM-1. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6015–6023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6015-6023.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlin S. D., Staunton D. E., Springer T. A., Stratowa C., Sommergruber W., Merluzzi V. J. A soluble form of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 inhibits rhinovirus infection. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):70–72. doi: 10.1038/344070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Casasnovas J. M., Staunton D. E., Springer T. A. Efficient neutralization and disruption of rhinovirus by chimeric ICAM-1/immunoglobulin molecules. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3561–3568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3561-3568.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson N. H., Kolatkar P. R., Oliveira M. A., Cheng R. H., Greve J. M., McClelland A., Baker T. S., Rossmann M. G. Structure of a human rhinovirus complexed with its receptor molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):507–511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Merluzzi V. J., Rothlein R., Barton R., Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. A cell adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, is the major surface receptor for rhinoviruses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):849–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomassini J. E., Graham D., DeWitt C. M., Lineberger D. W., Rodkey J. A., Colonno R. J. cDNA cloning reveals that the major group rhinovirus receptor on HeLa cells is intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4907–4911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uncapher C. R., DeWitt C. M., Colonno R. J. The major and minor group receptor families contain all but one human rhinovirus serotype. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):814–817. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90098-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]