Fig. 3.
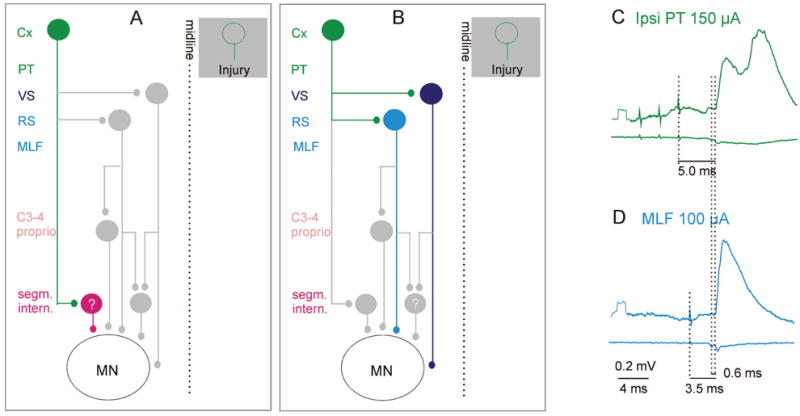
Relays between ipsilateral cortical neurons and motoneurons. A, Potential coupling between the motor cortex and spinal motoneurons via ipsilaterally located spinal premotor interneurons. The green cells represent ipsilaterally projecting cortical neurons that may substitute for injured corticospinal neurons on the opposite side (shown in the shaded box). The red cell in A represents premotor segmental interneurons contacted by the ipsilateral corticospinal neurons. B, Potential coupling between the motor cortex and spinal motoneurons via brainstem descending tract neurons. Light and dark blue cells in B represent reticulospinal and vestibulospinal neurons, respectively. In addition to direct connections with motoneurons, these also connect with spinal relay neurons, shown in gray, which are highlighted in Figures 4 to 6. C and D show averaged intracellular records from a hindlimb motoneuron (upper traces) and the surface of the spinal cord (lower traces) after administration of a K+ channel blocker 4-aminopyridine (4-AP, 0.2 mg/kg), which enhances synaptic transmission (see text). The green excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) were evoked by stimulation of the ipsilateral pyramid (PT); blue, EPSP evoked by direct stimulation of reticulospinal fibers (MLF). Dotted lines indicate the stimulus artifacts, the descending volleys, and the onset of the EPSPs. The small additional latency of the green EPSP is consistent with a single additional synaptic relay. In this experiment, the corticospinal tract fibers were cut bilaterally at the C2 level, excluding the pathway proposed in A. These EPSPs should be evoked by activation of brain stem neurons via the connections shown in B. (E Jankowska, A Cabaj, and L-G Petterson, unpublished records). Cx = cortex; C3–4 proprio = propriospinal neurons in the third and fourth cervical segments; ipsi = ipsilateral; MLF = medial longitudinal fascicle; PT = pyramidal tract; RS = reticulospinal neurons; VS = vestibulospinal neurons.
