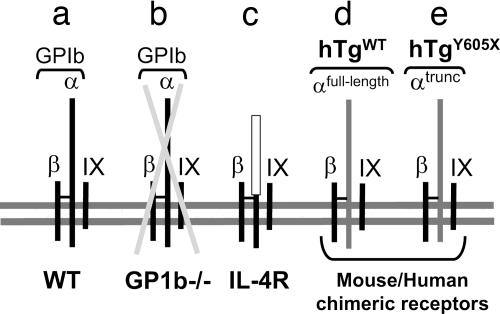
Fig. 1.
Variant platelet GP Ib-IX receptor complexes expressed on the surface of circulating platelets are schematically represented. (a) The WT GP Ib-IX complex consists of three distinct gene products. The disulfide-linked α- and β-subunits of GP Ib and the noncovalently associated GP IX. (b) A mouse model of GP Ib-IX deficiency (GP1b−/−) has been previously described mimicking the human BSS (21). This mouse model of BSS lacks the gene encoding GP Ibα, resulting in a missing complex owing to the three-subunit requirement for efficient surface expression of the complex (48). A hallmark feature of both human mouse BSS is macrothrombocytopenia. The complex depicted in c expresses a variant GP Ibα subunit with an ameliorated macrothrombocytopenia (22). The expressed GP Ibα variant is composed of an extracellular domain from the interleukin-4 receptor fused to coding sequence of a few residues from the GP Ibα extracellular domain and the complete GP Ibα transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains (IL-4R). The disulfide linkage occurring between the IL-4R/GP Ibα fusion and GP Ibβ was confirmed by biochemical analysis (22). (d) A rescue of mouse GP Ibα deficiency was performed by transgenic expression of the human GP Ibα subunit (hTgWT) as was a similar variant lacking the six terminal residues of the GP Ibα subunit (hTgY605X, e) (21, 23).