Figure 1.
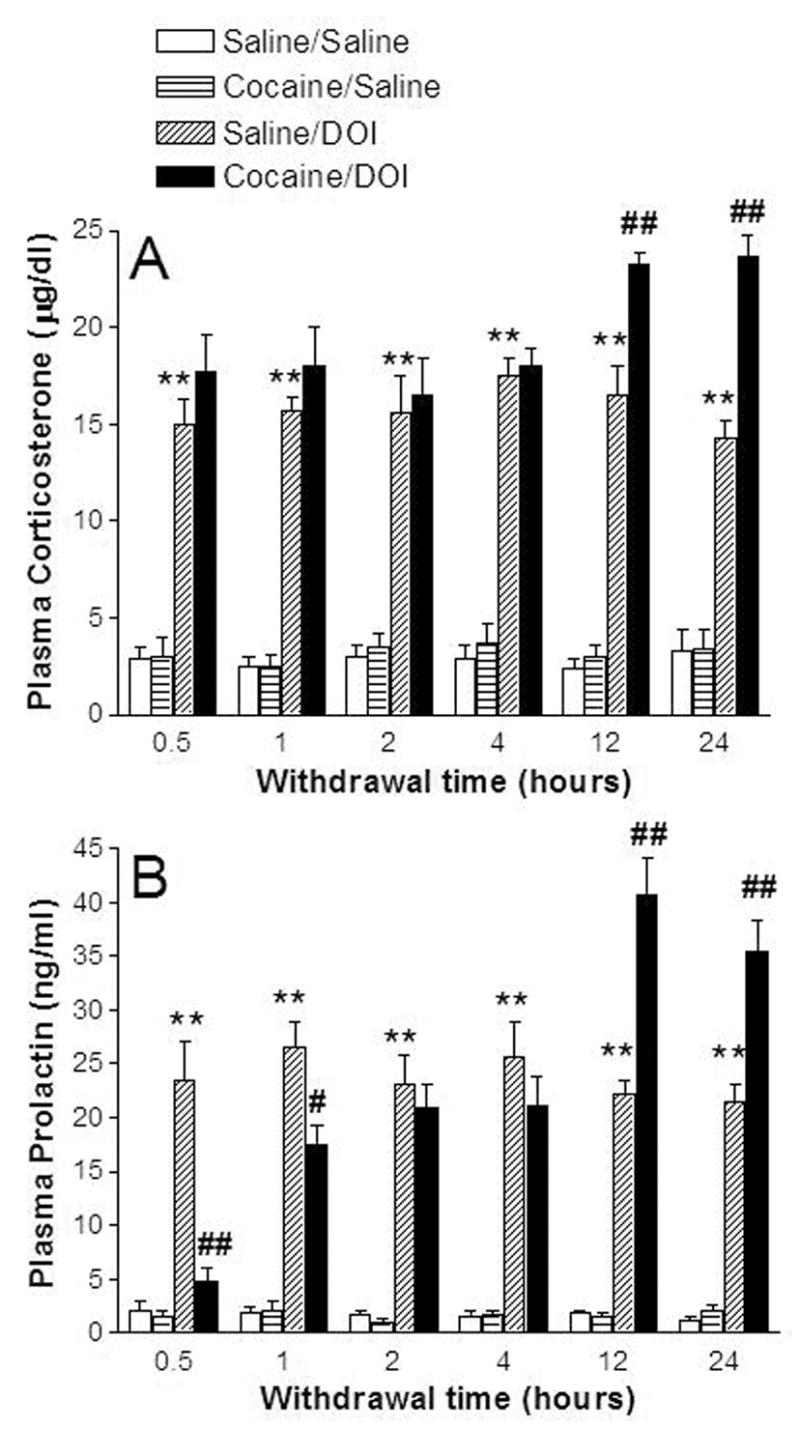
Time-dependent supersensitivity of the (−)DOI-induced neuroendocrine responses in cocaine-treated rats at various post-treatment withdrawal times. The data represent the plasma levels of corticosterone (A) and prolactin (B) in rats treated chronically with saline (1ml/kg, i.p., bid) or cocaine (15mg/kg, i.p., bid) and challenged with saline (1 ml/kg) or (−)DOI (0.5 mg/kg) (mean ± SEM of 8–12 rats per group). **p <0.01, significant effect of (−)DOI compared with the respective saline challenge group. ##p < 0.01, significant effect of (−)DOI challenge in cocaine-treated rats compared with (−)DOI challenge in saline-treated rats (three-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls multiple range test).
