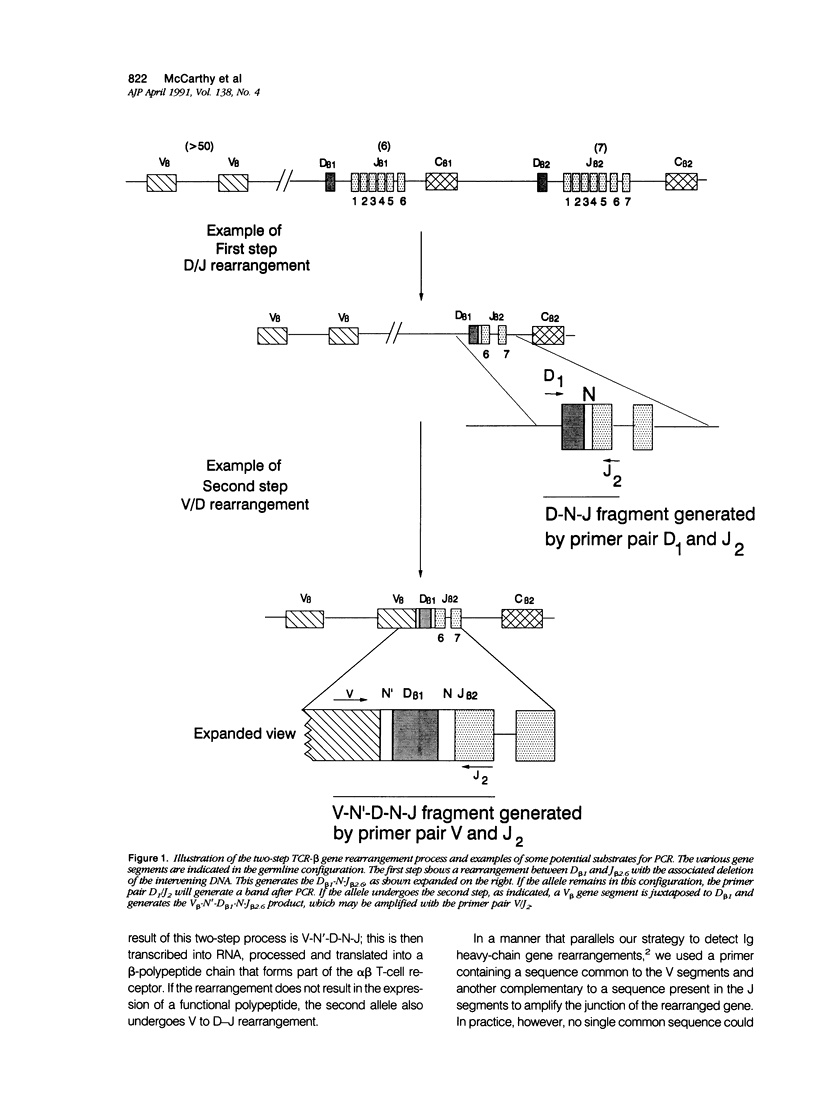
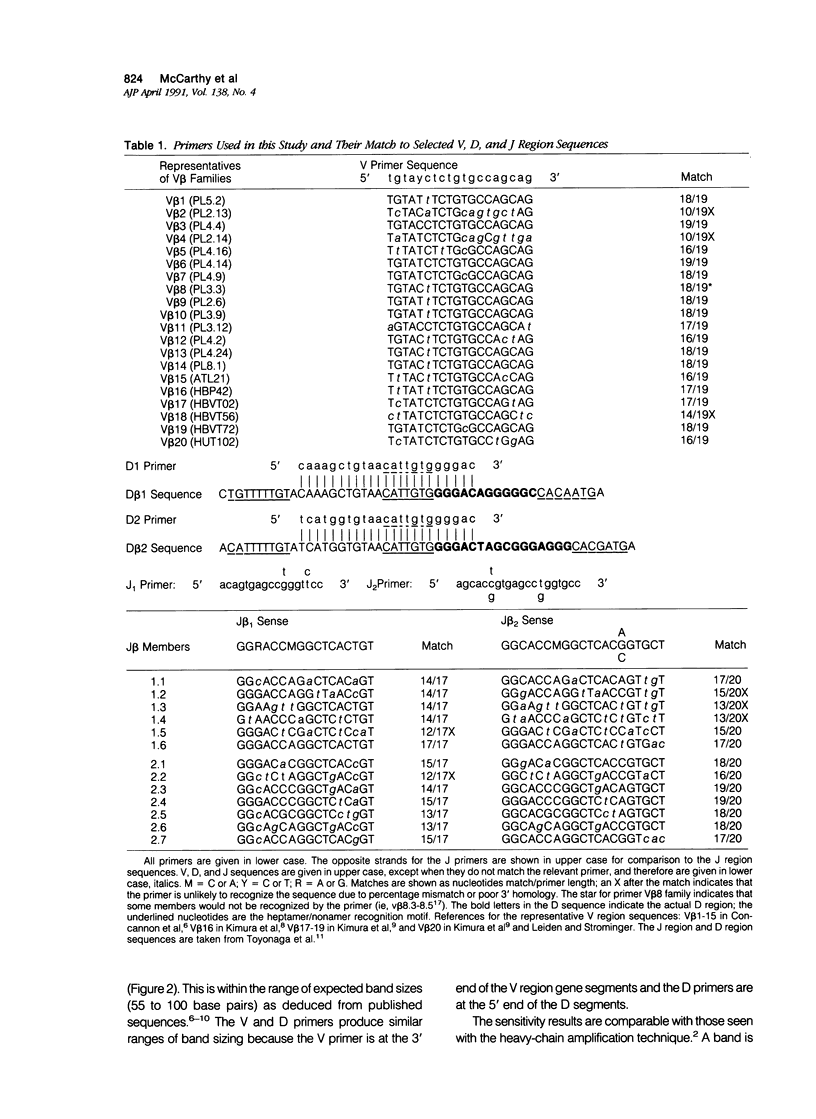
Abstract
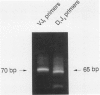
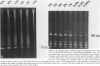
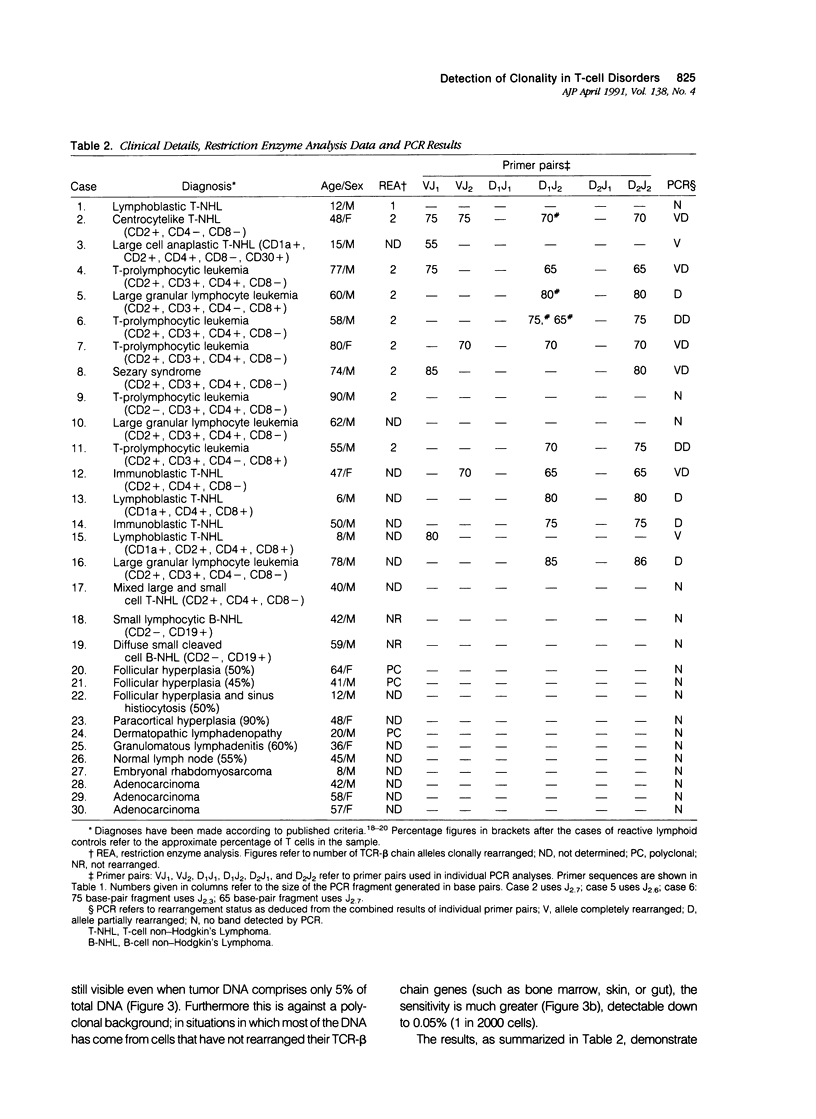
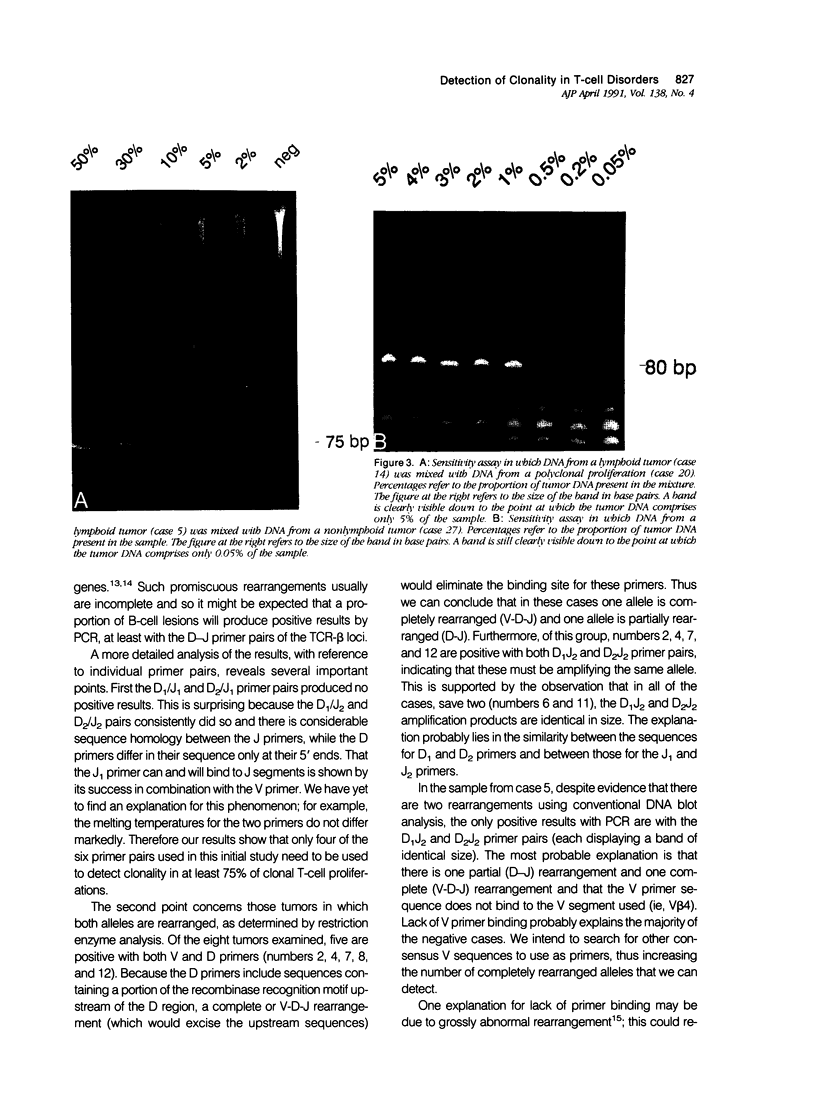
A series of T-cell proliferations in peripheral blood, bone marrow, or tissue samples were analyzed for clonality. The technique used employs the polymerase chain reaction to amplify portions of the rearranged T-cell receptor beta chain genes, using primers recognizing conserved sequences of the variable, diversity, and joining region segments. We examined 17 cases of T-cell lymphoma or leukemia; a clone was identified in 13 cases (76%) overall and in 7 of 8 cases (87.5%) in which both beta-chain alleles were known to be rearranged, as shown by restriction enzyme analysis. No clonal rearrangements were detected in samples from 13 non-T-cell disorders, including B-cell lymphomas, reactive lymphoid proliferations, and nonlymphoid tumors. This method is useful for detecting clones in thymic and post-thymic T-cell malignancies and has the advantages of being extremely rapid (a result is obtained within hours of the biopsy procedure), requiring no radiolabeling, using only a small amount of tissue, and being applicable to formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boehm T., Rabbitts T. H. The human T cell receptor genes are targets for chromosomal abnormalities in T cell tumors. FASEB J. 1989 Oct;3(12):2344–2359. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.12.2676678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concannon P., Pickering L. A., Kung P., Hood L. Diversity and structure of human T-cell receptor beta-chain variable region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6598–6602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duby A. D., Seidman J. G. Abnormal recombination products result from aberrant DNA rearrangement of the human T-cell antigen receptor beta-chain gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4890–4894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furley A. J., Chan L. C., Mizutani S., Ford A. M., Weilbaecher K., Pegram S. M., Greaves M. F. Lineage specificity of rearrangement and expression of genes encoding the T cell receptor-T3 complex and immunoglobulin heavy chain in leukemia. Leukemia. 1987 Sep;1(9):644–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furley A. J., Mizutani S., Weilbaecher K., Dhaliwal H. S., Ford A. M., Chan L. C., Molgaard H. V., Toyonaga B., Mak T., van den Elsen P. Developmentally regulated rearrangement and expression of genes encoding the T cell receptor-T3 complex. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90861-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griesser H., Feller A., Lennert K., Minden M., Mak T. W. Rearrangement of the beta chain of the T cell antigen receptor and immunoglobulin genes in lymphoproliferative disorders. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1179–1184. doi: 10.1172/JCI112700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura N., Toyonaga B., Yoshikai Y., Du R. P., Mak T. W. Sequences and repertoire of the human T cell receptor alpha and beta chain variable region genes in thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Mar;17(3):375–383. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura N., Toyonaga B., Yoshikai Y., Triebel F., Debre P., Minden M. D., Mak T. W. Sequences and diversity of human T cell receptor beta chain variable region genes. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):739–750. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M., Strominger J. L. Generation of diversity of the beta chain of the human T-lymphocyte receptor for antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4456–4460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matutes E., Brito-Babapulle V., Worner I., Sainati L., Foroni L., Catovsky D. T-cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: the spectrum of mature T-cell disorders. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1988;30(5-6):347–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy K. P., Sloane J. P., Wiedemann L. M. Rapid method for distinguishing clonal from polyclonal B cell populations in surgical biopsy specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1990 May;43(5):429–432. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.5.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu G., Strauss E. C., Lai E., Hood L. E. Analysis of a human V beta gene subfamily. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1600–1614. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillinghast J. P., Behlke M. A., Loh D. Y. Structure and diversity of the human T-cell receptor beta-chain variable region genes. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):879–883. doi: 10.1126/science.3755549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkachuk D. C., Griesser H., Takihara Y., Champagne E., Minden M., Feller A. C., Lennert K., Mak T. W. Rearrangement of T-cell delta locus in lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood. 1988 Jul;72(1):353–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyonaga B., Yoshikai Y., Vadasz V., Chin B., Mak T. W. Organization and sequences of the diversity, joining, and constant region genes of the human T-cell receptor beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8624–8628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann T. A. The arrangement of immunoglobulin and T cell receptor genes in human lymphoproliferative disorders. Adv Immunol. 1987;40:247–321. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]