Figure 1.
Overexpression of oskar mRNA Causes Its Mislocalization and Premature Translation in the Middle of the Oocyte
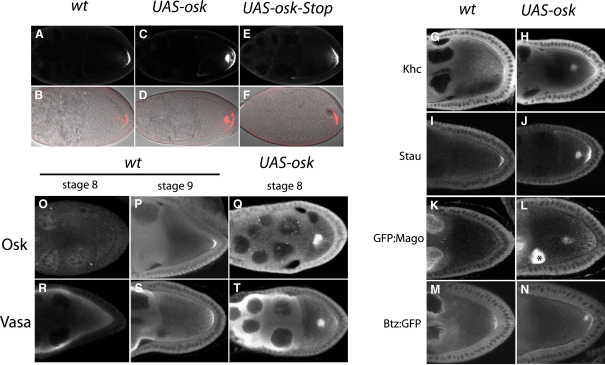
(A–F) Fluorescence in situ hybridizations to oskar mRNA in wild-type (A and B), UAS-osk (C and D) and UAS-osk-Stop (E and F) stage 9 oocytes ([B], [D], and [F] were obtained by overlaying confocal pseudo differential-interference-contrast images with the in situ stainings [red channel] from the top panel [A, C, and E]). Overexpressed oskar mRNA is localized to both the posterior pole and an ectopic site in the middle of the UAS-osk oocytes. In flies overexpressing an untranslatable version of oskar mRNA (UAS-osk-Stop), the incidence of the ectopic localization is reduced, and most egg chambers show a wild-type pattern of localization (E and F).
(G–N) Immunostainings for the Kinesin heavy chain (G and H), Stau (I and J), and localization of GFP-tagged variants of Mago nashi (K and L) and Barentsz (M and N) in wild-type (G, I, K, and M) and UAS-osk egg chambers (H, J, L, and N). All these components of the oskar mRNA localization complex are mislocalized to the center of the oocyte with overexpressed oskar mRNA. The asterisk in (L) indicates the strong accumulation of Mago:GFP in the oocyte nucleus.
(O–Q) Immunostainings for Oskar protein. In wild-type egg chambers, Oskar protein is not expressed at stage 8 (O) and is first translated at the posterior pole of the oocyte at stage 9 (P). In UAS-osk oocytes, Oskar protein is translated in the middle of the oocyte at stage 8 (Q).
(R–T) Immunostainings for Vasa protein. Oskar recruits Vasa protein to the posterior of the oocyte at stage 9 in wild-type egg chambers (R and S). In UAS-osk oocytes, the ectopic Oskar in the middle of the oocyte recruits Vasa at stage 8 (T).