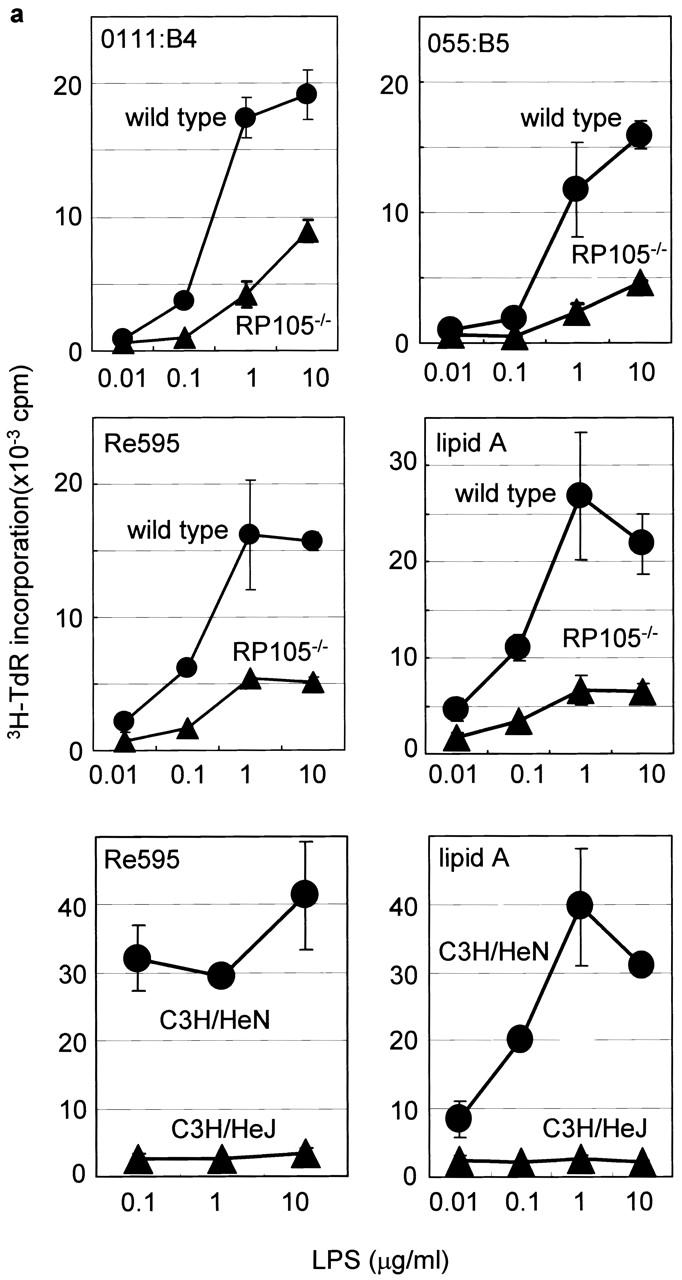
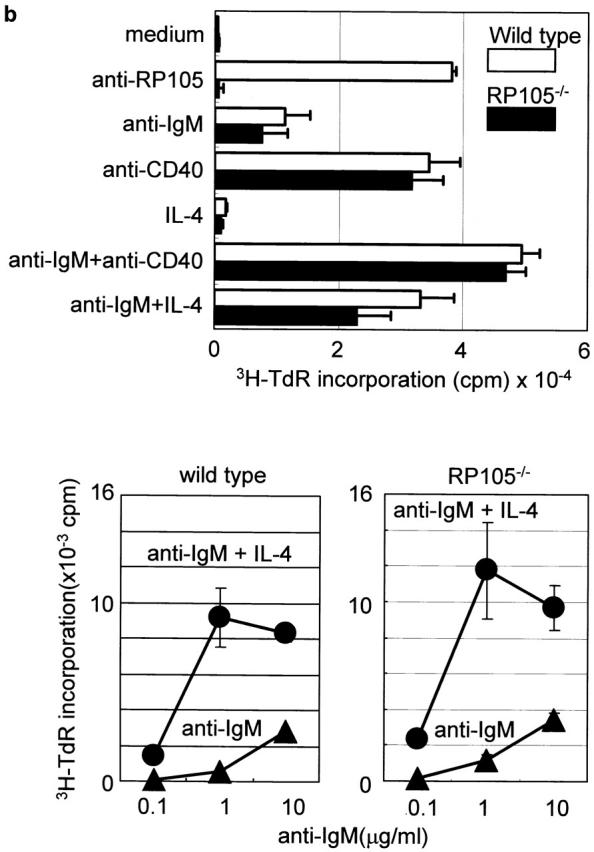
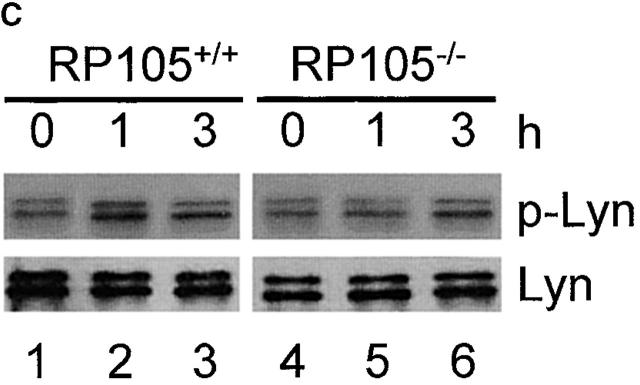
Figure 3.
B cell activation in vitro. (a) Purified cells were stimulated with LPS from E. coli 0111:B4, E. coli 055:B5, S. minnesota Re595, and synthetic lipid A. After 3 d, cells were pulsed with 1 μCi/well 3H-TdR and harvested, and [3H]thymidine incorporation was counted as described (reference 9). Results were shown as mean values of cpm from triplicate wells with standard errors. (b) Top: purified B cells were stimulated with the following stimuli: the goat anti–mouse IgM F(ab′)2 Ab (5 μg/ml), the mAb to CD40 (5 μg/ml), and recombinant mouse IL-4 (5 ng/ml). After 3 d, cells were pulsed with 1 μCi/well 3H-TdR, and B cell proliferation was measured as described above. (b) Bottom: purified B cells were stimulated with goat anti–mouse IgM F(ab′)2 Abs at various concentrations with or without IL-4, and proliferation was measured as described above. (c) Purified B cells were stimulated with lipid A (1 μg/ml) for 1 h (lanes 2 and 5) or 3 h (lanes 3 and 6). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Lyn mAb, and equally divided precipitates were subjected to SDS-PAGE (9% acrylamide) and electroblotting. Phosphotyrosine (top) or Lyn (bottom) was probed with antiphosphotyrosine or anti-Lyn mAb, respectively. Similar results were obtained from two independent experiments.