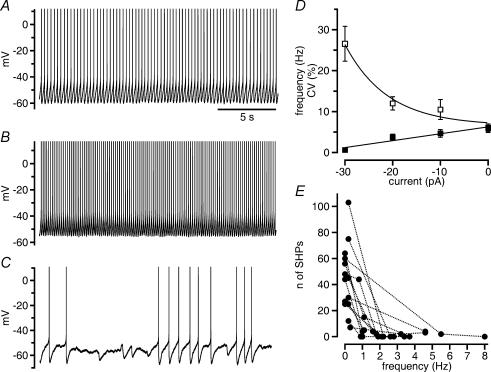
Figure 3. OCP-induced hyperpolarizations occur during pauses interrupting discharge.
A–C, frequency and modality of spontaneous firing change with membrane polarization by current injection. Spontaneous discharge (A) increased in frequency upon injection of depolarizing direct current (10 pA, B) and decreased in frequency upon injection of the same amount of hyperpolarizing current (C). In the latter, the decrease in frequency was associated with the occurrence of pauses during which action potential-independent hyperpolarizations are visible. Time scale in A applies also to B and C, action potentials truncated. D, plot of the dependence of firing frequency (▪) and coefficient of variation (CV, □) on current injection (n = 12 cells). There was a linear decrease in firing rate with the injection of hyperpolarizing direct current. CV increased markedly at very low firing rate. The point for the injection of –30 pA comprises only four neurons, because the other eight neurons stopped firing. E, the occurrence of action potential-independent spontaneous hyperpolarizations (SHPs) decreased rapidly with an increase in firing frequency. Points connected by lines are from the same cells (n = 14).