Abstract
Ewing's sarcoma and the related primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET) share a unique and specific t(11;22)(q24;q12) chromosomal translocation. The breakpoints have recently been cloned and shown to involve the EWS gene on chromosome 22 and the FLI-1 gene on chromosome 11. Translocation results in the fusion of these genes on the der(22) chromosome, resulting in the production of a novel chimeric EWS/FLI-1 message. Using oligonucleotide primers derived from EWS and FLI-1 complementary DNAs, we were able to amplify a specific fusion transcript from 18 of 18 cases containing t(11;22) and 10 of 14 cases of Ewing's sarcoma/PNET that had unsuccessful cytogenetics. No EWS/FLI-1 fusion transcripts were detected in five cell lines derived from cases of pediatric sarcomas having a histological diagnosis other than Ewing's sarcoma/PNET. The sensitivity and specificity of this PCR analysis demonstrates the usefulness of this approach for the primary diagnosis of t(11;22)-containing Ewing's sarcoma/PNET and for the detection of metastatic or residual disease.
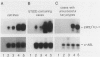
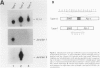
Full text
PDF


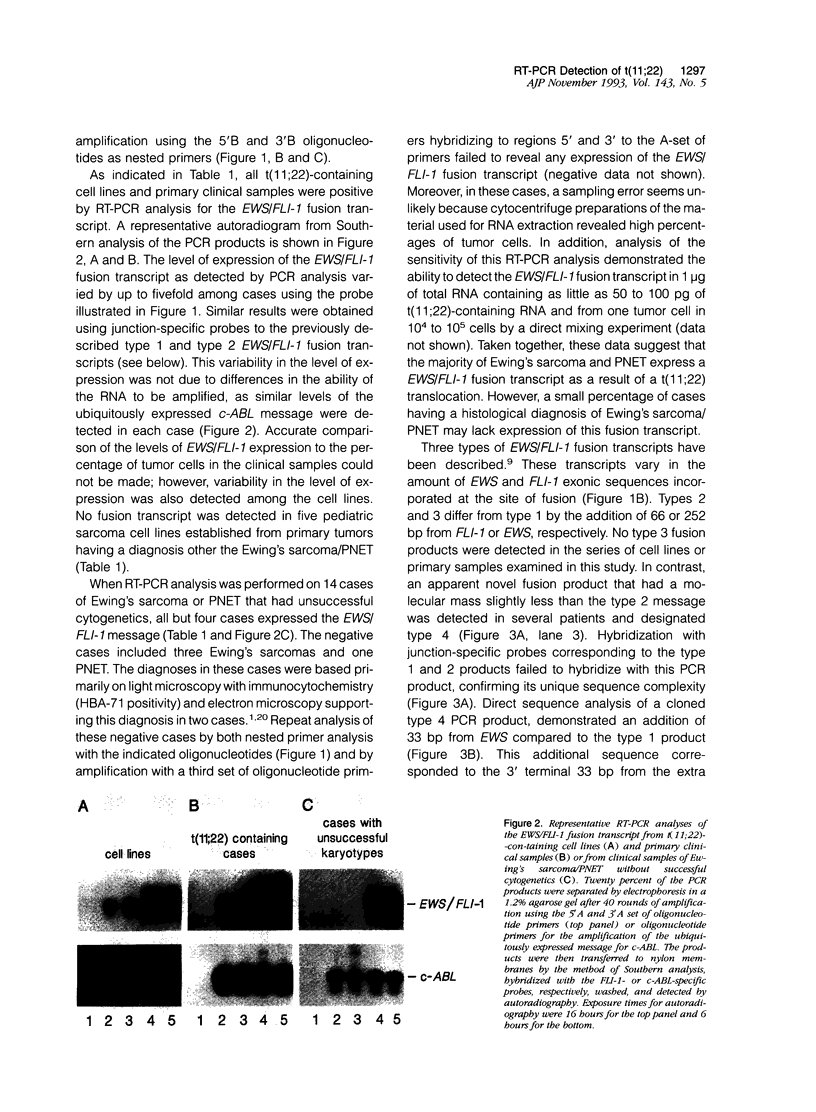
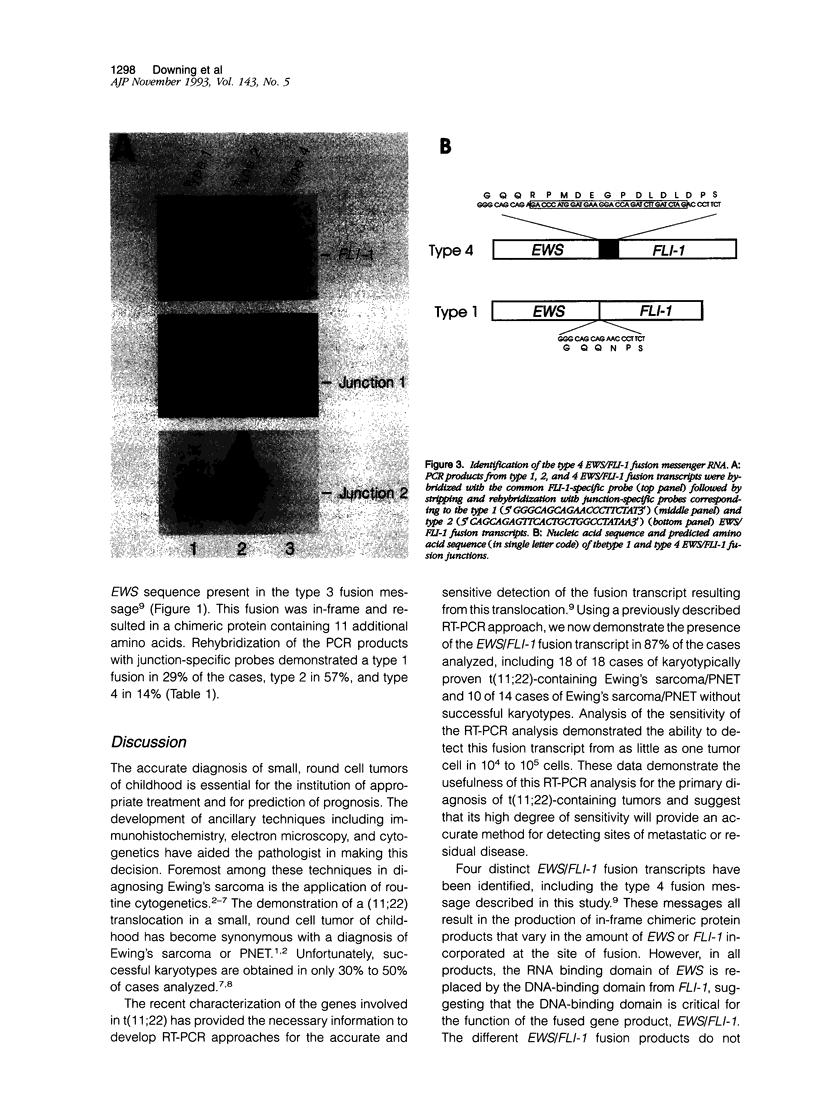


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aurias A., Rimbaut C., Buffe D., Zucker J. M., Mazabraud A. Translocation involving chromosome 22 in Ewing's sarcoma. A cytogenetic study of four fresh tumors. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1984 May;12(1):21–25. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(84)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baud V., Lipinski M., Rassart E., Poliquin L., Bergeron D. The human homolog of the mouse common viral integration region, FLI1, maps to 11q23-q24. Genomics. 1991 Sep;11(1):223–224. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90124-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-David Y., Giddens E. B., Letwin K., Bernstein A. Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia virus: insertional activation of a new member of the ets gene family, Fli-1, closely linked to c-ets-1. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):908–918. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L. Oncogenic conversion of transcription factors by chromosomal translocations. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):619–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehner L. P. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor and Ewing's sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993 Jan;17(1):1–13. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199301000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delattre O., Zucman J., Plougastel B., Desmaze C., Melot T., Peter M., Kovar H., Joubert I., de Jong P., Rouleau G. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):162–165. doi: 10.1038/359162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass E. C., Valentine M., Green A. A., Hayes F. A., Thompson E. I. t(11;22) and other chromosomal rearrangements in Ewing's sarcoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Dec;77(6):1211–1215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. R., Head D. R., Curcio-Brint A. M., Hulshof M. G., Motroni T. A., Raimondi S. C., Carroll A. J., Drabkin H. A., Willman C., Theil K. S. An AML1/ETO fusion transcript is consistently detected by RNA-based polymerase chain reaction in acute myelogenous leukemia containing the (8;21)(q22;q22) translocation. Blood. 1993 Jun 1;81(11):2860–2865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannini M., Selleri L., Biegel J. A., Scotlandi K., Emanuel B. S., Evans G. A. Interphase cytogenetics for the detection of the t(11;22)(q24;q12) in small round cell tumors. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1911–1918. doi: 10.1172/JCI116068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S., Higuchi R. Avoiding false positives with PCR. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):237–238. doi: 10.1038/339237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limon J., Dal Cin P., Sandberg A. A. Application of long-term collagenase disaggregation for the cytogenetic analysis of human solid tumors. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1986 Dec;23(4):305–313. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(86)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham D. M., Dias P., Kelly D. R., Rutledge J. C., Houghton P. Desmin positivity in primitive neuroectodermal tumors of childhood. Am J Surg Pathol. 1992 May;16(5):483–492. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199205000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raimondi S. C. Current status of cytogenetic research in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1993 May 1;81(9):2237–2251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. N., Valentine M. B., Rowe S. T., Sinclair A. E., Sublett J. E., Roberts W. M., Look A. T. Detection of N-myc gene amplification by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Diagnostic utility for neuroblastoma. Am J Pathol. 1993 May;142(5):1339–1346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Borrow J., Goddard A. D. Chromosome aberrations and cancer. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1153–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.1957167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson C. F., Bridge J. A., Sandberg A. A. Cytogenetic and pathologic aspects of Ewing's sarcoma and neuroectodermal tumors. Hum Pathol. 1992 Nov;23(11):1270–1277. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90295-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turc-Carel C., Aurias A., Mugneret F., Lizard S., Sidaner I., Volk C., Thiery J. P., Olschwang S., Philip I., Berger M. P. Chromosomes in Ewing's sarcoma. I. An evaluation of 85 cases of remarkable consistency of t(11;22)(q24;q12). Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1988 Jun;32(2):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(88)90285-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turc-Carel C., Philip I., Berger M. P., Philip T., Lenoir G. M. Chromosome study of Ewing's sarcoma (ES) cell lines. Consistency of a reciprocal translocation t(11;22)(q24;q12). Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1984 May;12(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(84)90002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang-Peng J., Triche T. J., Knutsen T., Miser J., Douglass E. C., Israel M. A. Chromosome translocation in peripheral neuroepithelioma. N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 30;311(9):584–585. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408303110907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship P. R. An improved method for directly sequencing PCR amplified material using dimethyl sulphoxide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1266–1266. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucman J., Delattre O., Desmaze C., Plougastel B., Joubert I., Melot T., Peter M., De Jong P., Rouleau G., Aurias A. Cloning and characterization of the Ewing's sarcoma and peripheral neuroepithelioma t(11;22) translocation breakpoints. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Nov;5(4):271–277. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870050402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]