Figure 3.
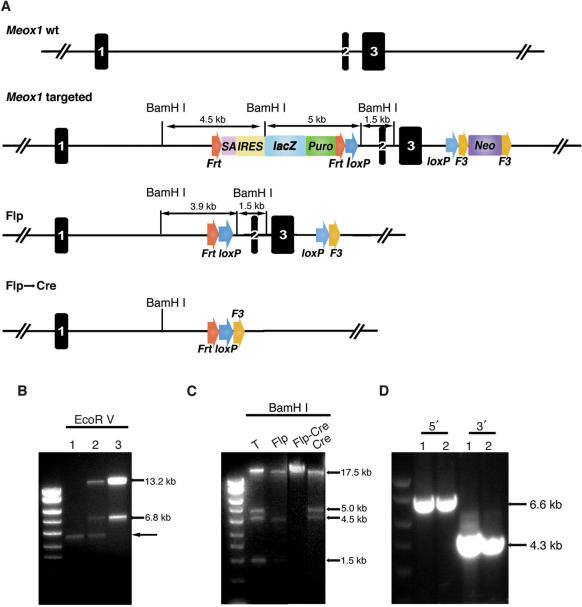
Targeting at the mouse Meox1 locus. (A) Construction of the Meox1 conditional knockout (cko) allele using the design depicted in Figure 2. The lacZ reporter is targeted to the intron 1 and the Neo cassette is in intron 3. Flp excises both lacZ reporter and the Neo cassette, leaving behind a cko allele. Cre recombinase deletes the region between the two loxP sites. One FRT, one loxP and one F3 site still remain after Cre-loxP-mediated deletion. (B) Elimination of retrieving background by re-transformation. After the Bsd and Neo cassettes were targeted to the BAC, the genomic DNA was retrieved to PL611 (AmpR). Many of the AmpR colonies were the rearranged PL611 backbone (lane 1). When the plasmid preparation from pooled AmpR colonies was examined, there were some true retrieved fragments besides the PL611 rearranged band (lane 2). Once the plasmid mixture was re-transformed into DH10B cells that were selected in Kan-LB, only the correctly recombined plasmid survived and background plasmids were eliminated (lane 3). The correctly retrieved plasmid had the Bsd cassette and produced the 13.2-kb and 6.8-kb fragments after EcoRV digestion. Arrow points to the rearranged retrieval vector backbone (PL611). (C) Test of the functionality of FRT, F3 and loxP sites. The final targeting vector was digested BamHI which generated four fragments: 17.5, 5.0, 4.5 and 1.5 kb. The digestion pattern changed after Flp or Cre excision of the selection cassettes as anticipated. T: targeting vector. (D) Long-range PCR identification of targeted ES clones. The internal primers were from the lacZ or the Neo cassette, and the external ones from genomic DNA immediately outside the homology arms. The gel image shows PCR amplification of two targeted clones. For the 5′ diagnosis, a 6.6-kb fragment was amplified (lanes 1 and 2) and for the 3′ side, the 4.3-kb junction fragment was detected in the targeted clones.