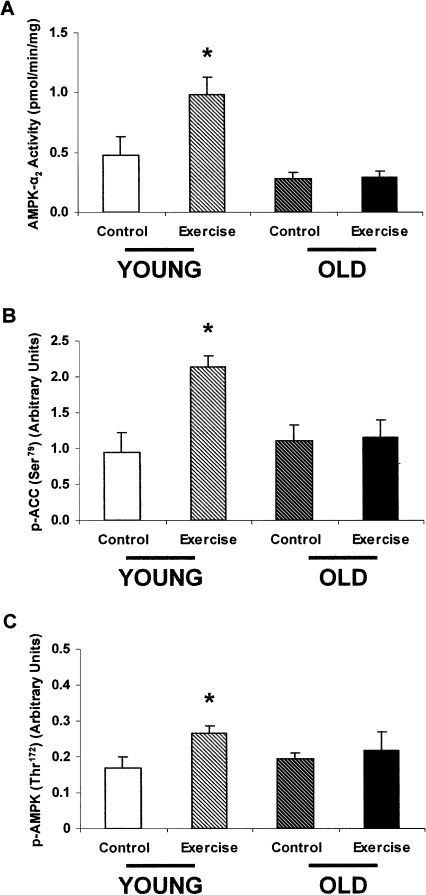
Figure 2.
The Effect of Exercise on AMPK in Young and Old Rats
(A) AMPK-α2 activity in the EDL muscle of exercising or sedentary young and old rats. AMPK-α2 activity was increased by 110% in the young exercising rats compared to the young sedentary rats. In contrast, there was no difference between the old exercising rats and old sedentary rats. (n = 8 in each group.) ∗p = 0.01.
(B) p-ACC (Ser79) in the EDL muscle of exercising or sedentary young and old rats. Exercise resulted in a 127% increase in p-ACC (Ser79) in the young rats. In contrast, there was no effect of exercise on p-ACC (Ser79) in the old rats. (n = 4 in each group.) ∗p < 0.05.
(C) p-AMPK (Thr172) in the EDL muscle of exercising or sedentary young and old rats. Exercise resulted in a 55% increase in p-AMPK (Thr172) in the young rats. In contrast, there was no effect of exercise on p-AMPK (Thr172) in the old rats. (n = 4 in each group.) ∗p < 0.05.