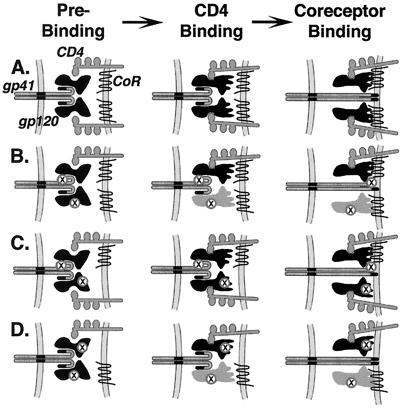
Figure 6.
Model for cooperative subunit interactions within the HIV-1 Env oligomer. For simplicity, only two gp120/gp41 complexes are shown. Labeling indicates gp120, gp41, CD4, and coreceptor (CoR); inactive Env regions are designated by X. Different shapes distinguish the preactivated and activated states of gp120; different shading distinguishes the gp120 subunits activated directly by CD4 binding (black) versus indirectly by subunit interactions (gray). (A) Wild-type Env. gp120 subunits on both complexes bind to CD4 and undergo a conformational change to expose determinants critical for coreceptor interaction. Both gp120 subunits bind to coreceptor, leading to activation of both gp41 subunits for fusion peptide insertion. (B) Complementation between one Env variant with a defective fusion peptide and another with a defective CD4 binding site. The gp120 subunit on one complex binds to CD4 and undergoes the conformational change exposing coreceptor interaction determinants. The functional gp41 subunit on the other complex is activated for fusion peptide insertion. We also presume that the coreceptor interaction determinants are indirectly exposed on the other gp120 subunit via concerted subunit interactions and contribute to gp41 activation (as described for D below). (C) Complementation between one Env variant with a defective fusion peptide and another with inactive coreceptor interaction determinants. The gp120 subunits on both complexes bind to CD4 and undergo the associated conformational changes. The coreceptor interaction determinants are functional on only one gp120 subunit; this is sufficient to activate the functional gp41 subunit on the other complex for fusion peptide insertion. (D) Complementation between one Env variant with a defective CD4 binding site and another with inactive coreceptor binding determinants. The gp120 subunit on one complex binds to CD4 and undergoes the associated conformational change. Although the coreceptor binding determinants on this subunit are inactive, cooperative interactions lead to a concerted conformational change in the other gp120 subunit, which then interacts with coreceptor and activates both gp41 subunits for fusion peptide insertion.