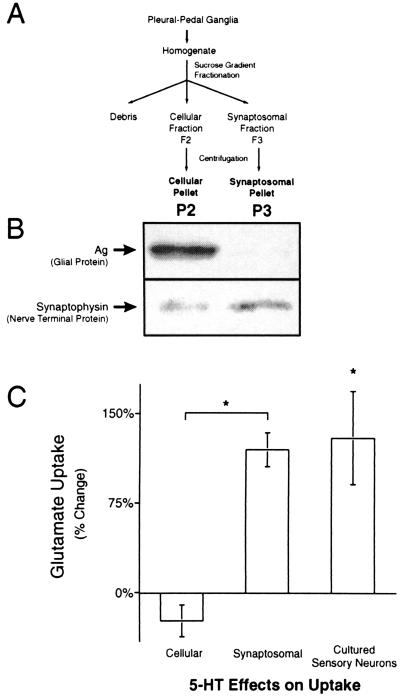
Figure 3.
Increases in Glu uptake were caused by neuronal Glu transporters. Glu uptake in two fractions generated by the synaptosomal isolation technique and in cultured sensory neurons was studied to determine if increases in Glu uptake were neuronal or glial. (A) A flow chart of the isolation technique for the synaptosome (P3) and cellular (P2) preparations. (B) Immunoblots of P2 (Left) and P3 (Right) preparations for Ag, a glial protein, and synaptophysin, a nerve terminal protein. Ag is at least tenfold enriched in the cellular (P2) relative to the synaptosomal (P3) preparation (n = 3). Synaptophysin is enriched at least threefold in the P3 relative to the P2 preparation (n = 4). Only one immunoreactive band was seen for both Ag and synaptophysin. Analysis of the Coomassie-stained transferred gel was used to verify equal protein loading. (C) Glu uptake in the P2 and P3 preparations 24 h after treatment in vivo with 500 μM 5-HT. Glu uptake was increased in the synaptosomal (n = 8), but not the cellular preparation (n = 5). There was a significant increase in Glu uptake by cultured sensory neurons 24 h after treatment with 5-HT (n = 4).