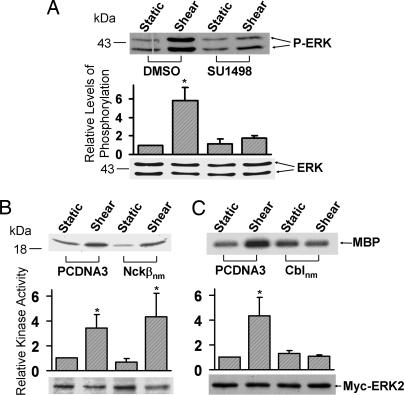
Fig. 4.
Flk-1, but not Nckβ, is essential for the shear-activated ERK. (A) BAECs were treated with 0.1% DMSO (the solvent of SU1498) as control or 5 μM SU1498 for 1 h. (B and C) Myc-ERK2 was cotransfected into BAECs with control vector PCDNA3 or Flag-Nckβnm (B) or HA-Cblnm (C). These cells were then subjected to shear stress (12 dyn/cm2) for 10 min or kept under static incubation. (A) The upper gel band shows the phosphorylated ERK levels, and the lower gel band represents the loaded ERK proteins under different conditions as indicated. (B and C) The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibodies for immunocomplex kinase assays by using MBP as the substrate. The upper gel bands are phosphorylated MBP, which indicates the level of ERK activation, and the bottom gel bands show IB with an anti-Myc antibody to indicate that the levels of the expressed exogenous Myc-tagged ERK proteins were comparable among the various samples. The bar graphs are the results of densitometry analysis showing mean ± SEM from three separate experiments. The asterisks indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) between the various samples and static controls.