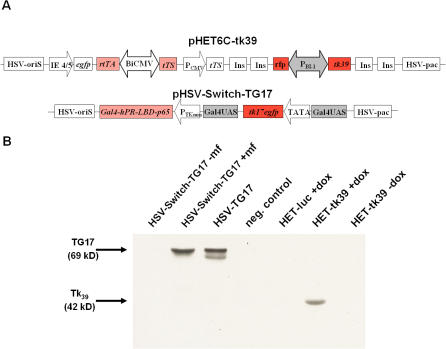
Figure 1. Inducible HSV-amplicon constructs.
(A) The doxycycline-regulated HET6C-tk39 vector consists of a bi-directional CMV promoter (BiCMV) controlling gene expression of the transactivator rtTA and the tetracycline controlled transcriptional silencer tTS [35]. A bi-directional tet-responsive promoter (PBI-1) controls expression of the marker genes rfp and HSV-1-tk39. In the absence of doxycycline, the silencer tTS binds to PBI-1, thus repressing background activity of this promoter. The presence of doxycycline leads to its release and binding of rtTA instead, thereby inducing gene expression of reporter genes rfp and tk39. The plasmid components of the mifepristone-inducible HSV-Switch-TG17 vector encode the chimeric transactivator Gal4-hPR-LBD-p65 and the PET-reporter gene HSV-1-tkgfp under the control of a synthetic promoter consisting of four GAL4 upstream response elements and a TATA box. TG17 gene expression is induced by the chimeric transactivator protein in the presence of mifepristone. (B) Western Blot analysis of reporter expression was performed by infecting human Gli36ΔEGFR cells with HSV-Switch-TG17, HSV-TG17, HET6C-tk39 or HET6C-luc, respectively. Protein signals for the fusion protein TG17 were only obtained by infection of cells with HSV-TG17, where expression of TG17 is under control of the constitutive CMV-promoter, or HSV-Switch-TG17 in the presence of the inducer mifepristone. The doublet band visible in HSV-TG17 infected cells may be due to sample processing with reducing agents and has already been seen and described for other TKGFP fusion constructs as well as wt HSV-thymidine kinase. TK39-protein signal was detectable only in cells that were infected with HET6C-tk39 and treated with doxycycline.