Abstract
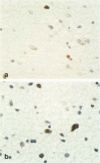
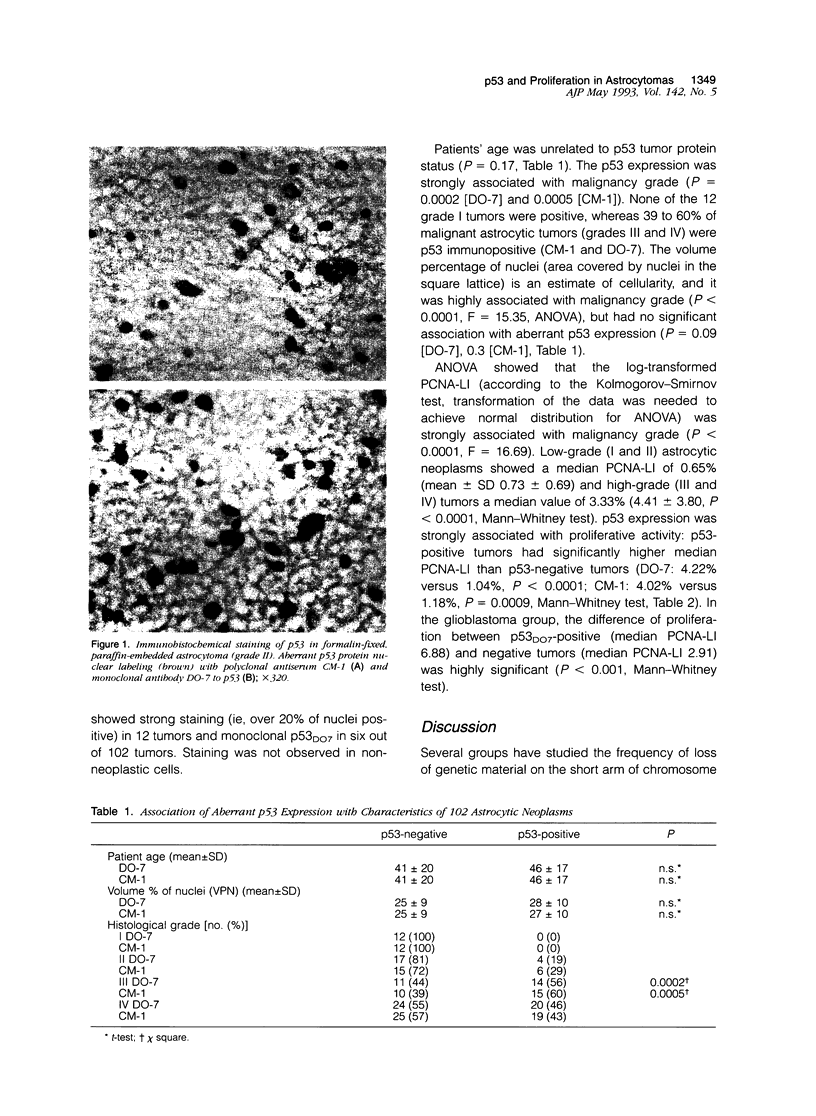
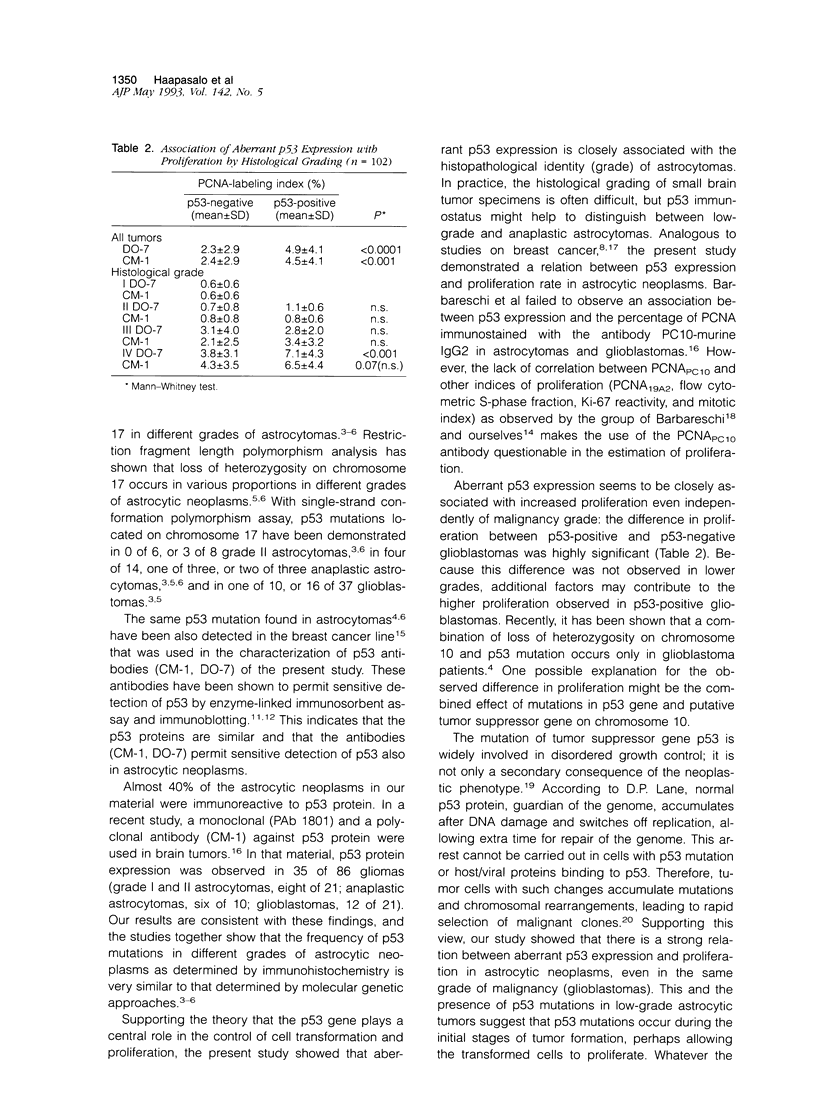
Aberrant expression of the p53 suppressor gene was evaluated in 102 cases of astrocytic neoplasms. Immunohistochemical staining with a monoclonal antibody (DO-7) and a polyclonal antibody (CM-1) to p53 protein (both wild type and mutant) on formalin-fixed paraffin sections showed a strong correlation with malignancy grade. The staining was positive in 49% of malignant neoplasms (grades III and IV) and in 19 to 29% of grade II astrocytomas, whereas none of the grade I tumors were positive. p53 expression was significantly associated with proliferation rate determined by immunohistochemical proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)-staining (median PCNA-labeling index (%): 4.22 (DO-7-positive) versus 1.18 (DO-7-negative), P < 0.0001; 4.02 (CM-1-positive) versus 1.18 (CM-1-negative), P < 0.001). Interestingly, in the glioblastoma group (n = 44), p53-positive tumors had higher proliferation indices, suggesting that histologically similar tumors could be divided into prognostically different subgroups by immunohistochemical demonstration of aberrant p53 expression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbareschi M., Iuzzolino P., Pennella A., Allegranza A., Arrigoni G., Dalla Palma P., Doglioni C. p53 protein expression in central nervous system neoplasms. J Clin Pathol. 1992 Jul;45(7):583–586. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.7.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartek J., Iggo R., Gannon J., Lane D. P. Genetic and immunochemical analysis of mutant p53 in human breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):893–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bártek J., Bártková J., Vojtesek B., Stasková Z., Lukás J., Rejthar A., Kovarík J., Midgley C. A., Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Aberrant expression of the p53 oncoprotein is a common feature of a wide spectrum of human malignancies. Oncogene. 1991 Sep;6(9):1699–1703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Rilke F., Andreola S., D'Amato L., Delia D. P53 expression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1988 Feb 15;41(2):178–183. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel R. H., Bayona W., Koslow M., Newcomb E. W. p53 mutations in human malignant gliomas: comparison of loss of heterozygosity with mutation frequency. Cancer Res. 1992 Mar 15;52(6):1427–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Yamashita J., Yamaguchi K. Timing and role of p53 gene mutation in the recurrence of glioma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 31;180(2):1145–1150. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isola J., Visakorpi T., Holli K., Kallioniemi O. P. Association of overexpression of tumor suppressor protein p53 with rapid cell proliferation and poor prognosis in node-negative breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Jul 15;84(14):1109–1114. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.14.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):15–16. doi: 10.1038/358015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonardi E., Girlando S., Serio G., Mauri F. A., Perrone G., Scampini S., Dalla Palma P., Barbareschi M. PCNA and Ki67 expression in breast carcinoma: correlations with clinical and biological variables. J Clin Pathol. 1992 May;45(5):416–419. doi: 10.1136/jcp.45.5.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashiyama S., Murakami Y., Yoshimoto T., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Detection of p53 gene mutations in human brain tumors by single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis of polymerase chain reaction products. Oncogene. 1991 Aug;6(8):1313–1318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley C. A., Fisher C. J., Bártek J., Vojtesek B., Lane D., Barnes D. M. Analysis of p53 expression in human tumours: an antibody raised against human p53 expressed in Escherichia coli. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jan;101(Pt 1):183–189. doi: 10.1242/jcs.101.1.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock C. S., Thompson I. W., Van Noorden S. Silver enhancement of polymerised diaminobenzidine: increased sensitivity for immunoperoxidase staining. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Sep;44(9):756–758. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.9.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siitonen S. M., Kallioniemi O. P., Isola J. J. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunohistochemistry using monoclonal antibody 19A2 and a new antigen retrieval technique has prognostic impact in archival paraffin-embedded node-negative breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):1081–1089. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtesek B., Bártek J., Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. An immunochemical analysis of the human nuclear phosphoprotein p53. New monoclonal antibodies and epitope mapping using recombinant p53. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Jul 6;151(1-2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(92)90122-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynford-Thomas D. P53 in tumour pathology: can we trust immunocytochemistry? J Pathol. 1992 Apr;166(4):329–330. doi: 10.1002/path.1711660402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Deimling A., Eibl R. H., Ohgaki H., Louis D. N., von Ammon K., Petersen I., Kleihues P., Chung R. Y., Wiestler O. D., Seizinger B. R. p53 mutations are associated with 17p allelic loss in grade II and grade III astrocytoma. Cancer Res. 1992 May 15;52(10):2987–2990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]