Figure 2.
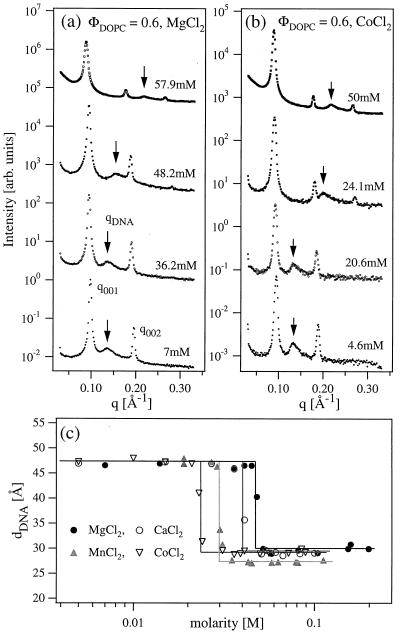
(a) Synchrotron XRD measurements of the powder isoelectric [ρ = (weight lipid)/(weight DNA) = 2.2, ΦDOPC = (weight DOPC)/(weight lipid) = mole fraction of DOPC = 0.6] CL-DNA complex samples in the presence of MgCl2. dDNA abruptly changes from 47 Å (set by ΦDOPC) at low MgCl2 concentrations (M) to 28.9 Å above M = M* = 48.2 mM. Also, the complex periodicity d increases to 70 ± 1 Å for M > M*. (b) Similar XRD measurements in the presence of CoCl2 show that Co2+ ions also cause a condensation transition of the 2D DNA arrays but at smaller M* ≈ 24 mM. The (003) peak appears for M > M* in a and b, while the (004) is visible below and above M*. This is because the (003) peak in the lipid-DNA lamellar structure factor is near a zero crossing of the form factor. For M > M*, the screening of the head groups in the presence of the trapped counterions leads to a decrease in the area per charged head group. To match the change in the area per head, the area per tail decreases through chain stretching, which leads to a different position for the zero-crossing of the form factor. (c) Variation of the dDNA with the concentrations of four different divalent salts.