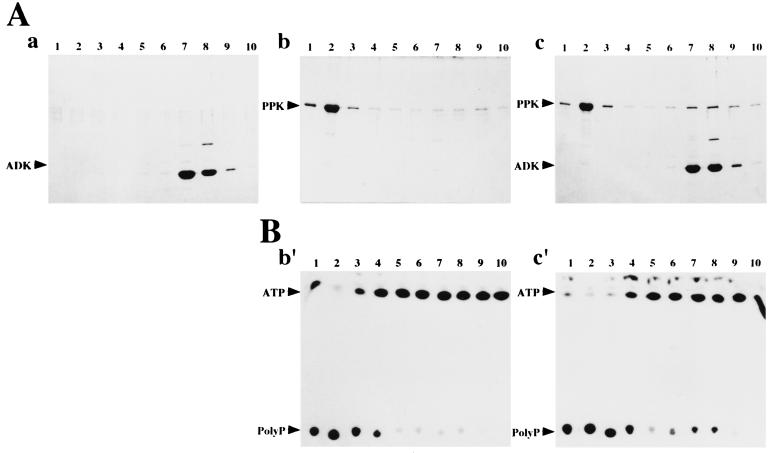
Figure 4.
Complex formation between PPK and ADK in the presence of polyP. The reaction mixture (1 ml) containing 0.5 mg of each or both of PPK and ADK, 50 mM Tris⋅HCl (pH 8.0), 50 mM ammonium sulfate, 10 mM MgCl2, 5 mM AMP and polyP (375 mM in terms of phosphate, chain lengths, 15–20) was incubated at 30°C for 30 min. The resultant mixtures were applied onto AKTA FPLC column system with HiLoad 16/60 Superdex 200pg (Amersham Pharmacia) and separated by isocratic elution with polyP-containing buffer [50 mM Tris⋅HCl, pH 8.0, 50 mM ammonium sulfate, 10 mM MgCl2 and polyP (15 mM in terms of phosphate, chain lengths, 15–20)]. After the void-volume (45 ml) of the eluent was wasted, each 5 ml of the eluent was fractionated and defined as fractions 1–10, respectively. Fraction 1 is the largest molecular weight fraction in this chromatography. (A) The results of SDS/PAGE analysis of fractions 1–10. Proteins in each fractions (200 μl) were precipitated by 5% trichloroacetic acid and analyzed. The fractions in the case that only ADK was incubated followed by the chromatography were analyzed in Aa, those in the case that only PPK was in Ab, and those in the case that PPK and ADK together were in Ac. Corresponding fraction numbers analyzed were designated at the top of each lane. (B) The result of polyP-forming assay of the fractions 1–10. The fractions in the case that only PPK was incubated followed by the chromatography were analyzed in Bb′, those in the case that PPK and ADK together were in Bc′. Corresponding fraction numbers analyzed were designated at the top of each lane.