Abstract
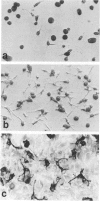
Colony-stimulating factors are important mediators of microglial growth and function. Microglia, derived from ameboid precursor cells, undergo a series of morphological changes in the central nervous system to become ramified, a morphological hallmark of differentiated microglia. The cellular mechanisms and environmental factors involved in microglial ramification in the developing brain are not known. In the present study, we examined the role of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) in the induction of ramification of microglia in human fetal glial cultures. Human fetal microglia underwent spontaneous conversion from ameboid to ramified shape when co-cultured with human fetal astrocytes. Concurrently, high levels of M-CSF also accumulated in cultures of unstimulated human fetal astrocytes. That the M-CSF was essential in inducing microglial ramification was demonstrated by almost complete inhibition of ramification by an antibody to human M-CSF receptor, c-fms. Furthermore, profound inhibition of microglial ramification was exerted by herbimycin A, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine kinase (a component of the signal cascade of c-fms), supporting the role of M-CSF/c-fms in the induction of microglial ramification. Our results suggest a pivotal role played by astrocytes and astrocyte-produced M-CSF in the induction of microglial maturation and differentiation in the developing human brain.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chen B. D. In vivo administration of recombinant human interleukin-1 and macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) induce a rapid loss of M-CSF receptors in mouse bone marrow cells and peritoneal macrophages: effect of administration route. Blood. 1991 May 1;77(9):1923–1928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Mattiace L. A., Kure K., Hutchins K., Lyman W. D., Brosnan C. F. Microglia in human disease, with an emphasis on acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Lab Invest. 1991 Feb;64(2):135–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esiri M. M., McGee J. O. Monoclonal antibody to macrophages (EMB/11) labels macrophages and microglial cells in human brain. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jun;39(6):615–621. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.6.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hao C., Guilbert L. J., Fedoroff S. Production of colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1) by mouse astroglia in vitro. J Neurosci Res. 1990 Nov;27(3):314–323. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490270310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey W. F., Kimura H. Perivascular microglial cells of the CNS are bone marrow-derived and present antigen in vivo. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):290–292. doi: 10.1126/science.3276004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchins K. D., Dickson D. W., Rashbaum W. K., Lyman W. D. Localization of morphologically distinct microglial populations in the developing human fetal brain: implications for ontogeny. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1990 Aug 1;55(1):95–102. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(90)90109-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson L. J., Perry V. H., Dri P., Gordon S. Heterogeneity in the distribution and morphology of microglia in the normal adult mouse brain. Neuroscience. 1990;39(1):151–170. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90229-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Liu W., Brosnan C. F., Dickson D. W. Characterization of primary human fetal dissociated central nervous system cultures with an emphasis on microglia. Lab Invest. 1992 Oct;67(4):465–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Liu W., Dickson D. W., Brosnan C. F., Berman J. W. Cytokine production by human fetal microglia and astrocytes. Differential induction by lipopolysaccharide and IL-1 beta. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 1;150(7):2659–2667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Liu W., Roth P., Dickson D. W., Berman J. W., Brosnan C. F. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human fetal astrocytes and microglia. Differential regulation by cytokines and lipopolysaccharide, and modulation of class II MHC on microglia. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):594–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling E. A., Wong W. C. The origin and nature of ramified and amoeboid microglia: a historical review and current concepts. Glia. 1993 Jan;7(1):9–18. doi: 10.1002/glia.440070105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Fujiwara M. Absence of donor-type major histocompatibility complex class I antigen-bearing microglia in the rat central nervous system of radiation bone marrow chimeras. J Neuroimmunol. 1987 Dec;17(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(87)90032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H., Hume D. A., Gordon S. Immunohistochemical localization of macrophages and microglia in the adult and developing mouse brain. Neuroscience. 1985 Jun;15(2):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Ashmun R. A., Downing J. R., Ohtsuka M., Quan S. G., Golde D. W., Roussel M. F. Inhibition of colony-stimulating factor-1 activity by monoclonal antibodies to the human CSF-1 receptor. Blood. 1989 May 15;73(7):1786–1793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. Colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Théry C., Hétier E., Evrard C., Mallat M. Expression of macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene in the mouse brain during development. J Neurosci Res. 1990 May;26(1):129–133. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490260117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tillotson M. L., Wood J. G. Phosphotyrosine antibodies specifically label ameboid microglia in vitro and ramified microglia in vivo. Glia. 1989;2(6):412–419. doi: 10.1002/glia.440020604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]