Abstract
Gastric cancer (GC) remains a leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide. Genetic factors are implicated, including DNA mismatch repair (MMR) deficiency manifested as tumor microsatellite instability (MSI). However, a standardized panel of markers and a definition of low-versus-high level MSI in GC are lacking. We examined a population-based cohort of early onset (≤50 yrs) gastric cancer. We identified 211 cases of early onset gastric cancer in Central-East Ontario from 1989 to 1993, with archival material available for 139 cases. Testing included a six-mononucleotide marker panel and a three-MMR immunohistochemical panel. Overall, 30% (41 of 139) of GC were MSI+, with allelic shifts at one to eight markers. An unexpected discordance between the BAT-25, BAT-26, and BAT-40 markers was observed in the MSI+ cases. Six cases showing multiple loci instability (≥3 markers MSI+/MSI-high) demonstrated MMR protein deficiency. Three novel hMLH1 mutations (two germline frameshift and one somatic nonsense) were also found. The only significant clinicopathological associations were increased tumor size in MSI+ cases (P = 0.04) and Lauren histotype (P = 0.006) and tumor grade (P = 0.007) in MSI-high cases. Tumor size, location, depth, nodal status, and Ming subtype were significant prognostic variables. Therefore, we propose a new definition of high-level MSI based on unifying characteristics of instability of more than or equal to three of six mononucleotide markers and loss of MMR protein expression.
Gastric carcinoma (GC) is a leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide. Genetic pathways involved in its development are not clearly delineated, although several genetic alterations are implicated including DNA mismatch repair (MMR) deficiency, manifesting as the microsatellite instability (MSI) phenotype.1 GC is also a manifestation of inherited cancer predisposition syndromes, including hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer syndrome (HNPCC; MIM 114500) due to germline mutations in MMR genes hMSH2,2,3 hMLH1,3,4 hMSH6,5 hPMS2,6 and hMLH3.7 hMSH2 and hMLH1 mutations account for most cases of colorectal cancer (CRC) exhibiting MSI as currently listed in mutation databases (eg, in the database of the International Collaborative Group on HNPCC [http://www.insight-group.org/] and in the human gene mutation database [http://archive.uwcm.ac.uk/uwcm/mg/hgmd0.html]). The human MMR system repairs DNA replication errors or physico-chemical induced damage. Microsatellite regions are susceptible to mutation due to slippage of DNA polymerase during DNA replication. Failure to excise these errors may lead to frameshift mutations in target genes such as TGFβRII, IGFIIR, E2F-4, and BAX.8,9,10,11,12,13 Carriers of MMR germline mutations have a fourfold increased risk of GC and a high risk of early onset CRC (early onset, CRC presenting at ≤50 years).14,15
Unlike MSI testing in CRC,16,17,18 there is no consensus on MSI testing in GC. Thus widely variable results on the frequency and definition of MSI in sporadic GC have been reported depending on the type (mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, or pentanucleotide) and number of microsatellites used. For instance, low-frequency MSI (MSI-L; allelic shifts in one locus) in sporadic GC in Japan varies from 16 to 39%. High-frequency MSI (MSI-H; variously defined as ≥30 to 40% of loci with allelic shifts and/or BAT-26 locus instability alone) is reported in about 5 to 10% of these cancers.19,20,21 This is similar to Western populations with 24 to 84% showing MSI-L and 2 to 15% MSI-H.22,23 The National Cancer Institute (NCI) developed guidelines for MSI testing in CRC using a panel of five microsatellite loci containing two mononucleotide repeats (BAT-25 and BAT-26) and three dinucleotide repeats (D2S123, D5S346, and D17S250) and defined MSI-L and MSI-H as instability in one and two or more markers, respectively. MSI analysis using BAT-25 and BAT-26 are usually sufficient to establish MSI-H in CRC,24,25 however, Suraweera et al26 proposed the addition of the quasimonomorphic mononucleotide markers NR-21, NR-22, and NR-24 that have a lower frequency of polymorphisms in African and Caucasian populations and are useful complements to BAT markers. Although the NCI criteria are effective in identifying MSI-H in CRC, they should be applied with caution for other malignancies. Therefore, the optimal set of markers to diagnose MSI in GC may be different and needs to be studied.
Despite the nonuniformity of MSI testing in GC, a number of investigators have reported clinicopathological associations and prognostic significance of MSI-H in sporadic GC. Some suggest that MSI positive (MSI+) tumors occur predominantly in the gastric antrum, whereas others demonstrate an even distribution throughout the stomach.27 Some authors report a higher frequency of MSI-H in GC with an intestinal/atypical appearance and in poorly differentiated subgroups.20,22,27,28 Patients with MSI-H GC have also been shown to have a lower incidence of lymph node metastasis and an improved long-term survival (64 to 88%) compared with patients with microsatellite stable (MSS; defined as the absence of allelic shifts in tumor versus normal DNA) tumors (39 to 53%).13,28 Of note, there are few studies specific to MSI in early onset gastric cancer (EOGC), and they have been limited to single-institution or multicenter collaborations showing variable MSI definitions, frequencies, and associations.29,30,31,32,33 EOGC has a more aggressive clinical course than older cases, and the characterization of molecular alterations responsible in this cohort can be important in the understanding and future management of these patients.
To clarify the role of MSI in EOGC, we used a well-defined population-based cohort of EOGC (≤50 years) and a hexaplex panel of quasimonomorphic mononucleotide markers (BAT-25, BAT-26, BAT-40, NR-21, NR-22, and NR-24) and two dinucleotide markers (D5S346 and D17S250) to determine MSI status. Five commonly used histological classifications were used to characterize the specific GC subtype. The objectives of this study were 1) to determine the frequency of MSI and MSI-H in EOGC; 2) to examine the loss of MMR protein expression (hMLH1, hMSH2, and hMSH6) in MSI+ cases using immunohistochemistry (IHC), methylation, and mutational analyses; and 3) to characterize genotype-phenotype correlations between MSI status and clinicopathological variables.
Materials and Methods
Patients, Tissue Collection, Pathology Review, and DNA Extraction
Using the Ontario Cancer Registry, 211 GC cases ≤50 years diagnosed between 1988 and 1993 in Central-East Ontario (population ∼ 4.8 million) were identified. Research Ethics Board of Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, Canada approved all study protocols. Formalin-fixed paraffin embedded tissue (resections or biopsies) and pathology reports were obtained from 35 hospitals in which these patients were treated. Patient identifiers were removed, and study numbers were assigned. Clinical information (age and gender), gross pathology (Borrmann type,34 tumor size, and tumor location), and lymph node involvement were obtained from pathology reports and/or clinical records where available. Histopathological features (tumor grade, tumor depth, and histological subtype) were assigned.35 Two pathologists (JB and RR) jointly assessed and classified cases according to five classification systems: Carneiro,36 Goseki,37 Lauren,38 Ming,39 and World Health Organization.40 Matched pairs of formalin-fixed paraffin embedded normal and tumor tissue were obtained where possible (n = 138 of 139). Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) slides were used as reference to microdissect unstained 7- to 10-μm slides. Laser capture microdissection (Arcturus, Mountain View, CA) was used for cases with low tumor cellularity (<70%) and volume (biopsies, n = 35). Normal and tumor DNA was extracted using QIAamp DNA minikit (Qiagen Inc., Mississauga, ON, Canada) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
MSI Analysis
Five markers endorsed by the NCI consensus panel16,18 of microsatellite markers to define MSI in CRC (three mononucleotide markers: BAT-25, BAT-26, and BAT-40; two dinucleotide markers: D5S346 and D17S250) and three described by Suraweera et al26 in CRC and GC (NR-21, NR-22, and NR-24) were used (Supplemental Table S1; http://jmd.amjpathol.org/). Oligonucleotides were radioactively labeled using T4 PNK (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA). Polymerase chain reactions (PCRs) were performed in a 15-μl volume containing a minimum of 20 ng of DNA; 0.4–0.6 mmol/L forward, reverse, and γ-33P-labeled reverse primers (Canadian Life Technologies, Burlington, ON, Canada); 2.5 mmol/L MgCl2; 166 μmol/L dNTPs; and 0.5 U Platinum TaqDNA polymerase (Invitrogen Canada Inc., Burlington, ON, Canada). Thirty-five cycles of 94°C for 30 s, 56 to 58°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 40 seconds were performed with an initial denaturation step of 94°C for 4 minutes and final extension step of 72°C for 10 minutes using the Perkin Elmer GeneAmp PCR system 9600 (PerkinElmer Life and Analytical Science Inc., Boston, MA). PCR products were diluted 1:1 with a loading buffer (98% formamide, 0.1% xylene cyanol, 0.1% bromophenol blue, and 10 mmol/L ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid [pH 8.0]), denatured for 4 minutes at 94°C, and rapidly cooled on ice before gel loading. From each case, 3.5 μl was electrophoresed on 7% denaturing polyacrylamide gels for 2 to 3 hours at 60 to 70W, dried, and visualized by autoradiography. Three independent evaluators (JB, ND, and SG) read the autoradiograms. Cases demonstrating MSI were confirmed by a repeat PCR and electrophoresis. The results of the repeat PCR were consistent in all cases.
Definition of MSI and Characterization of MSI-H Cases
Microsatellite positive (MSI+) cases were initially defined as cases showing instability in at least one marker. Tumors in which allelic shifts were not detected in any of the markers were defined as MSS. In the absence of standardized criterion for defining MSI-H status in GC, MSI-H was defined as multiple loci instability in more than or equal to three of six to eight (38 to 50%) markers tested, and MSI-L was defined as one to two loci instability.
IHC for hMLH1, hMSH2, and hMSH6
Monoclonal antibodies (Abs) against human hMLH1 (clone G168728; BD Biosciences, Mississauga, ON, Canada), hMSH2 (clone FE11; Oncogene Research Products, Mississauga, ON, Canada), and hMSH6 (clone 44; BD Biosciences) were used. Sections (4 μm) were deparaffinized and dehydrated. Endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched in 3% H2O2 for 15 minutes. Sections were washed in water, pretreated using heat-induced epitope retrieval in 0.01 mol/L citrate buffer, pH 6.0, and cooled for 10 minutes. Sections were placed in 0.05 mol/L Tris-buffered saline, pH 7.6, where all intervening washes were carried and all incubations done in RT. Nonspecific Ig-binding sites were blocked using 20% protein block with avidin for 15 minutes. Primary Ab incubations (hMLH1, 1:40; hMSH2, 1:100; and hMSH6, 1:300) were done for 60 minutes. Secondary Ab (1:200) (biotinylated horse anti-mouse; Vector Laboratories, Burlington, ON, Canada) was applied for 30 minutes. The Vectastain Elite avidin and biotinylated horseradish peroxidase complex (Vector Laboratories) was applied for 30 minutes. Sections were incubated for 10 minutes in a chromogen mixture containing 3,3′-diaminobenzidinetetrahydrochloride (Sigma, Diagnostics, Mississauga, ON, Canada) in 0.05 mol/L Tris-buffered saline and 0.03% H2O2. A final wash and counterstain in Mayer’s hematoxylin was done before final dehydration steps and mounting in permount (Fisher Scientific Ltd., Ottawa, ON, Canada).
The normal IHC staining pattern for hMLH1, hMSH2, and hMSH6 MMR proteins is nuclear. Notably, lymphocytes, normal gastric epithelium, and smooth muscle served as internal positive controls for each case. Pathologists (JB, RR, and AP) scored IHC slides using a semiquantitative system. A case was designated “immuno-negative” when complete loss or reduction (minimum 95% to maximum 100% loss) in tumor nuclei staining and corresponding intact gastric mucosae/lymphocyte staining was observed for any MMR proteins. Cases with at least 10% tumor nuclei staining were scored “intact,” and cases with crush artifact or absent internal control staining were scored “equivocal.”
Hypermethylation of hMLH1 Promoter
hMLH1 immunonegative cases were analyzed for hMLH1 methylation using methylation-specific PCR (MSP) for the 5′ CpG promoter of hMLH1. DNA from normal and tumor from cases of interest were chemically modified using the CpGenome DNA Modification kit (Chemicon International, Temecula, CA) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Two sets of oligonucleotides, one specific for the methylated and the other for the unmethylated promoter, were used to amplify bisulfite-modified normal and tumor DNA as previously described.41 Cell lines SW48 and HCT116 were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Cases showing PCR amplification of tumor DNA using the methylation-specific primer set were scored hMLH1 methylation positive.
hMLH1 Mutational Analyses
Germline (normal) and tumor DNA from hMLH1 immunonegative cases were analyzed for mutations in all 19 exons and intron-exon boundaries of hMLH1 (oligonucleotide sequences, PCR, and denaturing high performance liquid chromatography [d-HPLC] conditions are available on request). Each amplicon was electrophoresed on 2% agarose for confirmation. Denaturing high performance liquid chromatography was used to screen 18 of 19 exons for mutations/variants (Transgenomics Inc., Omaha, NE), except for exon 12, which was sequenced.42,43 Chromatograms generated from normal DNA of noncancer patients were used as normal controls for each exon. Samples showing any variations in peak morphology relative to the normal chromatogram were sequenced using Thermosequenase Radiolabeled Terminator Cycle Sequencing kit (Amersham Biosciences Corp., Piscataway, NJ) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. Results were obtained after autoradiography. Variations and mutations were confirmed by a second manual sequencing reaction from a separate amplification from the original DNA extraction at least twice in both forward and reverse directions.
Statistical Analyses
Clinicopathological parameters were obtained for most cases. Age, gender, overall survival, cause of death, tumor grade, Carneiro, and World Health Organization histotypes were available for all cases. Tumor site/region (proximal, middle, or distal), Goseki, Lauren, and Ming histotypes were known for 130, 123, 135, and 101 cases, respectively. Analyses of tumor size, Borrmann type, tumor depth of invasion, and nodal status were restricted to resection specimens only (n = 104). Tumor size was available for 100 of 104 resections. Three resections did not have Borrmann morphology, and one resection did not have nodal status specified. All resections had complete tumor depth data. Testing for associations between MSI and clinicopathological variables was performed using Pearson’s χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables and Student’s t-test for continuous variables. Survival data were complete. Univariate analyses for survival were generated using the Kaplan and Meier method, and distributions were compared using the log-rank test.44 Multivariate analyses for survival, hazard ratios (HRs), and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were done using the Cox proportional-hazards regression model.45 Sensitivities and specificities of MSI markers in identifying multiple positive loci and MMR immunonegative tumors were calculated. All tests were carried out using SPSS v12.0 statistical software package (SPSS, Chicago, IL) or SAS v.9.0 (SAS, Cary, NC). A P value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Clinicopathological Characteristics
Clinical and gross pathological characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Most EOGC were male with a 1.7:1 male-to-female ratio. The mean age was 42.0 ± 6.2 years (SD). Sixty-six percent (92 of 139) of the cases were in the fourth decade, 27% (37 of 139) in the third decade, and the remaining cases in the second decade (7%; 10 of 139). The predominant Borrmann gross morphology was B3/ulcerating type (74%; 76 of 103). The average tumor was 5.0 ± 3.3 cm. More tumors were located in the distal stomach (63 of 130). Histopathological characteristics are summarized in Table 2. The majority showed tumor invasion to the subserosa (55%; 73 of 104) with lymph node involvement (75%; 77 of 103). Fifty-seven percent (78 of 136) of the cases were poorly differentiated. Isolated cell type (54 of 139), tubular poor/intracytoplasmic mucin-rich (43 of 122), diffuse (81 of 135), infiltrating (81 of 101), and tubular (79 of 139) subtypes were the predominant histotypes according to the Carneiro, Goseki, Lauren, Ming, and World Health Organization classification systems, respectively.
Table 1.
Clinical, Gross Characteristics, and MSI Status of EOGC Cases
| Characteristics | Total cases | MSS | MSI | MSI-L (1–2+) | MSI-H(≥3+) | P value | P value (MSI-H versus others) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (n) | 139 | 98 | 41 | 34 | 7 | ||
| Mean | 42.0 | 41.4 | 43.4 | 43.9 | 40.9 | 0.08 | 0.62 |
| SD | 6.2 | 6.4 | 5.6 | 5.1 | 7.2 | ||
| Gender (n) | 139 | 98 | 41 | 34 | 7 | 0.07 | 0.06 |
| Female | 52 | 38 | 14 | 9 | 5 | ||
| Male | 87 | 60 | 27 | 25 | 2 | ||
| Male:Female | 1.7:1 | 1.6:1 | 1.9:1 | 2.8:1 | 1:2.5 | ||
| Borrmann (n) | 103 | 70 | 33 | 27 | 6 | 0.66 | 0.65 |
| I: Polypoid | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| II: Fungating | 11 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 1 | ||
| III: Ulcerating | 76 | 54 | 22 | 18 | 4 | ||
| IV: Linitis type | 14 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 1 | ||
| Tumor size (n) | 100 | 69 | 31 | 25 | 6 | 0.03 | 0.14 |
| Mean | 5.0 | 4.5 | 6.1 | 5.9 | 7.0 | ||
| Median | 4.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 7.2 | ||
| SD | 3.3 | 3.2 | 3.5 | 3.2 | 4.6 | ||
| Tumor site (n) | 130 | 91 | 41 | 32 | 7 | 0.41 | 0.59 |
| Proximal* | 46 | 29 | 17 | 15 | 2 | ||
| Middle† | 21 | 17 | 4 | 4 | 0 | ||
| Distal‡ | 63 | 45 | 18 | 13 | 5 |
Proximal tumor site includes gastroesophageal junction, cardia, and fundus.
Middle tumor site includes body.
Distal tumor site includes antrum and pylorus.
n, number of cases.
Table 2.
Histopathological Characteristics and MSI Status of EOGC Cases
| Characteristics | Total cases | MSS | MSI | MSI-L | MSI-H | P value | P value (MSI-H versus others) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor depth (n) | 104 | 70 | 34 | 28 | 6 | 0.46 | 0.35 |
| T1 | 11 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 0 | ||
| T2 | 73 | 50 | 23 | 19 | 4 | ||
| T3 | 12 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | ||
| T4 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 0 | ||
| Nodal status (n) | 103 | 69 | 34 | 28 | 6 | 0.09 | 0.22 |
| N0 | 26 | 18 | 8 | 8 | 0 | ||
| N1 | 54 | 32 | 22 | 16 | 6 | ||
| N2 | 16 | 15 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| N3 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Tumor grade (n) | 136 | 96 | 40 | 33 | 7 | 0.09 | 0.007 |
| Well/G1 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 | ||
| Moderate/G2 | 16 | 12 | 4 | 4 | 0 | ||
| Poor/G3 | 78 | 57 | 21 | 20 | 1 | ||
| Anaplastic/G4 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Mixed* | 29 | 19 | 10 | 7 | 3 | ||
| Carneiro type (n) | 139 | 98 | 41 | 34 | 7 | 0.56 | 0.32 |
| Isolated cell | 54 | 42 | 12 | 9 | 3 | ||
| Glandular | 37 | 26 | 11 | 9 | 2 | ||
| Mixed* | 43 | 26 | 17 | 15 | 2 | ||
| Solid | 5 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | ||
| Goseki type (n) | 122 | 86 | 36 | 30 | 6 | n.s. | n.s. |
| I | 25 | 19 | 6 | 5 | 1 | ||
| II | 17 | 10 | 7 | 7 | 0 | ||
| III | 32 | 22 | 10 | 9 | 1 | ||
| IV | 43 | 32 | 11 | 7 | 4 | ||
| Mixed* | 5 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | ||
| Lauren type (n) | 135 | 95 | 41 | 34 | 7 | 0.006 | 0.05 |
| Diffuse | 81 | 62 | 19 | 16 | 3 | ||
| Intestinal | 47 | 32 | 15 | 13 | 2 | ||
| Atypical | 7 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 2 | ||
| Ming type (n) | 101 | 67 | 34 | 28 | 6 | 0.19 | 0.33 |
| Expanding | 20 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 2 | ||
| Infiltrating | 81 | 57 | 24 | 20 | 4 | ||
| WHO type (n) | 139 | 98 | 41 | 34 | 7 | 0.21 | n.s. |
| Tubular | 79 | 53 | 26 | 22 | 4 | ||
| Signet | 28 | 24 | 4 | 3 | 1 | ||
| Mucinous | 15 | 11 | 4 | 3 | 1 | ||
| Undifferentiated | 7 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Tubulopapillary | 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Adenosquamous | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Mixed, more than one type of morphology (grade, Carneiro, Goseki, and Ming type) seen where at least 25% of the second (or third) morphological entity is found in the tumor population.
n.s., nonsignificant P value > 0.05. WHO, World Health Organization.
MSI Testing
All six mononucleotide loci were successfully amplified in all 139 cases. One case did not have normal DNA available for dinucleotide marker testing. Twenty-five cases failed to amplify using D5S346, and 28 cases failed D17S250 amplification. Each mononucleotide marker was at least 97% monomorphic (normal DNA did not show variably sized alleles/shifts seen in the tumor DNA) in 138 normal samples tested. Furthermore, 131 of 138 individuals (95%) in this cohort were monomorphic in all six loci. Two subjects were monomorphic in only four of six loci, and five cases were monomorphic in five of six loci. BAT-40 exhibited the greatest polymorphic rate at 2.9%
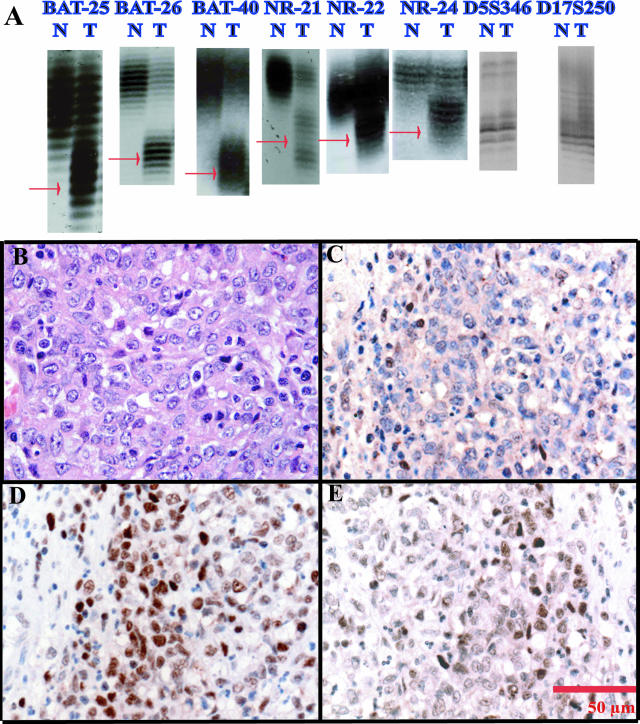
An overall frequency of 30% or 41 of 139 GC cases were MSI+ (allelic shifts in at least one marker) (Table 3). The nature of the instability was variable. Only one case showed instability in all eight mononucleotide markers (case 100). Figure 1A shows a representative example of allelic shifts in case 4. One case was unstable in seven of eight markers (case 192). Two cases were unstable in six of the eight markers (cases 4 and 87). Cases 88 and 101 showed instability in five markers. Case 58 showed instability in three markers. Nine cases were unstable in two loci (Cases 8, 21, 24, 25, 35, 57, 62, 162, and 191). Thirty-four cases showed instability in only one marker. Representative H&E photomicrographs of two MSI+ tumors, cases 4 and 100, are shown in Figures 1Band 2A, respectively. An unexpected discordance among the BAT-25, BAT-26, and BAT-40 markers was also observed. The remaining 98 cases were designated as MSS. Clinicopathological features of MSS (n = 98) cases and MSI cases (n = 41) are also summarized in Table 1. Complete MSI results for all 139 cases are summarized in Supplemental Table S2 (http://jmd.amjpathol.org/).
Table 3.
MSI-Positive Cases (n = 41)
| ID | BAT-25 | BAT-26 | BAT-40 | NR-21 | NR-22 | NR-24 | D5S346 | D17S250 | No. of + loci | Final MSI status | IHC status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥3 | ||||||||||||
| 100 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 8 | MSI-H | hMLH1− | |
| 192 | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | 7 | MSI-H | hMLH1− | |
| 4 | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | 6 | MSI-H | hMLH1− | |
| 87 | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | 6 | MSI-H | hMLH1− | |
| 88 | + | − | + | + | + | + | F | F | 5 | MSI-H* | Equivocal | |
| 101 | + | + | + | − | + | − | − | + | 5 | MSI-H | hMLH1− | |
| 58 | + | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | 3 | MSI-H | hMSH6− | |
| <3 | ||||||||||||
| 8 | + | − | − | + | − | − | F | F | 2 | MSI-L* | nd | |
| 21 | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | 2 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 24 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | 2 | MSI-L‡ | Intact | |
| 25 | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | 2 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 35 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | 2 | MSI-L‡ | nd | |
| 57 | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | 2 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 62 | − | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | 2 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 162 | + | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | 2 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 191 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | + | 2 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 5 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 9 | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | F | 1 | MSI-L† | nd | |
| 11 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 20 | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 26 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 29 | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | nd | |
| 39 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 41 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 42 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 47 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 52 | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | F | 1 | MSI-L† | Intact | |
| 59 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 65 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 70 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | 1 | MSI-L‡ | Intact | |
| 73 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | nd | |
| 89 | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 112 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | 1 | MSI-L‡ | Intact | |
| 146 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | 1 | MSI-L‡ | Intact | |
| 150 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 152 | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | nd | |
| 156 | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 161 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | 1 | MSI-L‡ | Intact | |
| 169 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact | |
| 175 | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | 1 | MSI-L‡ | Intact | |
| 200 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | 1 | MSI-L | Intact |
+, tumor DNA shows allelic shift relative to normal DNA. F, amplification failure or ran out of sample. Intact, normal hMLH1, hMSH2, and hMSH6 staining; hMLH1−, loss of hMLH1 nuclear staining in tumor; hMSH6−, loss of hMSH6 nuclear staining in tumor. nd, not done.
Six of eight markers successfully amplified because of failure of amplification in dinucleotide markers.
Seven of eight markers successfully amplified.
Dinucleotide markers showed shift but not mononucleotide markers.
Figure 1.
Case 4 is an MSI+/hMLH1-immunonegative case with six of eight loci instability. A: Microsatellite instability in all six mononucleotide loci (red arrows, extra alleles in tumor genomic DNA) and normal-sized alleles in both normal and tumor using both dinucleotide markers D5S346 and D17S25. Note allelic shifts in DNA from tumor (T) samples compared with DNA from corresponding normal (N) tissue. B through E: Photomicrographs taken at 40× magnification. B: H&E showing mixed-type gastric cancer using the Carneiro system; C: hMLH1 immunostaining; D: hMSH2 immunostaining; E: hMSH6 immunostaining. Note the lack of tumor nuclear staining by hMLH1 and normal hMSH2 and hMSH6 immunostaining. Internal positive control immunostaining is demonstrated in nuclear staining of lymphocytes.
Figure 2.
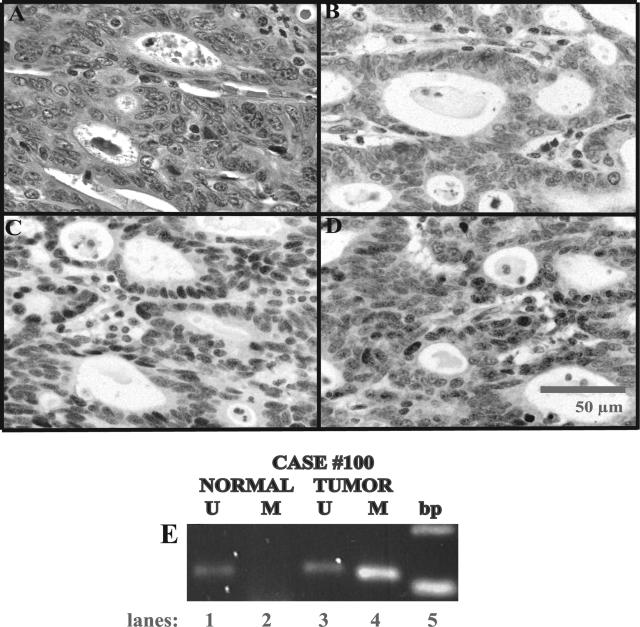
Case 100 is an MSI+/hMLH1-immunonegative case with eight of eight marker instability. A through D: Photomicrographs taken at 40× magnification. A: H&E shows glandular type gastric cancer using the Carneiro system; B: hMLH1 immunostaining; C: hMSH2 immunostaining; D: hMSH6 immunostaining. Note the lack of tumor nuclear staining by hMLH1 and intact hMSH2 and hMSH6 immunostaining. Internal positive control immunostaining is demonstrated in nuclear staining of lymphocytes. E: Methylation-specific PCR for hMLH1 in case 100. Note the band in tumor DNA and the absence of PCR products in normal DNA using specific primers for the methylated (M) hMLH1 in lanes 4 and 2, respectively. Lanes 1 and 3: As expected, both normal and tumor DNA show unmethylated (U) hMLH1 PCR products.
hMLH1, hMSH2, and hMSH6 Protein Expression
Sixty-one of 139 cases were tested for loss of expression of hMLH1, hMSH2, and hMSH6 by IHC. The 61 cases included 21 of 25 MSI-1+ (single-locus shift) cases, 7 of 9 cases with MSI-2+ (two-loci shift), 7 of 7 cases with MSI-H (≥3 MSI+ loci shift), and a random sample of 26 of 98 MSS cases (Table 4). All 21 MSI-1+ cases, 7 MSI-2+ cases, and 25 of 26 MSS cases were intact. One MSS case (67) demonstrated equivocal staining attributed to fixation artifacts. Of the remaining seven MSI-≥3+ loci, six were MMR-immunonegative and one (case 88, a biopsy with crush artifact and MSI-5+) showed equivocal staining. Five of six MSI+/MMR immunonegative cases showed loss of expression of hMLH1 (case 4 in Figure 1C and case 100 in Figure 2B). The last case was hMSH6 immunonegative. All MSI+ cases were immunointact for hMSH2. Table 4 demonstrates the correlation between loss of MMR-IHC and MSI-H status.
Table 4.
Correlation between MMR-IHC and MSI in Three or More Loci
| MMR-IHC status | MSS | MSI status
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSI-L | MSI-H | Total | ||
| Intact | 25 | 28 | 0 | 53 |
| Deficient | 0 | 0 | 6 | 6 |
| Equivocal | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Total | 26 | 28 | 7 | 61 |
hMLH1 MSP and Mutational Screening of hMLH1 Immunonegative Cases
Table 5 shows patient characteristics and results of methylation and mutational studies for MSI ≥3+ cases. All MSI+/hMLH1 immunonegative cases were tested by MSP, and 60% (three of five; cases 100, 101, and 192) exhibited hypermethylation of tumor DNA relative to normal DNA. Figure 2B shows case 100 methylation results. hMLH1 methylation testing was also carried out in six random MSS and four random MSI-L cases. As expected, all MSI-L and MSS cases showed an unmethylated-specific product in both tumor and normal DNA, supporting intact hMLH1 expression. All but one MSS case (case 33) showed a methylated-specific product in the tumor DNA (not shown) despite intact hMLH1 IHC.
Table 5.
MSH-H Cases and hMLH1 Methylation and Mutational Analyses (n = 7)
| Case | CPC | MMR-IHC | MSP | Variants mutations | Exon/s | Nucleotide | Codon | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 35 years, male, mixed proximal | hMLH1- | U | Missense | 6 | C506T/CCA | Pro169Leu | Tol’d by SIFT (GL) |
| Silent | 10 | C861T | Asn287Asn | Silent, novel SNP (GL) | ||||
| Deletion and nonsense | 12 | delT (nt1190) stop 400 | del397→ stop 400 | FS→nonsense, novel (GL/Som) | ||||
| Intronic | 15 | a1668g(−19) | IVS15(−19) | Known SNP (GL/Som) | ||||
| 87 | 43 years, female, isolated proximal | hMLH1- | U | Missense | 8 | A655G | Ile219Val | Known SNP (Som) |
| Deletion and nonsense | 16 | delAT(nt1831–32) stop(1836–38) | del611→ stop 612–613 | FS→nonsense, novel (GL/som) | ||||
| 100 | 49 years, female, glandular distal | hMLH1- | M | Intronic | 13 | g1558a(+17) | IVS13(+17) | Novel SNP (known g→a,+10,+11,+13) donor splice variant (Som) |
| 101 | 40 years, female, mixed distal | hMLH1- | M | Intronic | 15 | a1668g(−19) | IVS14(−19) | Known SNP |
| Missense | 12 | C1141T | His381Tyr | Novel, Tol;d by SIFT(GL) | ||||
| Nonsense | 16 | G1793A/TGG | Trp597stop | Nonsense, novel (Som) | ||||
| 192 | 41 years, male, isolated distal | hMLH1- | M | Intronic | 15 | a1668g(−19) | IVS14(−19) | Known SNP (GL/Som) |
| 58 | 29 years, isolated distal | hMSH6- | Nd | Na | Na | Na | Na | Na |
| 88 | 49 years, intestinal distal | Equiv | Nd | Na | Na | Na | Na | Na |
CPC, clinicopathological variables including age, gender, Carneiro histotype, and tumor location; MMR-IHC, mismatch repair protein immunohistochemistry result. hMLH1−, hMLH1 immunonegative. hMSH6−, hMSH6 immunonegative. Equiv, equivocal result. MSP, hMLH1 methylation-specific PCR results. Nd, not done. Na, not applicable. U, unmethylated by hMLH1 methylation-specific PCR; M, methylated by hMLH1 methylated-specific PCR; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; SIFT, sorting intolerant from tolerant (http://blocks.fhcrc.org/sift/SIFT.html; mathematical prediction model for missense mutations); Tol’d, substitution predicted to be tolerated by SIFT analyses; FS, frameshift; GL, found in germline/normal DNA; Som, found in tumor/somatic DNA; nucleotide and codon positions based on hMLH1 (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov) nucleotide and coding sequence NM_000249.
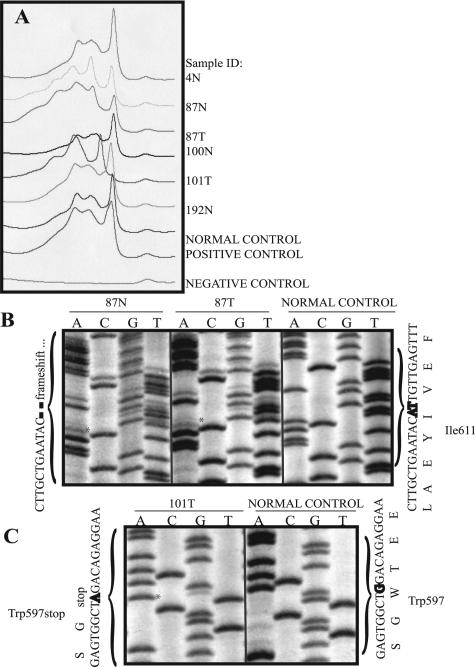
Three novel functional mutations based on the Human Gene Mutation Database (http://uwcmml1s.uwcm.ac.uk/uwcm/mg/search/249617.html) and International Collaborative Group on HNPCC Database (http://www.insight-group.org/) were found in three cases. The two hMLH1 immunonegative cases that did not show tumor methylation had germline hMLH1 deletions, causing a frameshift and subsequent premature stop codon in exons 12 (case 4) and 16 (case 87) of hMLH1 (Table 5). Figure 3 shows the corresponding d-HPLC chromatogram of hMLH1 exon 16 and manual sequencing results for cases 87 and 101. Case 101 showed a novel somatic nonsense mutation in exon 16.
Figure 3.
hMLH1 exon 16 d-HPLC analyses and manual sequencing results. A: Representative chromatogram showing absorption/wave patterns of cases: 4N, 87N, 87T, 100N, 101T, 192N, and controls including normal (genomic DNA from a noncancer patient), positive (genomic DNA from a colon cancer patient with known hMLH1 exon 16 mutation), and negative control (hMLH1 exon 16 sample without a DNA template). Note the variable absorption patterns seen in mutation-positive samples 87N, 87T, 101T, and positive control relative to the wave pattern in the normal control. B: hMLH1 exon 16 manual sequencing results for samples 87N/T (asterisks) and normal control. C: hMLH1 exon 16 manual sequencing results for sample 101T (asterisk) and normal control. B and C were sequenced in the forward direction. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences are shown along the margins. All mutations were also confirmed in the reverse direction (not shown). N, normal/genomic DNA sample; T, tumor DNA sample.
Genotype-phenotype and Clinicopathological Associations
We initially compared MSS (n = 98) with all MSI+41 cases (Table 2). No significant clinicopathological features were noted except for increased size associated with MSI+ cases (tumor size [mean ± SD], 6.1 ± 3.5 cm (MSI+), 4.5 ± 3.2 (MSS); P = 0.03, Student’s t-test). Because MMR protein deficiency was found only in cases showing MSI+ in at least three markers, further tests for association were done with MSI status divided into three groups: MSS (n = 98), MSI-L defined as cases with shifts in one or two of eight markers (n = 34) and MSI-H defined as shifts in more than or equal to three of eight markers (n = 7). Lauren classification was significantly associated with MSI status (P = 0.006, χ2 test). MSS cases were predominantly associated with diffuse subtype, whereas MSI+ cases were associated with intestinal or atypical subtypes. Grade was significantly associated with MSI status (P = 0.007, χ2 test) in which non-MSI-H cases were associated with poor differentiation (G3), whereas MSI-H cases were primarily of mixed differentiation.
Survival Analyses
Univariate and multivariate survival analyses are summarized in Table 6. Univariate analyses showed size, location, depth, grade, and nodal status as significant prognostic factors (P < 0.01, log rank test). As expected, increased size and depth, proximal location, and lymph node involvement were associated with worse survival. Ming histological type was also a significant prognostic factor (P = 0.002, log-rank test; and P = 0.02, HR = 2.5, 95% CI 1.2–5.5) with infiltrating type showing adverse 10-year survival (24%) versus the expanding type (63%). Anaplastic grade was associated with worse prognosis (0% 10-year survival) on univariate testing (P = 0.01, log-rank test) but was not significant in multivariate testing (P = 0.19, HR = 0.69, 95% CI 0.4–1.2). The remaining variables and MSI status were not statistically significant prognostic variables by univariate analyses and were therefore not included in multivariate analyses.
Table 6.
Survival Analysis in EOGC
| Variable | Univariate (KM, log-rank) P value | Multivariate*
|
Comments on 10-year survival | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P value | HR | 95% CI | |||
| Tumor size (0 to 5, 5 to 10 versus >10 cm) | 0.0002 | 0.09 | 1.1 | 1.0–1.2 | Worse in larger tumor sizes |
| Tumor site proximal versus middle versus distal | 0.01 | 0.19 | 1.2 | 0.9–1.6 | Worse in proximal |
| Tumor depth (T1, T2, T3 versus T4) | <0.0001 | 0.0002 | 2.1 | 1.4–3.1 | Worse in deepest invading tumors |
| Nodal status (N0 versus N+) | <0.0001 | 0.001 | 3.2 | 1.3–7.6 | Worse in N+ |
| Tumor grade (G1, G2, G3, G4 versus mixed) | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.7 | 0.4–1.3 | Worse in anaplastic type |
| Ming (infiltrating versus expanding type) | 0.002 | 0.02 | 2.5 | 1.2–5.5 | Worse in infiltrating type |
Six covariates (age, tumor size, depth of invasion, nodal status, Ming histotype, and tumor location) were tested in the multivariate survival analysis using the Cox regression model. KM, Kaplan-Meier.
Discussion
The definition of MSI and features of the MSI-H phenotype in GC have not been standardized. Various types and numbers of markers have been used, and the utility of IHC in the detection of MSI-H is only more recently being applied. The cut-off for defining MSI-H versus MSI-L is unclear and varied. By using a hexapanel of mononucleotide markers and MMR-IHC, we report a more biologically relevant definition, frequency, and molecular and clinicopathological characteristics of MSI-H in a population-based series of EOGC in Central-East Ontario, the largest population-based study to date.
Studying EOGC is important because young cases are clinically more aggressive and may result from different genetic alterations that accumulate more rapidly compared with subjects presenting at an older age.33 The involvement of MSI in GC is not only important in hereditary cases but is also seen in a subset of sporadic GC, as shown by Oliveira et al13 in a single-institution-based series of 152 patients. EOGC is rare, and how it is defined is largely arbitrary. In our population, we established an age cut-off of ≤50, which comprises 10% of all GC cases based on age distribution data from Cancer Care Ontario in 1989 to 2002.
Various markers have been used in studying MSI in GC, and few studies have specifically examined the role of MMR-IHC status in defining MSI-H. Hamelin and colleagues24,25 have shown that the BAT-25 and BAT-26 mononucleotide repeats are quasimonomorphic in normal DNA and are useful markers for MSI status of human tumors. Some investigators relied on a single marker (BAT-26),32 whereas others used up to 59 markers to determine MSI in GC.46 In our study, BAT-26 alone was not adequate and showed variable electrophoretic patterns in 5.9% (8 of 138) of cases. The combined use of BAT-25 and BAT-26 also yielded discordant results (Table 3). Of the 41 MSI+ cases, 20 cases were discordant for BAT-25 and BAT-26, and 14 cases were concordant with 6 showing stability in both loci and 8 cases showing instability in both loci. MMR-IHC (hMLH1, hMSH2, and hMSH6) was added to determine potential MMR protein abnormality, and this assay unequivocally identified all MSI-H cases in this series, with the exception of an MSI-H biopsy case (Table 3). Of the eight cases showing instability in both BAT-25 and BAT-26, only six were MMR immunonegative. Therefore, the use of BAT-25 and BAT-26 alone would overestimate the MSI-H phenotype. However, the combined use of the mononucleotide hexapanel increases sensitivity and specificity to 100% in detecting MSI+/MMR immunonegative GC cases (Table 7) and may also obviate the need for matched normal DNA. Although amplification of all six loci was performed separately and was labor intensive, Suraweera et al26 multiplexed five markers (BAT-25, BAT-26, NR-21, NR-22, and NR-24), making MSI testing more practical. We believe the addition of BAT-40 remains important because of its optimal sensitivity (100%) and specificity (89%) profile (Table 7). However, it may not be multiplexed because of the size of the BAT-40 amplicon (Supplemental Table S1; BAT-40 and BAT-25 amplicons 1-bp size difference can be difficult to resolve).
Table 7.
MSI Status, MMR-IHC, and Sensitivity and Specificity of Each Mononucleotide Marker in Detecting MMR Status
| MSI status | IHC | Marker
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAT-25 | BAT-26 | BAT-40 | NR-21 | NR-22 | NR-24 | D5S346 | D17S250 | ||
| MSS | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 23 | 23 |
| MSI-L | 28 | 18 | 17 | 23 | 27 | 28 | 28 | 26 | 26 |
| Total IHC+ | 53 | 43 | 42 | 48 | 52 | 53 | 53 | 49 | 44 |
| Specificity (%) | 81 | 79 | 91 | 98 | 100 | 100 | 92 | 83 | |
| Total MSI-H/IHC− | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 3 |
| Sensitivity (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 67 | 83 | 50 | 33 | 50 | |
Fifty-nine of 61 cases were included for specificity and sensitivity calculations. Two cases were excluded because of equivocal IHC staining. Fifty-three of 59 IHC eligible cases were intact for all three mismatch repair proteins, and 6 of 59 demonstrated loss of at least one of three mismatch repair proteins. IHC+, mismatch repair protein immunohistochemistry intact, all MMR proteins (hMLH1, hMSH2, and hMSH6) are expressed in tumor and normal cell nuclei; MSI-H/IHC−, multiple loci unstable in at least three loci/immunohistochemistry negative in at least one of the MMR proteins and demonstrate a decrease or loss (at least 90%) of protein expression in tumor nuclei.
Another controversy in MSI testing is the use of non-mononucleotide markers. Tri-, tetra-, and pentanucleotide markers are generally considered not useful for assessment of MSI due to MMR deficiency.47 Dinucleotide markers are the most widely used, but the interpretation of size alterations is more difficult than with mononucleotide markers and can lead to misclassification.48 Furthermore, some MSI+ tumors with hMSH6 deficiency (caused by hMSH6 mutation) are not detected by dinucleotide markers.5,26 Our study supports this shortcoming because our hMSH6-deficient case (case 58) would be misclassified as MSS had we solely used dinucleotide markers. Another important disadvantage is that dinucleotide marker instability correlated poorly with MSI-H because D5S346 and D17S250 detected only two of the six (33% sensitivity) and three of six (50% sensitivity) MSI-H cases, respectively (Table 7). However, addition of dinucleotide markers to the mononucleotide panel lead to seven additional cases classified as MSI-L (Table 3; cases 24, 35, 70, 112, 146, 161, and 175), although it is not known whether MSI-L represents a distinctly different molecular phenotype than MSS.
Our results lend further support to growing evidence that 1) it may be disadvantageous to rely on a single or only a few loci and that 2) MMR-IHC is an indispensable adjunct to detect the mutator phenotype in GC. Therefore, we propose a more biologically appropriate definition in which tumors with more than or equal to three of six (≥50%) shifted mononucleotide microsatellite loci are scored as MSI-H. If ≤2 loci are mutated in tumor DNA, then the tumor is scored as MSI-low (MSI-L). If none of the six quasimonomorphic mononucleotide microsatellite sequences are mutated, then the tumor is termed MSS. Other investigators have suggested a similar threshold albeit using a different marker panel in sporadic GC.47,49
Frequency of MSI and MSI-H
Frequencies of MSI in GC range from 15 to 39% depending on the population studied and methods used for screening.19,20,21,27,28,50,51 Our results demonstrate that a significant proportion (41 of 139, 30%) of EOGC show MSI of at least one mononucleotide marker. However, only a subset of these cases can be characterized as having an MSI-H/mutator phenotype. Seven of 139 (5%) EOGC cases would be considered MSI-H in our study.
Molecular Characteristics of MSI-H:hMLH1 Methylation and Mutation
hMLH1 protein loss by IHC was the most common MMR IHC abnormality in our study, in contrast to CRC in which hMSH2 and hMLH1 account for the majority of MMR protein loss found in MSI-H cases. A number of studies have shown methylation as an important mechanism for loss of expression of hMLH1 in sporadic GC.52,53 Our results confirm that hMLH1 methylation is also an important mechanism in EOGC with 60% (three of five cases) exhibiting methylation of tumor DNA relative to the normal DNA. Also, hMLH1 mutational inactivation is an important mechanism for protein loss; and germline mutations are generally the cause of MSI-H tumors in HNPCC; and somatic mutations occur in only a small fraction of hMLH1 and hMSH2 genes in sporadic CRC cases.18,54,55 Our study shows that in the absence of methylation, mutational inactivation played a more important role in the two MSI-H-hMLH1-IHC/methylation-negative cases (Table 6) in which two novel germline mutations were found. Both cases 4 and 87 had deletions leading to a frameshift and premature stop codon in exon 12 and 16, respectively. Based on limited clinical data available at the cancer registry, case 87 had a positive family history of GC in her father. Case 4 had a negative family history for cancer. Somatic hMLH1 mutation (nonsense) was found in case 101, which also showed hMLH1 silencing by tumor methylation. Thus, our results provide a reasonably powerful estimate of hereditary MMR defects in a population-based cohort of EOGC. Of the 7 MSI-H cases, 2 had germline hMLH1 mutations for a prevalence estimate of 2 of 139 (1.4%).
Clinicopathological and Survival Characteristics of MSI and MSI-H
In general, our analysis of associations between clinicopathological characteristics and MSI status were negative, however, we found statistically significant associations between MSI status, Lauren subtype, and tumor grade. Seruca and colleagues13,50 showed a trend toward an association between mutator phenotype, advanced age, poor differentiation, and intestinal type sporadic GC. Previous studies of sporadic GC report that MSI+ cases tended to show poor differentiation.20,27,50 Our study also shows that MSI is associated with Lauren histotype (particularly atypical and intestinal) and grade (poor/anaplastic and mixed grade). Although our MSI-H cases were predominantly female with larger and distally located tumors, gender and tumor location were not significantly associated with MSI-H status. MSI status was not significantly associated with survival, but a trend toward better prognosis was observed. Well-established prognostic factors such as tumor depth of invasion, nodal status, and tumor size were also prognostically significant in this group. Ming histotype was also independently prognostic both by univariate and multivariate analyses and underscores its importance in diagnostic use.
Summary
MSI in at least one marker was found in 30% (41 of 138) of EOGC. The combined use of a six-mononucleotide marker panel and a three-MMR-immunohistochemical panel identified six early onset MSI-H/MMR-deficient GC cases with 100% specificity and sensitivity. We therefore propose a definition of MSI-H as instability in ≥3 mononucleotide markers with concomitant loss of MMR protein expression. Few statistically significant clinicopathological associations were found to be associated with MSI status except for Lauren histotype, grade, and tumor size. Univariate and multivariate survival analyses validated tumor depth of invasion, nodal status, and Ming histotype as independent prognostic factors. MSI status was not a significant prognostic marker, however, a trend toward better prognosis was observed. Approximately 1% of EOGC is caused by germline MMR mutations.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Deborah Hogarth for assistance in the hMLH1 mutational analyses using the d-HPLC WAVE system. We acknowledge Ellen Juiqing Shi and Michael Manno for assistance in statistical analysis and Maria Minakakis, Jegan Jegathesan, and Senthuran Vijayarajah for software assistance.
Footnotes
Supported by Clinician Investigator Program of the University of British Columbia (to J.B.), by National Cancer Institute of Canada–Terry Fox Foundation Post MD Biomedical Research Fellowship (to J.B.), by Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of Toronto, and by National Cancer Institute of Canada grants 06924 (to S.G.) and 15227 (to D.H.).
References
- Bevan S, Houlston RS. Genetic predisposition to gastric cancer. Q J Med. 1999;92:5–10. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/92.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach FS, Nicolaides NC, Papadopoulos N, Liu B, Jen J, Parsons R, Peltomaki P, Sistonen P, Aaltonen LA, Nystrom-Lahti M, Guan XY, Zhang J, Meltzer PS, Yu JW, Kao FT, Chen DJ, Cerosaletti KM, Fournier REK, Todd S, Lewis T, Leach RJ, Naylor SL, Weissenbach J, Mecklin JP, Järvinen H, Petersen GM, Hamilton SR, Green J, Jass J, Watson P, Lynch HT, Trent JM, de la Chapelle A, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Mutations of a mutS homolog in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Cell. 1993;75:1215–1225. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90330-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q, Lasset C, Desseigne F, Saurin JC, Maugard C, Navarro C, Ruano E, Descos L, Trillet-Lenoir V, Bosset JF, Puisieux A. Prevalence of germline mutations of hMLH1, hMSH2, hPMS1, hPMS2, and hMSH6 genes in 75 French kindreds with nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Hum Genet. 1999;105:79–85. doi: 10.1007/s004399900064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos N, Nicolaides NC, Wei YF, Ruben SM, Carter KC, Rosen CA, Haseltine WA, Fleischmann RD, Fraser CM, Adams MD, Venter JC, Hamilton SR, Petersen GM, Watson P, Lynch HT, Peltomaki P, Mecklin JP, de la Chapelle A, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. Mutation of a mutL homolog in hereditary colon cancer. Science. 1994;263:1625–1629. doi: 10.1126/science.8128251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama Y, Sato H, Yamada T, Nagasaki H, Tsuchiya A, Abe R, Yuasa Y. Germ-line mutation of the hMSH6/GTBP gene in an atypical hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer kindred. Cancer Res. 1997;57:3920–3923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaides NC, Papadopoulos N, Liu B, Wei YF, Carter KC, Ruben SM, Rosen CA, Haseltine WA, Fleischmann RD, Fraser CM, Adams MD, Venter JC, Dunlop MG, Hamilton SR, Petersen GM, de la Chapelle A, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. Mutations of two PMS homologues in hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer. Nature. 1994;371:75–80. doi: 10.1038/371075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y, Berends MJ, Sijmons RH, Mensink RG, Verlind E, Kooi KA, van der Sluis T, Kempinga C, van der Zee AG, Hollema H, Buys CH, Kleibeuker JH, Hofstra RM. A role for MLH3 in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Nat Genet. 2001;29:137–138. doi: 10.1038/ng1001-137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakachi A, Miyazato H, Shimoji H, Hiroyasu S, Isa T, Shiraishi M, Muto Y. Microsatellite instability in patients with gastric remnant cancer. Gastric Cancer. 1999;2:210–214. doi: 10.1007/s101200050065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb LA. Microsatellite instability: marker of a mutator phenotype in cancer. Cancer Res. 1994;54:5059–5063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb LA. A mutator phenotype in cancer. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3230–3239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung YJ, Song JM, Lee JY, Jung YT, Seo EJ, Choi SW, Rhyu MG. Microsatellite instability-associated mutations associate preferentially with the intestinal type of primary gastric carcinomas in a high-risk population. Cancer Res. 1996;56:4662–4665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung YJ, Park SW, Song JM, Lee KY, Seo EJ, Choi SW, Rhyu MG. Evidence of genetic progression in human gastric carcinomas with microsatellite instability. Oncogene. 1997;15:1719–1726. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira C, Seruca R, Seixas M, Sobrinho-Simoes M. The clinicopathological features of gastric carcinomas with microsatellite instability may be mediated by mutations of different “target genes”: a study of the TGFbeta RII, IGFII R, and BAX genes. Am J Pathol. 1998;153:1211–1219. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65665-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson P, Lynch HT. Extracolonic cancer in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Cancer. 1993;71:677–685. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930201)71:3<677::aid-cncr2820710305>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch HT, Smyrk T. Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome): an updated review. Cancer. 1996;78:1149–1167. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960915)78:6<1149::AID-CNCR1>3.0.CO;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boland CR, Thibodeau SN, Hamilton SR, Sidransky D, Eshleman JR, Burt RW, Meltzer SJ, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Fodde R, Ranzani GN, Srivastava S. A National Cancer Institute Workshop on Microsatellite Instability for cancer detection and familial predisposition: development of international criteria for the determination of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5248–5257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M. Correspondence. Cancer Res. 1999;59:249–256. In response to: Boland CR, Thibodeau SN, Hamilton SR, Sidransky D, Eshleman JR, Burt RW, Meltzer SJ, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Fodde R, Ranzani GN, Srivastava S: Cancer Res 1998, 58: 5248–5257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umar A, Boland CR, Terdiman JP, Syngal S, de la Chapelle A, Ruschoff J, Fishel R, Lindor NM, Burgart LJ, Hamelin R, Hamilton SR, Hiatt RA, Jass J, Lindblom A, Lynch HT, Peltomaki P, Ramsey SD, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Vasen HF, Hawk ET, Barrett JC, Freedman AN, Srivastava S. Revised Bethesda guidelines for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome) and microsatellite instability. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:261–268. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djh034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renault B, Calistri D, Buonsanti G, Nanni O, Amadori D, Ranzani GN. Microsatellite instability and mutations of p53 and TGF-beta RII genes in gastric cancer. Hum Genet. 1996;98:601–607. doi: 10.1007/s004390050267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han HJ, Yanagisawa A, Kato Y, Park JG, Nakamura Y. Genetic instability in pancreatic cancer and poorly differentiated type of gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 1993;53:5087–5089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhyu MG, Park WS, Meltzer SJ. Microsatellite instability occurs frequently in human gastric carcinoma. Oncogene. 1994;9:29–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden JD, Cawkwell L, Quirke P, Dixon MF, Goldstone AR, Sue-Ling H, Johnston D, Martin IG. Prognostic significance of microsatellite instability in patients with gastric carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 1997;33:2342–2346. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(97)00343-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theuer CP, Campbell BS, Peel DJ, Lin F, Carpenter P, Ziogas A, Butler JA. Microsatellite instability in Japanese vs European American patients with gastric cancer. Arch Surg. 2002;137:960–965. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.137.8.960. ; discussion, 965–966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoang JM, Cottu PH, Thuille B, Salmon RJ, Thomas G, Hamelin R. BAT-26, an indicator of the replication error phenotype in colorectal cancers and cell lines. Cancer Res. 1997;57:300–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou XP, Hoang JM, Li YJ, Seruca R, Carneiro F, Sobrinho-Simoes M, Lothe RA, Gleeson CM, Russell SE, Muzeau F, Flejou JF, Hoang-Xuan K, Lidereau R, Thomas G, Hamelin R. Determination of the replication error phenotype in human tumors without the requirement for matching normal DNA by analysis of mononucleotide repeat microsatellites. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1998;21:101–107. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1098-2264(199802)21:2<101::aid-gcc4>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suraweera N, Duval A, Reperant M, Vaury C, Furlan D, Leroy K, Seruca R, Iacopetta B, Hamelin R. Evaluation of tumor microsatellite instability using five quasimonomorphic mononucleotide repeats and pentaplex PCR. Gastroenterology. 2002;123:1804–1811. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.37070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin JT, Wu MS, Shun CT, Lee WJ, Wang JT, Wang TH, Sheu JC. Microsatellite instability in gastric carcinoma with special references to histopathology and cancer stages. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:1879–1882. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(95)00349-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickler JG, Zheng J, Shu Q, Burgart LJ, Alberts SR, Shibata D. p53 mutations and microsatellite instability in sporadic gastric cancer: when guardians fail. Cancer Res. 1994;54:4750–4755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden JD, Cawkwell L, Sue-Ling H, Johnston D, Dixon MF, Quirke P, Martin IG. Assessment of microsatellite alterations in young patients with gastric adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 1997;79:684–687. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0142(19970215)79:4<684::aid-cncr4>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiao YH, Bovo D, Guido M, Capella C, Cassaro M, Busatto G, Russo V, Sidoni A, Parenti AR, Rugge M. Microsatellite instability and/or loss of heterozygosity in young gastric cancer patients in Italy. Int J Cancer. 1999;82:59–62. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19990702)82:1<59::aid-ijc11>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden JD, Cawkwell L, Dixon MF, Pardal F, Murgatroyd H, Gray S, Quirke P, Martin IG. A comparison of microsatellite instability in early onset gastric carcinomas from relatively low and high incidence European populations. Int J Cancer. 2000;85:189–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S, Lee HS, Kim HS, Kim YI, Kim WH. Alteration of E-cadherin-mediated adhesion protein is common, but microsatellite instability is uncommon in young age gastric cancers. Histopathology. 2003;42:128–136. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2559.2003.01546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho R, Milne AN, van Rees BP, Caspers E, Cirnes L, Figueiredo C, Offerhaus GJ, Weterman MA. Early-onset gastric carcinomas display molecular characteristics distinct from gastric carcinomas occurring at a later age. J Pathol. 2004;204:75–83. doi: 10.1002/path.1602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrmann R. Geshwulste des Magens und Duodenums. Berlin: Springer-Verlag,; 1926 [Google Scholar]
- Sobin L, Wittekind C. UICC, International Union against Cancer: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. New York: Wiley-Liss,; 2002 [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro F, Seixas M, Sobrinho-Simoes M. New elements for an updated classification of the carcinomas of the stomach. Pathol Res Pract. 1995;191:571–584. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(11)80878-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goseki N, Takizawa T, Koike M. Differences in the mode of the extension of gastric cancer classified by histological type: new histological classification of gastric carcinoma. Gut. 1992;33:606–612. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.5.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauren P. The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: diffuse and so-called intestinal-type carcinoma. An attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:31–49. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ming SC. Gastric carcinoma: a pathobiological classification. Cancer. 1977;39:2475–2485. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197706)39:6<2475::aid-cncr2820390626>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H, Jass JR, Sobin LH. Histological Typing of Oesophageal and Gastric Tumours. Berlin: Springer-Verlag,; 1990 [Google Scholar]
- Herman JG, Umar A, Polyak K, Graff JR, Ahuja N, Issa JP, Markowitz S, Willson JK, Hamilton SR, Kinzler KW, Kane MF, Kolodner RD, Vogelstein B, Kunkel TA, Baylin SB. Incidence and functional consequences of hMLH1 promoter hypermethylation in colorectal carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:6870–6875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.12.6870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W, Smith DI, Rechtzigel KJ, Thibodeau SN, James CD. Denaturing high performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) used in the detection of germline and somatic mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998;26:1396–1400. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.6.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuklin A, Munson K, Gjerde D, Haefele R, Taylor P. Detection of single-nucleotide polymorphisms with the WAVE DNA fragment analysis system. Genet Test. 1997;1:201–206. doi: 10.1089/gte.1997.1.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan E, Meier P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc. 1958;53:457–481. [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. Regression models and life-tables. J R Stat Soc B. 1972;34:187–202. [Google Scholar]
- Wu CW, Chen GD, Jiang KC, Li AF, Chi CW, Lo SS, Chen JY. A genome-wide study of microsatellite instability in advanced gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 2001;92:92–101. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(20010701)92:1<92::aid-cncr1296>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietmaier W, Wallinger S, Bocker T, Kullmann F, Fishel R, Ruschoff J. Diagnostic microsatellite instability: definition and correlation with mismatch repair protein expression. Cancer Res. 1997;57:4749–4756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loukola A, Eklin K, Laiho P, Salovaara R, Kristo P, Jarvinen H, Mecklin JP, Launonen V, Aaltonen LA. Microsatellite marker analysis in screening for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC). Cancer Res. 2001;61:4545–4549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos NR, Seruca R, Constancia M, Seixas M, Sobrinho-Simoes M. Microsatellite instability at multiple loci in gastric carcinoma: clinicopathologic implications and prognosis. Gastroenterology. 1996;110:38–44. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8536886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seruca R, Santos NR, David L, Constancia M, Barroca H, Carneiro F, Seixas M, Peltomaki P, Lothe R, Sobrinho-Simoes M. Sporadic gastric carcinomas with microsatellite instability display a particular clinicopathologic profile. Int J Cancer. 1995;64:32–36. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910640108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G, Rotter M, Vogelsang H, Bischoff P, Becker KF, Mueller J, Brauch H, Siewert JR, Hofler H. Microsatellite instability in adenocarcinomas of the upper gastrointestinal tract: relation to clinicopathological data and family history. Am J Pathol. 1995;147:593–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang DC, Wang RQ, Yang SM, Yang JM, Liu HF, Peng GY, Xiao TL, Luo YH. Mutation and methylation of hMLH1 in gastric carcinomas with microsatellite instability. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9:655–659. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i4.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleisher AS, Esteller M, Tamura G, Rashid A, Stine OC, Yin J, Zou TT, Abraham JM, Kong D, Nishizuka S, James SP, Wilson KT, Herman JG, Meltzer SJ. Hypermethylation of the hMLH1 gene promoter is associated with microsatellite instability in early human gastric neoplasia. Oncogene. 2001;20:329–335. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jass JR, Walsh MD, Barker M, Simms LA, Young J, Leggett BA. Distinction between familial and sporadic forms of colorectal cancer showing DNA microsatellite instability. Eur J Cancer. 2002;38:858–866. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(02)00041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shitoh K, Konishi F, Miyaki M, Iijima T, Furukawa T, Tsukamoto T, Nagai H. Pathogenesis of non-familial colorectal carcinomas with high microsatellite instability. J Clin Pathol. 2000;53:841–845. doi: 10.1136/jcp.53.11.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.