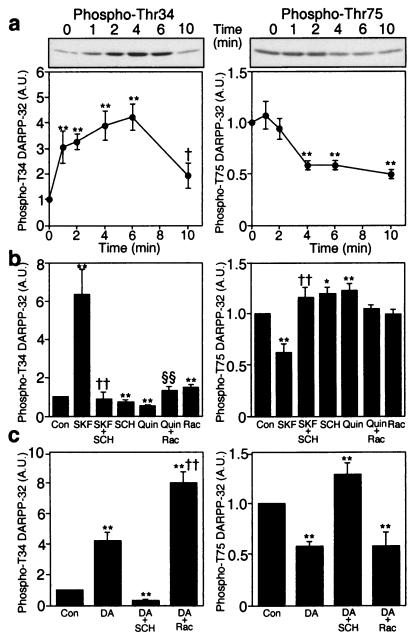
Figure 1.
Regulation of DARPP-32 phosphorylation at Thr-34 and Thr-75 by dopamine via D1- and D2-type receptors in neostriatum. (a) Effect of dopamine on the level of phospho-Thr-34 and phospho-Thr-75 DARPP-32. Slices were incubated with dopamine (100 μM) in the presence of a dopamine uptake inhibitor, nomifensine (10 μM), for the indicated times. Immunoblots are shown (Upper) for the detection of phospho-Thr-34 (Left) and phospho-Thr-75 (Right), using phosphorylation state-specific antibodies and the same nitrocellulose membrane. Quantitative results, normalized to values obtained with untreated slices, are shown below each blot. A.U., arbitrary units. Data represent means ± SEM for four experiments. **, P < 0.01 compared with 0 min; †, P < 0.05 compared with 6 min, Student's t test. (b) Regulation of DARPP-32 phosphorylation at Thr-34 (Left) and Thr-75 (Right) by dopamine D1 and D2 receptor agonists and antagonists. Data are shown for untreated neostriatal slices (Con) and slices treated with a D1 agonist, SKF81297 (SKF) (1 μM); a D1 antagonist, SCH23390 (SCH) (1 μM); a D2 agonist, quinpirole (Quin) (1 μM); and a D2 antagonist, raclopride (Rac) (1 μM), as indicated. Data represent means ± SEM for 5–15 experiments. *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01 compared with control; ††, P < 0.01 compared with SKF81297 alone; §§, P < 0.01 compared with quinpirole alone, Student's t test. (c) Effect of SCH23390 and raclopride on dopamine regulation of DARPP-32 phosphorylation on Thr-34 (Left) and Thr-75 (Right). Data are shown for treatment of neostriatal slices with dopamine (100 μM), SCH23390 (1 μM), and raclopride (1 μM), as indicated. Data represent means ± SEM for five experiments. **, P < 0.01 compared with control; ††, P < 0.01 compared with dopamine alone, Student's t test.