Figure 1.
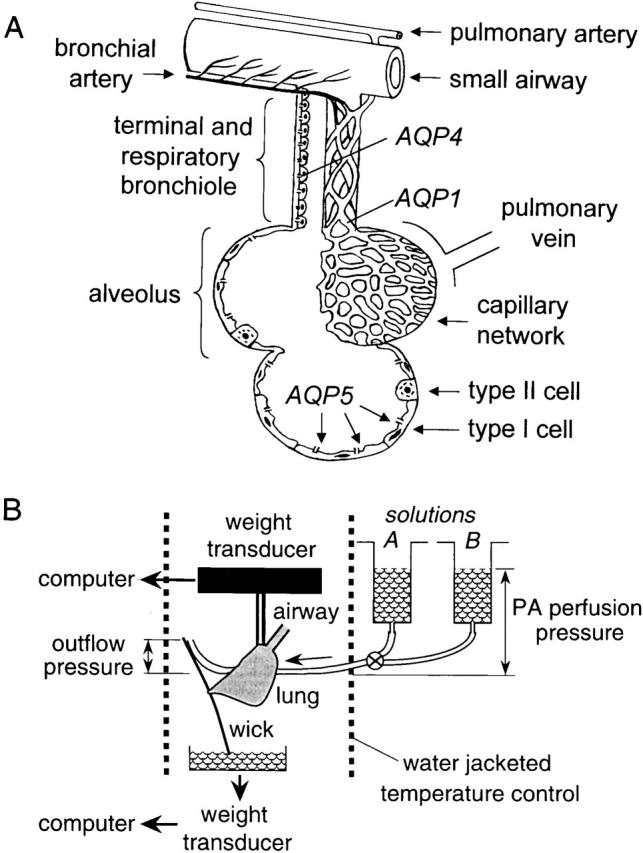
(A) Anatomy of distal lung showing blood supply, airspace epithelia, and locations of aquaporin water channels. Movement of water from the airspace to capillary compartments involves passage across alveolar/airway epithelial, interstitial, and microvascular endothelial barriers. See text for further explanations. (B) Apparatus for continuous measurement of lung weight during perfusion. The airspace compartment is filled with saline or an inert perfluorocarbon via the trachea, and the pulmonary artery perfused with solutions of specified osmolality (solutions A and B) at specified pulmonary artery (PA) perfusion and outflow pressures. Lung weight is measured continuously by a gravimetric transducer and perfusate exit via the transected left atrium or the outflow catheter is measured by second transducer. See text for details.
