Abstract
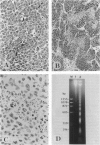
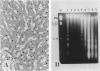
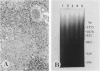
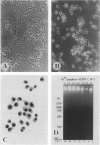
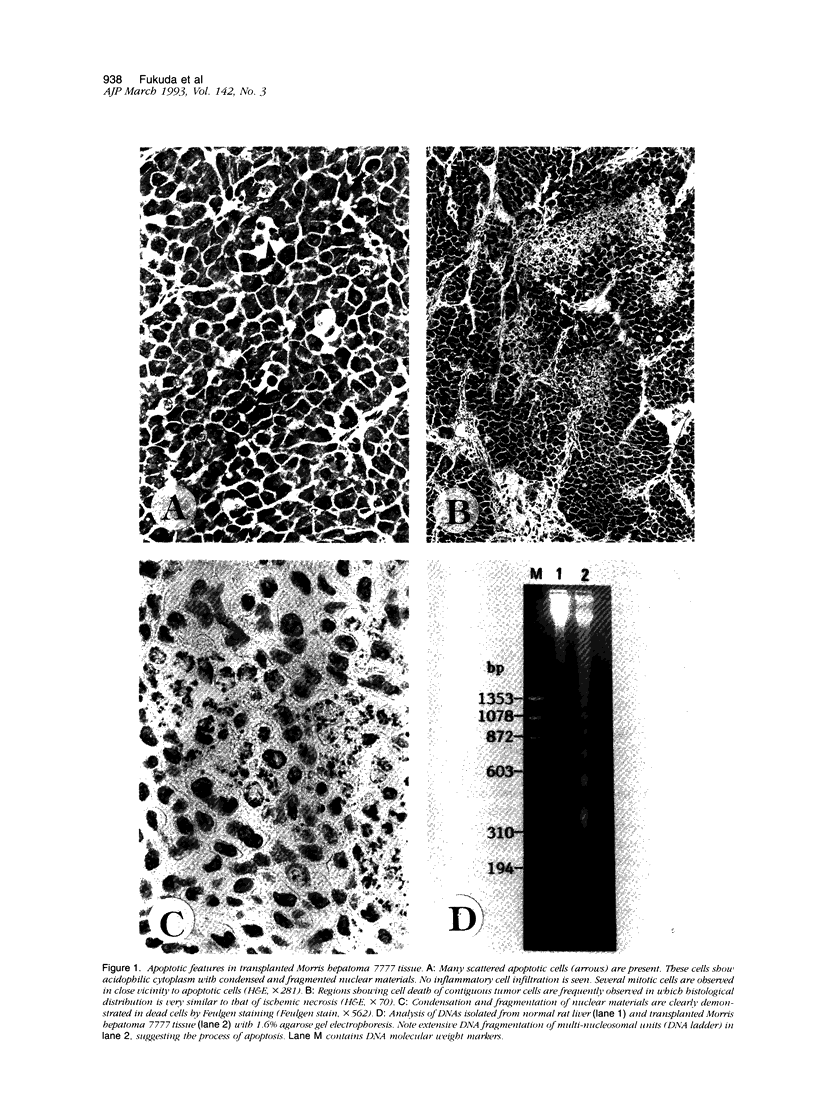
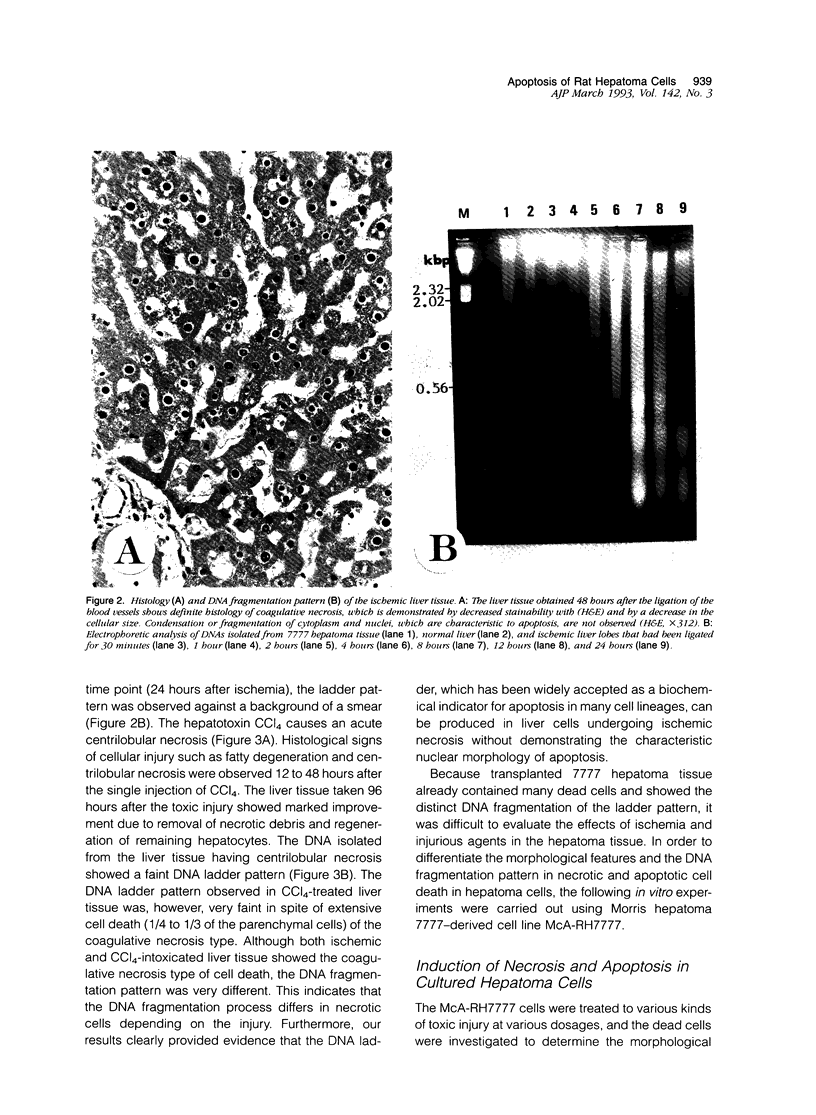
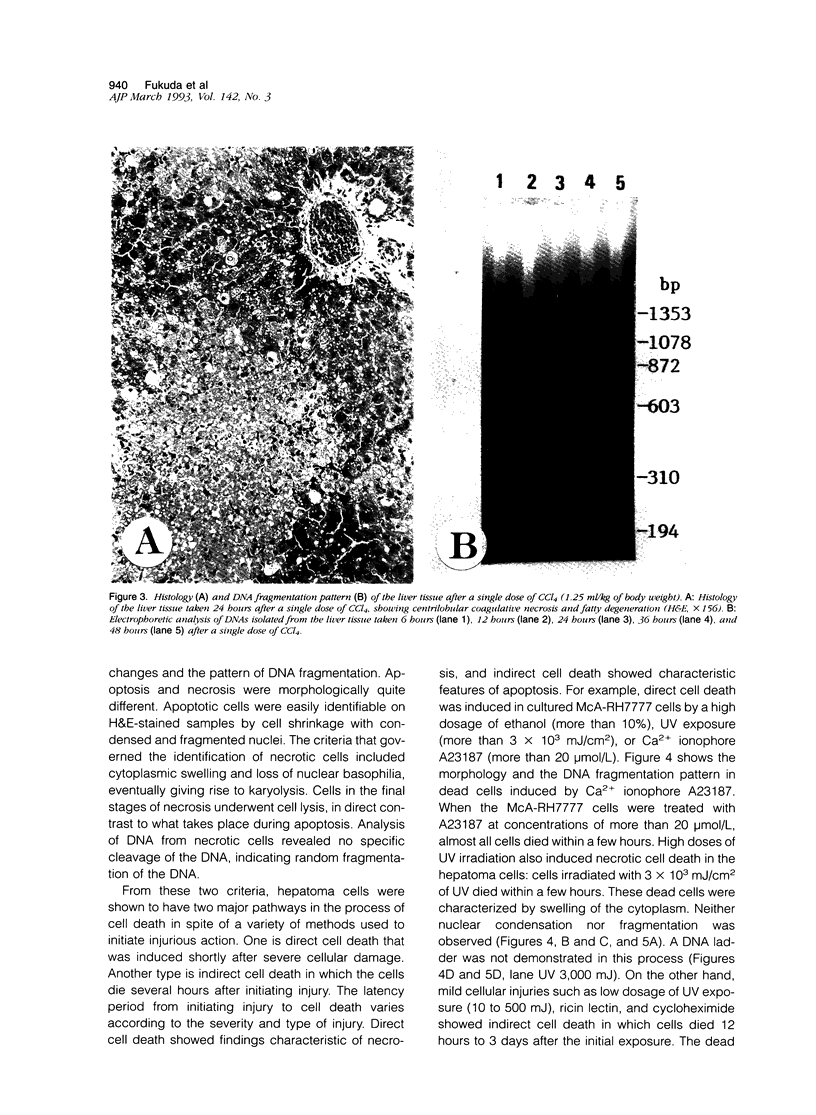
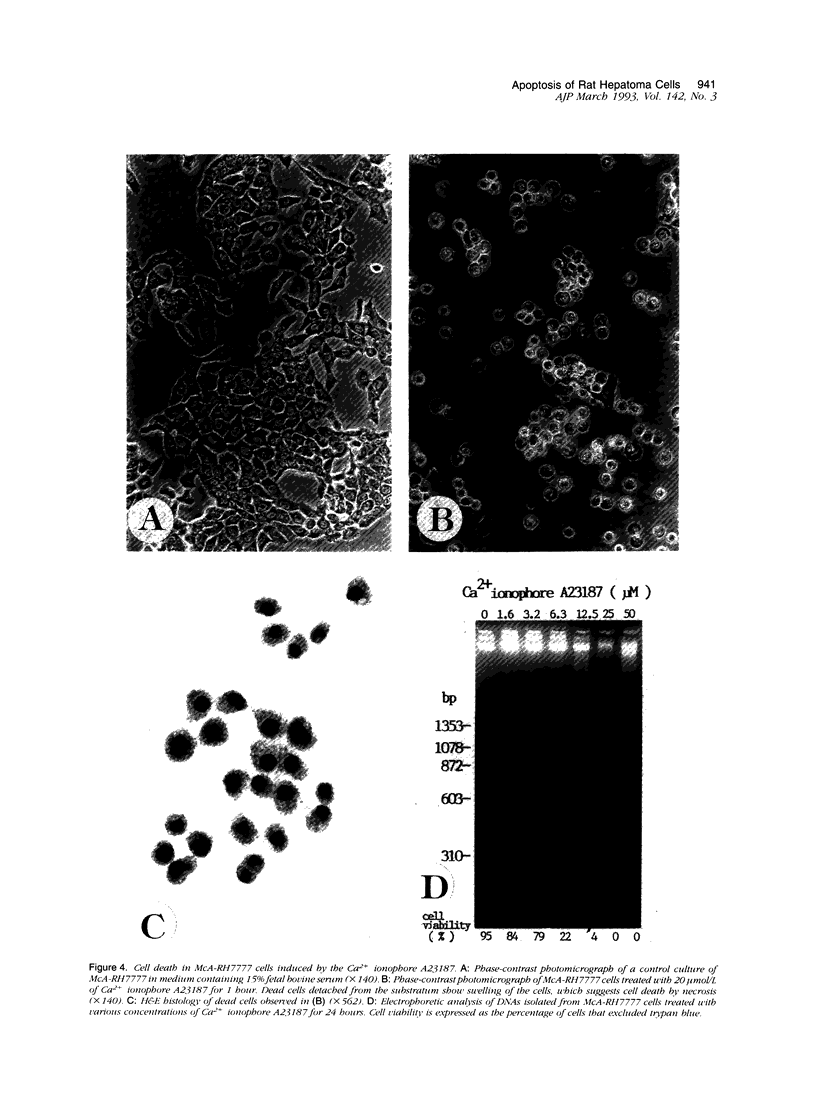
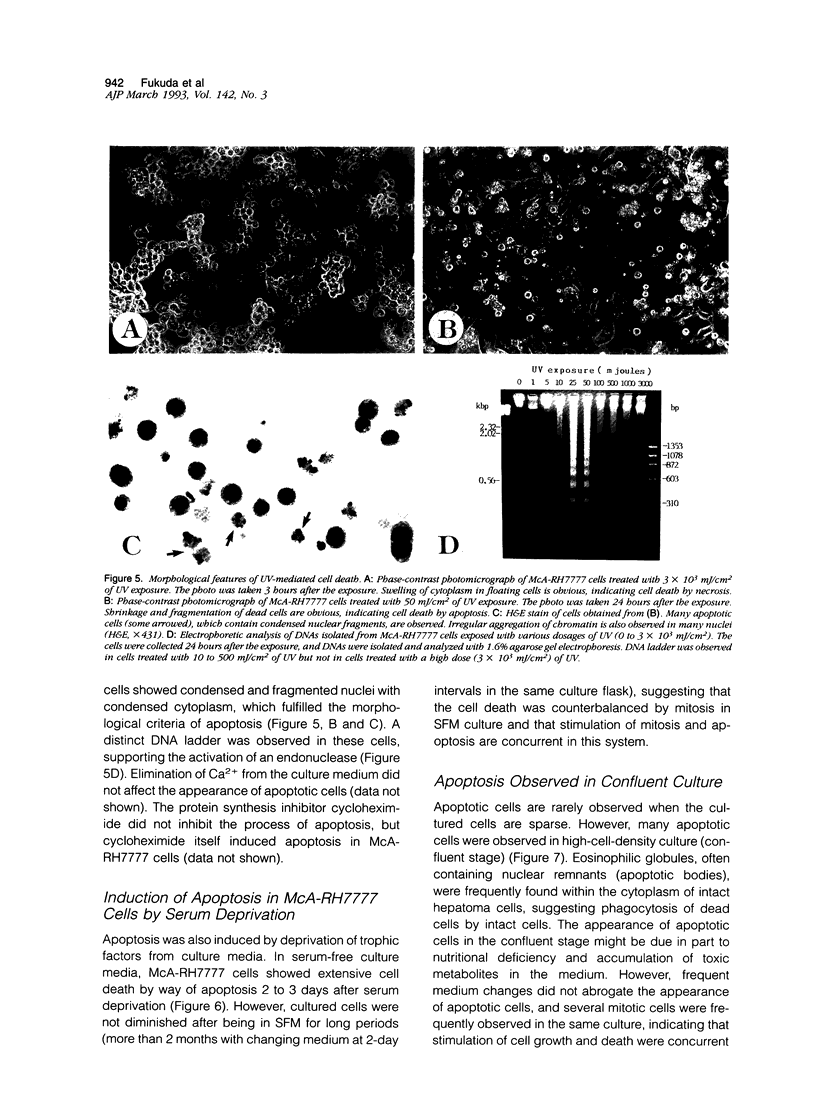
Cell death may occur by either of two mechanisms: necrosis or apoptosis (programmed cell death). In this paper, we demonstrate extensive chromatin cleavage into oligonucleosome-length fragments (DNA ladder) in transplanted Morris hepatoma 7777 tissue, which is suggestive of the stimulation of an endogenous endonuclease activity previously found to be involved in the process of apoptosis. The existence of many apoptotic cells, which are morphologically characterized by condensed cytoplasm and basophilic nuclear fragments, were also seen in this tissue. In vivo and in vitro experiments were designed to further differentiate the morphological and biochemical features of necrosis and apoptosis in liver and hepatoma cells. Liver tissue undergoing ischemic necrosis showed a distinct DNA ladder pattern without demonstrating the morphology of apoptosis, indicating that chromatin cleavage into oligonucleosomal-length fragments is not confined to apoptotic cell death, at least in liver cells. In in vitro-cultured McA-RH7777 cells, however, DNA ladder pattern was detected only in cells showing characteristic morphology of apoptosis. From these two criteria (i.e., characteristic morphology and DNA ladder), it was strongly suggested that the apoptotic process is highly activated in the transplanted 7777 tissue. Based on the results obtained from in vitro experiments, it was suggested that tumor apoptosis may represent a residual attempt at autoregulation within the expanding tumor population and/or may result from mild cellular injuries such as hypoxia, nutrient deficiency, or other unknown noxious factor(s). We also showed evidence that apoptosis is inducible in hepatoma cells in vitro by a wide range of mild injuries or stimuli.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alnemri E. S., Litwack G. Activation of internucleosomal DNA cleavage in human CEM lymphocytes by glucocorticoid and novobiocin. Evidence for a non-Ca2(+)-requiring mechanism(s). J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17323–17333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arends M. J., Morris R. G., Wyllie A. H. Apoptosis. The role of the endonuclease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Mar;136(3):593–608. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry M. A., Behnke C. A., Eastman A. Activation of programmed cell death (apoptosis) by cisplatin, other anticancer drugs, toxins and hyperthermia. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 15;40(10):2353–2362. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90733-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursch W., Lauer B., Timmermann-Trosiener I., Barthel G., Schuppler J., Schulte-Hermann R. Controlled death (apoptosis) of normal and putative preneoplastic cells in rat liver following withdrawal of tumor promoters. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Apr;5(4):453–458. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.4.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursch W., Taper H. S., Lauer B., Schulte-Hermann R. Quantitative histological and histochemical studies on the occurrence and stages of controlled cell death (apoptosis) during regression of rat liver hyperplasia. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1985;50(2):153–166. doi: 10.1007/BF02889898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C. Glucocorticoid activation of a calcium-dependent endonuclease in thymocyte nuclei leads to cell death. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):38–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins R. J., Harmon B. V., Souvlis T., Pope J. H., Kerr J. F. Effects of cycloheximide on B-chronic lymphocytic leukaemic and normal lymphocytes in vitro: induction of apoptosis. Br J Cancer. 1991 Sep;64(3):518–522. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Columbano A., Ledda-Columbano G. M., Rao P. M., Rajalakshmi S., Sarma D. S. Occurrence of cell death (apoptosis) in preneoplastic and neoplastic liver cells. A sequential study. Am J Pathol. 1984 Sep;116(3):441–446. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper E. H., Bedford A. J., Kenny T. E. Cell death in normal and malignant tissues. Adv Cancer Res. 1975;21:59–120. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60971-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dive C., Hickman J. A. Drug-target interactions: only the first step in the commitment to a programmed cell death? Br J Cancer. 1991 Jul;64(1):192–196. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. L. Biology of disease: membrane injury and calcium homeostasis in the pathogenesis of coagulative necrosis. Lab Invest. 1982 Aug;47(2):114–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. L., Chien K. R., Mittnacht S., Jr Myocardial ischemia: the pathogenesis of irreversible cell injury in ischemia. Am J Pathol. 1981 Feb;102(2):271–281. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. P., McConkey D. J., Nicotera P., Orrenius S. Calcium-activated DNA fragmentation in rat liver nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6398–6403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F. Shrinkage necrosis: a distinct mode of cellular death. J Pathol. 1971 Sep;105(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/path.1711050103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyprianou N., English H. F., Isaacs J. T. Programmed cell death during regression of PC-82 human prostate cancer following androgen ablation. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 15;50(12):3748–3753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennon S. V., Martin S. J., Cotter T. G. Dose-dependent induction of apoptosis in human tumour cell lines by widely diverging stimuli. Cell Prolif. 1991 Mar;24(2):203–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1991.tb01150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Hartzell P., Nicotera P., Orrenius S. Calcium-activated DNA fragmentation kills immature thymocytes. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1843–1849. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.7.2497041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakabayashi H., Taketa K., Yamane T., Miyazaki M., Miyano K., Sato J. Phenotypical stability of a human hepatoma cell line, HuH-7, in long-term culture with chemically defined medium. Gan. 1984 Feb;75(2):151–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressman B. C. Biological applications of ionophores. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:501–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotello R. J., Lieberman R. C., Purchio A. F., Gerschenson L. E. Coordinated regulation of apoptosis and cell proliferation by transforming growth factor beta 1 in cultured uterine epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3412–3415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte-Hermann R., Timmermann-Trosiener I., Barthel G., Bursch W. DNA synthesis, apoptosis, and phenotypic expression as determinants of growth of altered foci in rat liver during phenobarbital promotion. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 15;50(16):5127–5135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle J., Kerr J. F., Bishop C. J. Necrosis and apoptosis: distinct modes of cell death with fundamentally different significance. Pathol Annu. 1982;17(Pt 2):229–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano Y. S., Harmon B. V., Kerr J. F. Apoptosis induced by mild hyperthermia in human and murine tumour cell lines: a study using electron microscopy and DNA gel electrophoresis. J Pathol. 1991 Apr;163(4):329–336. doi: 10.1002/path.1711630410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. E., Reed D. J. Current status of calcium in hepatocellular injury. Hepatology. 1989 Sep;10(3):375–384. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderbilt J. N., Bloom K. S., Anderson J. N. Endogenous nuclease. Properties and effects on transcribed genes in chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13009–13017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring P. DNA fragmentation induced in macrophages by gliotoxin does not require protein synthesis and is preceded by raised inositol triphosphate levels. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14476–14480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. T. Programmed cell death: apoptosis and oncogenesis. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1097–1098. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90002-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Morris R. G., Smith A. L., Dunlop D. Chromatin cleavage in apoptosis: association with condensed chromatin morphology and dependence on macromolecular synthesis. J Pathol. 1984 Jan;142(1):67–77. doi: 10.1002/path.1711420112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Resnitzky D., Lotem J., Sachs L., Kimchi A., Oren M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):345–347. doi: 10.1038/352345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]