Figure 3.
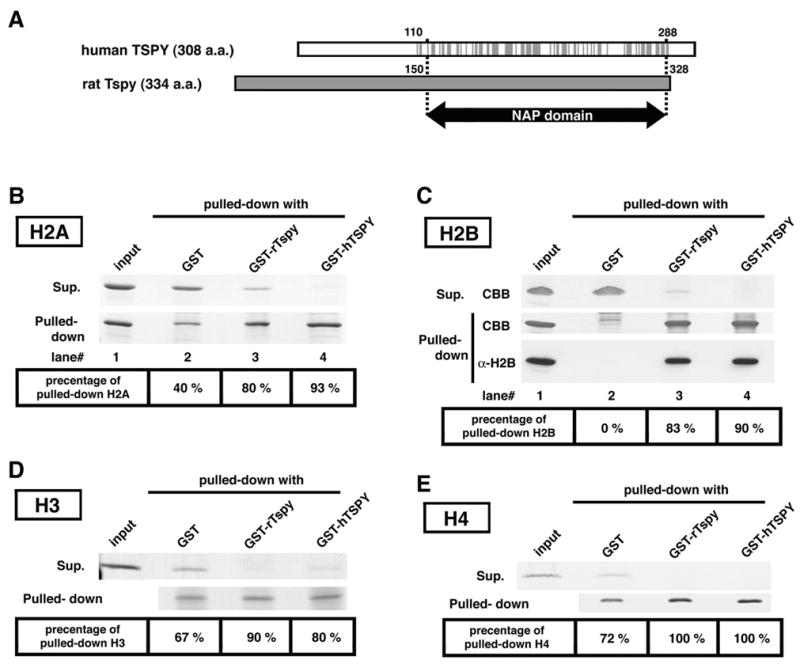
Interactions of rTspy and hTSPY with histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. (A) Alignment of hTSPY and rTspy proteins showing the homologous region encompassing the TSPY/SET/NAP1 domain. Gray lines on the hTSPY indicate positions with identical amino acid as the rTspy. The ~170 amino acid TSPY/SET/NAP1 domain is located between residue #110–288 of the hTSPY and residue #150–328 of the rTspy. The TSPY/SET/NAP1 domain is indicated by arrow (NAP domain). (B) GST pull-down assay of histone H2A using GST or GST-fusion proteins as indicated. Pulled-down proteins (pulled-down) and proteins of supernatant (supernatant) were subjected to SDS-PAGE, and visualized by Coomassie blue staining. Histone H2A was preferentially retained by Sepharose 4B resins conjugated with either GST-rTspy (lane 3) or GST-hTSPY (lane 4) but not by those conjugated with GST alone (lane 2). The numbers on bottom column indicate the approximate percentage of pulled-down H2A to total amount of H2A. Input represents equivalent material used for each GST pull-down assay. (C) GST pull-down assays of histone H2B using GST-fusion proteins. The experiment was performed similarly as described in B. Both GST-rTspy and GST-hTSPY fusion proteins (lane 3 and 4, respectively) showed significant affinity to histone H2B than GST alone (lane 2). The input represents the material used for GST pull-down assay. The authenticity of the pulled-down material as H2B was confirmed by Western-blot with anti-H2B antibody (bottom row, α-H2B). (D and E) GST pull-down assay of histones H3 (D) and H4 (E) performed similarly as described in B. Abbreviations; CBB, Coomassie blue stained band; α-H2B, Western-blot with anti-H2B antibody.
