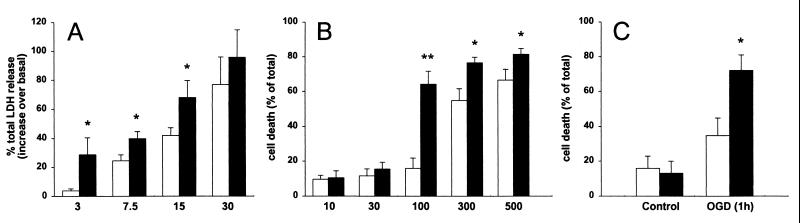
Figure 1.
Effect of PS1 FAD mutation on in vitro excitotoxicity. (A) Primary cortical neurons from wt (open bars) or PS1 L286V tg (filled bars) mice were exposed to increasing concentrations of NMDA, as indicated. Cell death was quantified by measuring the release of LDH enzyme in the culture media and was expressed as the percentage of total LDH release elicited by 100 μM NMDA. (B) Primary cerebellar neurons from wt (open bars) or PS1 L286V tg (filled bars) mice were exposed to increasing concentrations of NMDA, as indicated. Cell death was quantified by determining intravital staining with fluorescein diacetate and propidium iodide and was expressed as the percentage of dead cells over total cell number. (C) Primary cerebellar neurons from wt (open bars) or PS1 L286V tg (filled bars) mice were subjected to OGD for 1 h. Neuronal viability was assessed 24 h later by intravital staining with fluorescein diacetate and propidium iodide. Data are expressed as the percentage of dead cells over total cell number. Numbers represent mean ± SEM of at least six different experiments, run in triplicate, each from different cell preparations. **, P < 0.01, and *, P < 0.05, vs. the corresponding values of wt group.