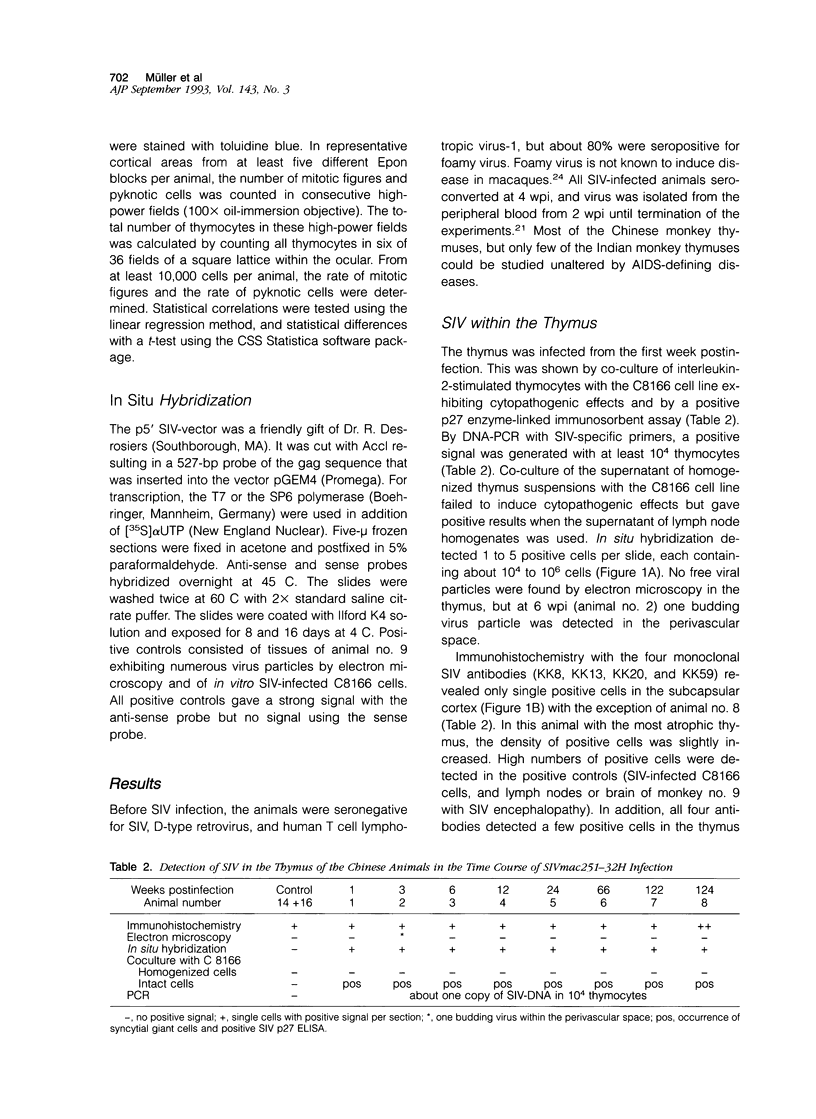
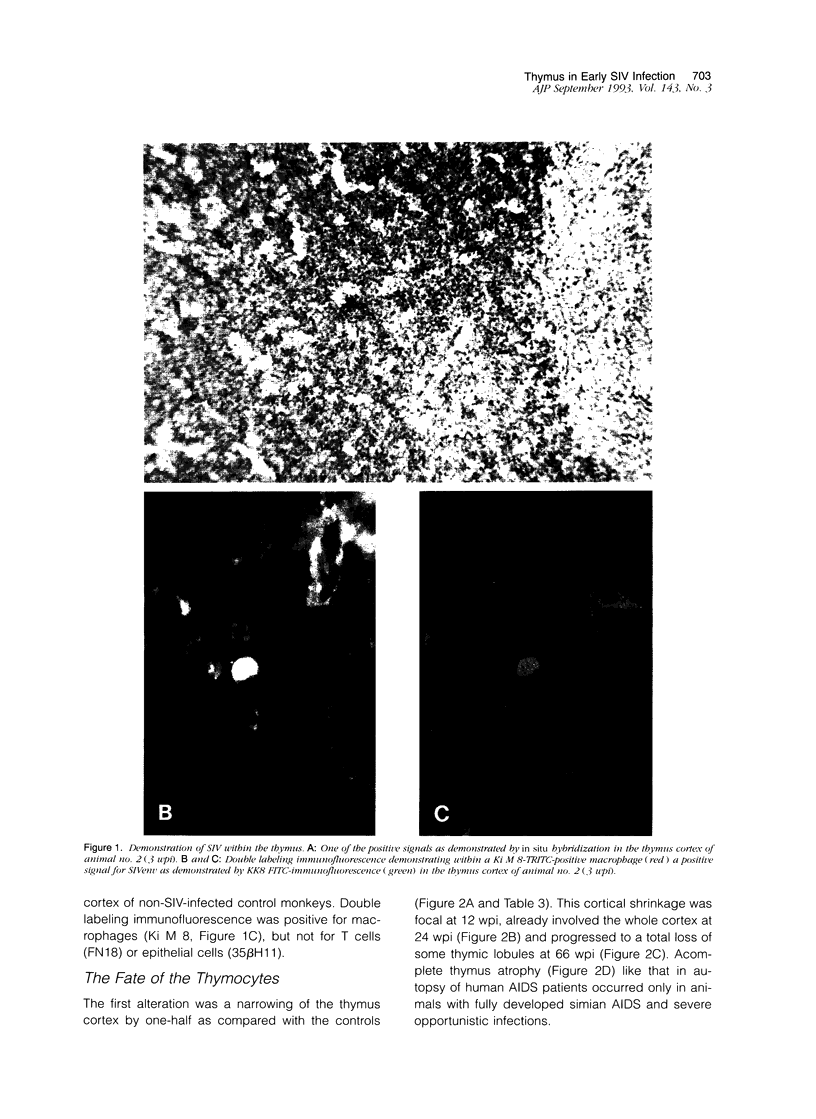
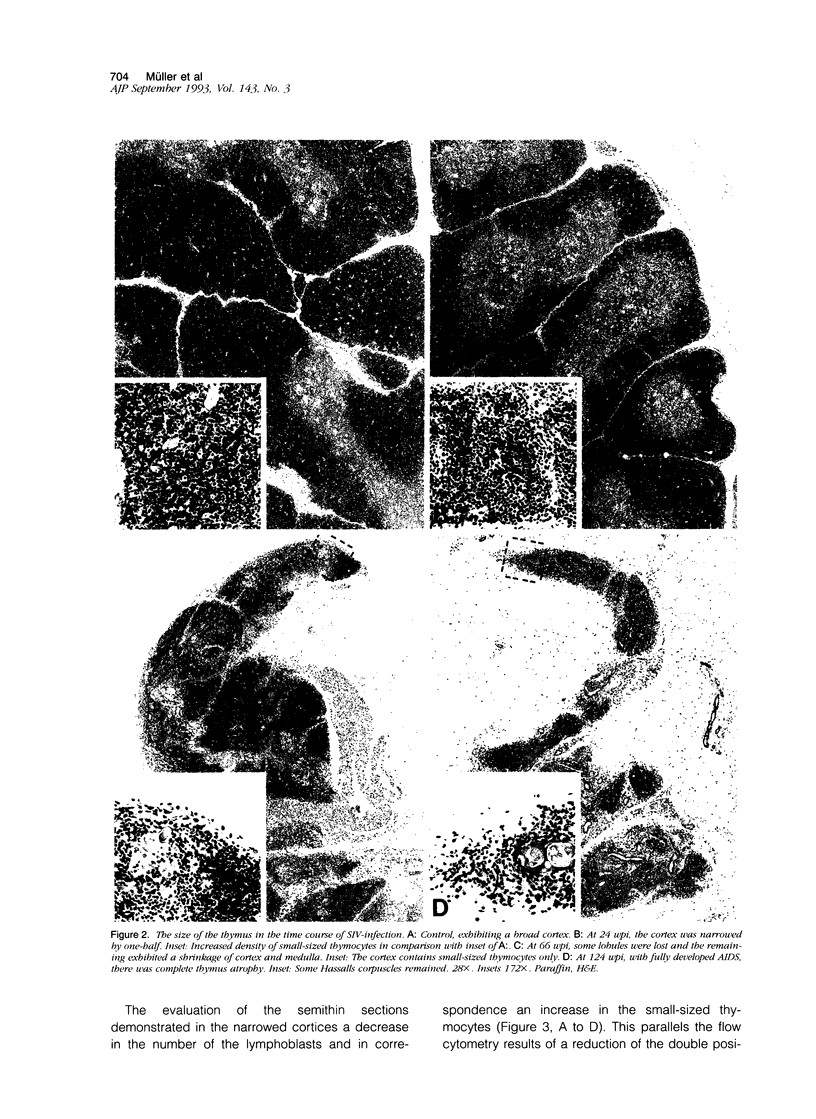
Abstract
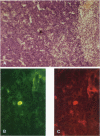
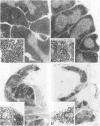
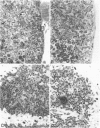
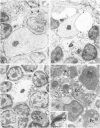
The role of the thymus in the pathogenesis of simian acquired immunodeficiency syndrome was investigated in 18 juvenile rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatto). The thymus was infected from the first week post-SIVmac inoculation, but the amount of virus-positive cells was very low (< 1 in 104 T cells) as demonstrated by polymerase chain reaction and in situ hybridization. First morphological alteration was a narrowing of the cortex at 12 and 24 wpi. Morphometry revealed no increase of pyknotic T cells but a decrease of the proliferation rate and flow cytometry showed a reduction of the immature CD4+/CD8+ double-positive T cells. Ultrastructural analysis revealed vacuolization, shrinkage, and finally cytolysis of the cortical epithelial cells and the interdigitating dendritic cells. Immunofluorescence staining exhibited a widespread loss of cortical epithelial cells. This damage to the thymic microenvironment could explain the breakdown of the intrathymic T cell proliferation. It preceded fully developed simian acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and is therefore considered to play a major role in its pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF


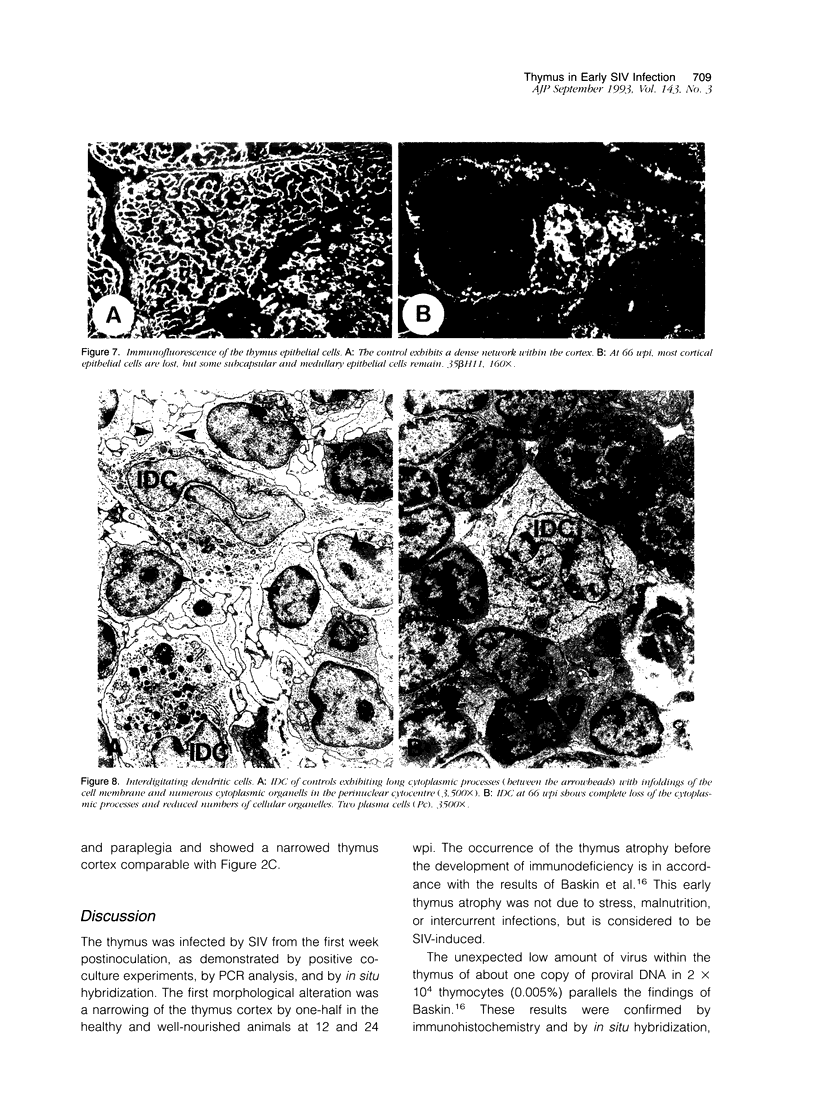
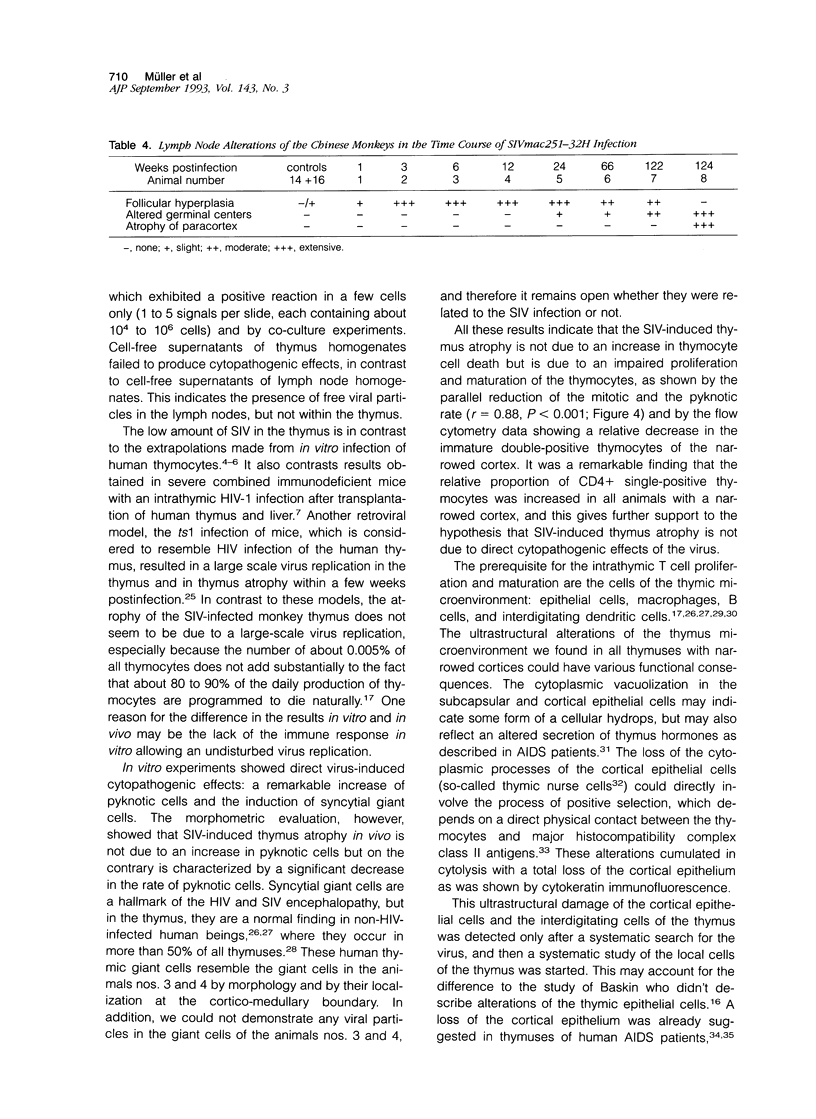



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amadori A., Zamarchi R., Ciminale V., Del Mistro A., Siervo S., Alberti A., Colombatti M., Chieco-Bianchi L. HIV-1-specific B cell activation. A major constituent of spontaneous B cell activation during HIV-1 infection. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2146–2152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arthur L. O., Bess J. W., Jr, Sowder R. C., 2nd, Benveniste R. E., Mann D. L., Chermann J. C., Henderson L. E. Cellular proteins bound to immunodeficiency viruses: implications for pathogenesis and vaccines. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1935–1938. doi: 10.1126/science.1470916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barinaga M. AIDS education could be working, but it is hard to tell. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):487–487. doi: 10.1038/333487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskin G. B., Murphey-Corb M., Martin L. N., Davison-Fairburn B., Hu F. S., Kuebler D. Thymus in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus monkeys. Lab Invest. 1991 Oct;65(4):400–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beretta A., Grassi F., Pelagi M., Clivio A., Parravicini C., Giovinazzo G., Andronico F., Lopalco L., Verani P., Buttò S. HIV env glycoprotein shares a cross-reacting epitope with a surface protein present on activated human monocytes and involved in antigen presentation. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1793–1798. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd R. L., Hugo P. Towards an integrated view of thymopoiesis. Immunol Today. 1991 Feb;12(2):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90161-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinchmann J. E., Albert J., Vartdal F. Few infected CD4+ T cells but a high proportion of replication-competent provirus copies in asymptomatic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2019–2023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2019-2023.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COWAN W. K., SORENSON G. D. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS OF ACUTE THYMIC INVOLUTION PRODUCED BY HYDROCORTISONE. Lab Invest. 1964 Apr;13:353–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Guyader M., Alizon M., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from macaque and its relationship to other human and simian retroviruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):543–547. doi: 10.1038/328543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. E., Jr The histopathological changes in the thymus gland in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;437:493–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb37173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Rossi A., Calabro M. L., Panozzo M., Bernardi D., Caruso B., Tridente G., Chieco-Bianchi L. In vitro studies of HIV-1 infection in thymic lymphocytes: a putative role of the thymus in AIDS pathogenesis. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Mar;6(3):287–298. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding H., Robey F. A., Gates F. T., 3rd, Linder W., Beining P. R., Hoffman T., Golding B. Identification of homologous regions in human immunodeficiency virus I gp41 and human MHC class II beta 1 domain. I. Monoclonal antibodies against the gp41-derived peptide and patients' sera react with native HLA class II antigens, suggesting a role for autoimmunity in the pathogenesis of acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):914–923. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez J. C., Palacios R. Heterogeneity of thymic epithelial cells in promoting T-lymphocyte differentiation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):642–646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Marselle L. M., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Detection of lymphocytes expressing human T-lymphotropic virus type III in lymph nodes and peripheral blood from infected individuals by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):772–776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi V. V., Oleske J. M. Pathologic appraisal of the thymus gland in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in children. A study of four cases and a review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Feb;109(2):142–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiserling E., Stein H., Müller-Hermelink H. K. Interdigitating reticulum cells in the human thymus. Cell Tissue Res. 1974;155(1):47–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00220283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent K. A., Gritz L., Stallard G., Cranage M. P., Collignon C., Thiriart C., Corcoran T., Silvera P., Stott E. J. Production and of monoclonal antibodies to simian immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoproteins. AIDS. 1991 Jul;5(7):829–836. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199107000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kestler H., Kodama T., Ringler D., Marthas M., Pedersen N., Lackner A., Regier D., Sehgal P., Daniel M., King N. Induction of AIDS in rhesus monkeys by molecularly cloned simian immunodeficiency virus. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1109–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.2160735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King N. W., Hunt R. D., Letvin N. L. Histopathologic changes in macaques with an acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Am J Pathol. 1983 Dec;113(3):382–388. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner T., Schalke B., Melms A., von Kügelgen T., Müller-Hermelink H. K. Immunohistological patterns of non-neoplastic changes in the thymus in Myasthenia gravis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1986;52(3):237–257. doi: 10.1007/BF02889966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kneitz C., Kerkau T., Müller J., Coulibaly C., Stahl-Hennig C., Hunsmann G., Hünig T., Schimpl A. Early phenotypic and functional alterations in lymphocytes from simian immunodeficiency virus infected macaques. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1993 Apr;36(3):239–255. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(93)90022-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. R., Ho D. D., Gurney M. E. Functional interaction and partial homology between human immunodeficiency virus and neuroleukin. Science. 1987 Aug 28;237(4818):1047–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.3039662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., King N. W. Immunologic and pathologic manifestations of the infection of rhesus monkeys with simian immunodeficiency virus of macaques. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(11):1023–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. F. Analysis of the thymus influence in leukaemogenesis. Nature. 1961 Jul 15;191:248–249. doi: 10.1038/191248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M. HIV-1: the infective process in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):351–363. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90644-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Namikawa R., Shih C. C., Rabin L., Kaneshima H. Suppression of HIV infection in AZT-treated SCID-hu mice. Science. 1990 Feb 2;247(4942):564–566. doi: 10.1126/science.2300816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hermelink H. K., Sale G. E., Borisch B., Storb R. Pathology of the thymus after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in man. A histologic immunohistochemical study of 36 patients. Am J Pathol. 1987 Nov;129(2):242–256. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabarra B., Andrianarison I. Pattern of secretion in thymic epithelial cells: ultrastructural studies of the effect of blockage at various levels. Cell Tissue Res. 1987 Jul;249(1):171–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00215431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor P. H., Naylor C. W., Badamchian M., Wada S., Goldstein A. L., Wang S. S., Sun D. K., Thornton A. H., Sarin P. S. Human immunodeficiency virus contains an epitope immunoreactive with thymosin alpha 1 and the 30-amino acid synthetic p17 group-specific antigen peptide HGP-30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2951–2955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numazaki K., Bai X. Q., Goldman H., Wong I., Spira B., Wainberg M. A. Infection of cultured human thymic epithelial cells by human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 May;51(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ost A., Baroni C. D., Biberfeld P., Diebold J., Moragas A., Noël H., Pallesen G., Rácz P., Schipper M., Tenner-Rácz K. Lymphadenopathy in HIV infection: histological classification and staging. APMIS Suppl. 1989;8:7–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papiernik M., Brossard Y., Mulliez N., Roume J., Brechot C., Barin F., Goudeau A., Bach J. F., Griscelli C., Henrion R. Thymic abnormalities in fetuses aborted from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 seropositive women. Pediatrics. 1992 Feb;89(2):297–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmentier H. K., van Wichen D. F., Meyling F. H., Goudsmit J., Schuurman H. J. Epitopes of human immunodeficiency virus regulatory proteins tat, nef, and rev are expressed in normal human tissue. Am J Pathol. 1992 Nov;141(5):1209–1216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parravicini C. L., Klatzmann D., Jaffray P., Costanzi G., Gluckman J. C. Monoclonal antibodies to the human immunodeficiency virus p18 protein cross-react with normal human tissues. AIDS. 1988 Jun;2(3):171–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savino W., Dardenne M., Marche C., Trophilme D., Dupuy J. M., Pekovic D., Lapointe N., Bach J. F. Thymic epithelium in AIDS. An immunohistologic study. Am J Pathol. 1986 Feb;122(2):302–307. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Denning S. M., Greenhouse J. J., Justement J. S., Baseler M., Kurtzberg J., Haynes B. F., Fauci A. S. Evidence for susceptibility of intrathymic T-cell precursors and their progeny carrying T-cell antigen receptor phenotypes TCR alpha beta + and TCR gamma delta + to human immunodeficiency virus infection: a mechanism for CD4+ (T4) lymphocyte depletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7727–7731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Singer K. H., Greenhouse J. J., Stanley S. K., Whichard L. P., Le P. T., Haynes B. F., Fauci A. S. Thymic microenvironment induces HIV expression. Physiologic secretion of IL-6 by thymic epithelial cells up-regulates virus expression in chronically infected cells. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2553–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuurman H. J., Krone W. J., Broekhuizen R., van Baarlen J., van Veen P., Golstein A. L., Huber J., Goudsmit J. The thymus in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Comparison with other types of immunodeficiency diseases, and presence of components of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jun;134(6):1329–1338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemayer T. A., Laroche A. C., Russo P., Malebranche R., Arnoux E., Guérin J. M., Pierre G., Dupuy J. M., Gartner J. G., Lapp W. S. Precocious thymic involution manifest by epithelial injury in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Hum Pathol. 1984 May;15(5):469–474. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. F., Sahai B. M., Green D. R. Cyclosporin A inhibits activation-induced cell death in T-cell hybridomas and thymocytes. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):625–626. doi: 10.1038/339625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl-Hennig C., Herchenröder O., Nick S., Evers M., Stille-Siegener M., Jentsch K. D., Kirchhoff F., Tolle T., Gatesman T. J., Lüke W. Experimental infection of macaques with HIV-2ben, a novel HIV-2 isolate. AIDS. 1990 Jul;4(7):611–617. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199007000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoica G., Floyd E., Illanes O., Wong P. K. Temporal lymphoreticular changes caused by ts1, a paralytogenic mutant of Moloney murine leukemia virus TB. Lab Invest. 1992 Apr;66(4):427–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay M., Numazaki K., Goldman H., Wainberg M. A. Infection of human thymic lymphocytes by HIV-1. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(4):356–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wekerle H., Ketelsen U. P., Ernst M. Thymic nurse cells. Lymphoepithelial cell complexes in murine thymuses: morphological and serological characterization. J Exp Med. 1980 Apr 1;151(4):925–944. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.4.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Callahan G. N., Klein J., Dennert G. Cytotoxic T cells learn specificity for self H-2 during differentiation in the thymus. Nature. 1978 Jan 19;271(5642):251–253. doi: 10.1038/271251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wijngaert F. P., Kendall M. D., Schuurman H. J., Rademakers L. H., Kater L. Heterogeneity of epithelial cells in the human thymus. An ultrastructural study. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;237(2):227–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00217140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gaudecker B. Functional histology of the human thymus. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1991;183(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00185830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gaudecker B. Ultrastructure of the age-involuted adult human thymus. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Jan 31;186(3):507–525. doi: 10.1007/BF00224939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]