Fig. 8.
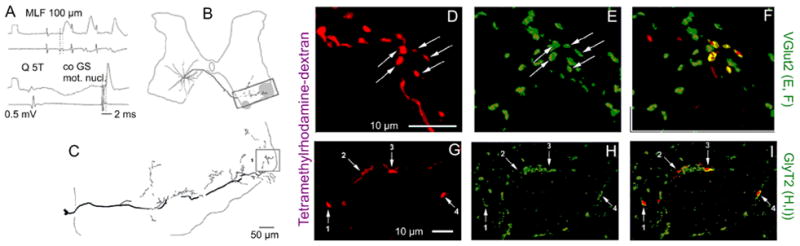
Examples of reconstructions of the axonal projections of commissural interneurons with monosynaptic input from medial longitudinal fascicle (MLF) and immunoreactivity of their terminals for glutamate and glycine transporters (VGLUT2 and GlyT2). A, Records from a commissural interneuron labeled with a mixture of tetramethylrhodamine and neurobiotin showing monosynaptic excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) evoked by MLF stimulation, an inhibitory postsynaptic potential evoked by group II afferent stimulation (quadriceps nerve), and antidromic action potential evoked from the contralateral gastrocnemius-soleus motor nucleus. B and C, Location of the cell body of this interneuron, the trajectory of its axon, and the reconstruction of the most ventral axon collateral (on a larger scale). The contralateral motor nuclei are shaded. D–F, Single optical section confocal images of terminals showing rhodamine fluorescence (D) and immunoreactivity for VGLUT2 (E) and a merged view of D and E (F). G–H, A similar series of confocal images of GlyT2 immunoreactive axon terminals from a different neuron. Modified from Figures 4, 6, and 9 in Bannatyne and others (2003). Reproduced with permission of Blackwell Publishing.
