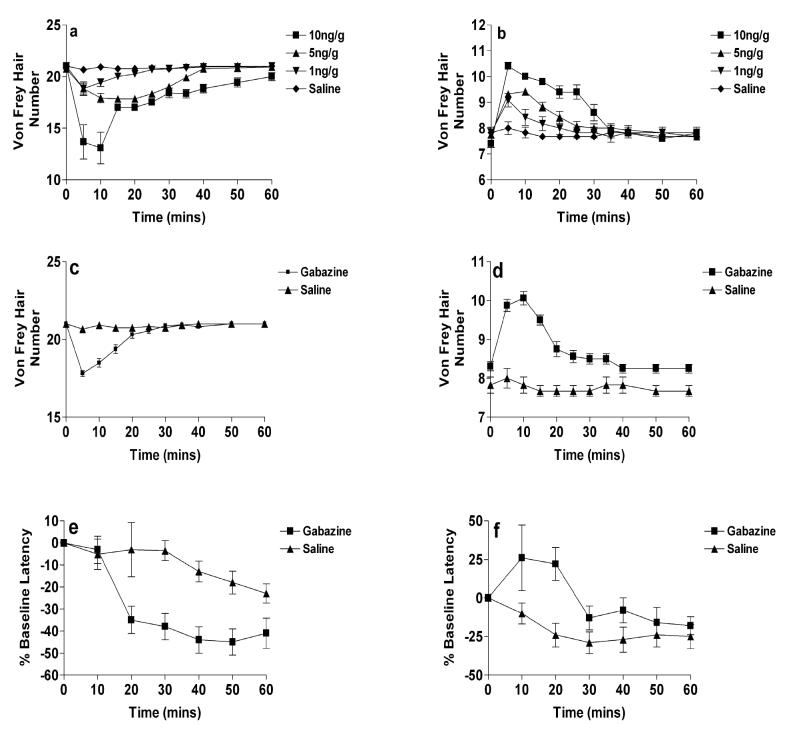
Figure 1.
The effects of intrathecal bicuculline upon hindpaw mechanical and thermal withdrawal thresholds (see supplementary methods). Thresholds are expressed as mean vFh number ± SEM, or as a percentage of baseline in hot plate withdrawal latency compared to controls (n=8-14 rats per point). (a) In P21 rats thresholds were decreased significantly within five minutes of injection (P<0.05; n=12) at all doses when compared to saline treated animals. (b) In P3 rats all doses of bicuculline significantly increased withdrawal thresholds within five minutes of injection when compared to saline (P<0.05; n=12). In both age groups values returned to baseline values within sixty minutes. (c & d) Intrathecal gabazine(1ng/g) had the same effect on mechanical thresholds as bicuculline at (c) P21 and (d) P3. (e & f) The hot plate withdrawal latency was decreased by intrathecal gabazine in (d) P21 rats and increased in (e) P3 rats when compared to saline treated animals. Time zero (0 mins) reflects baseline, drug-free, responses in all cases.