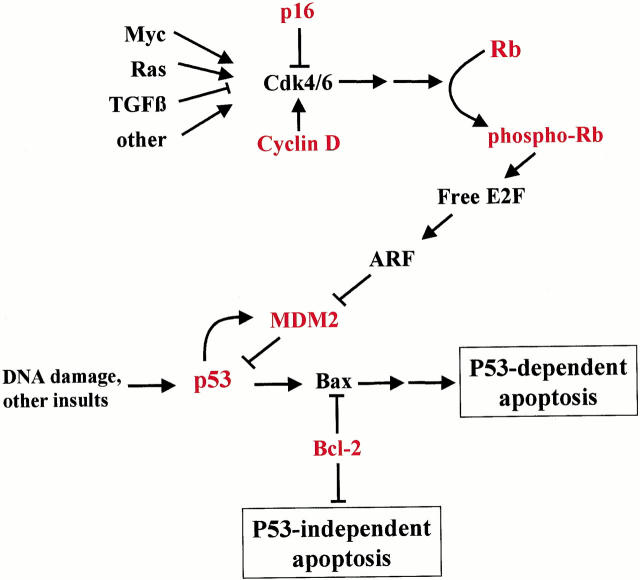
Figure 3.
Diagram illustrating how the Rb and p53 pathways are linked to form a complex tumor suppressor network. Rb regulates the cell cycle by arresting cells in G1 phase. Rb can be temporarily inactivated to allow cell division by phosphorylation of the protein. Pathological inactivation of the Rb pathway can result from direct mutation of the Rb gene, or from inappropriate phosphorylation of Rb because of disruption of upstream regulators. The ARF-MDM2 axis links the Rb and p53 pathways and can trigger apoptosis as a result of uncontrolled proliferation. Thus, most cancers acquire mutations in both pathways during malignant progression to evade cell cycle control and apoptosis. Proteins in red were analyzed in this study. See text for details.