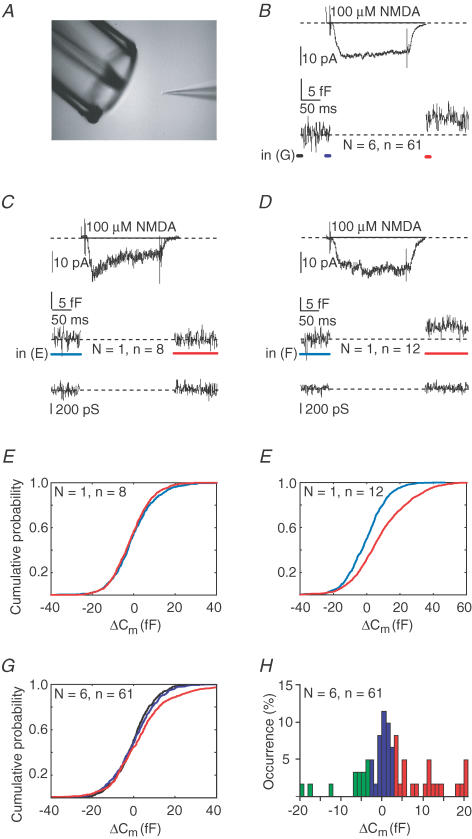
Figure 5. NMDAR activation induces exocytosis without action potential firing of postsynaptic compartment.
A, experimental set-up, with the nucleated patch positioned in front of a double-barrelled electrode attached to a piezo-element. NMDA (100 μm) is rapidly applied (200 ms) by repositioning of the double barrelled electrode. B, average NMDA-induced current and corresponding membrane capacitance during NMDA application recorded from adult (6–8 weeks, n = 6) male animals voltage-clamped at −70 mV (pooled data, 6 nucleated patches, total of 61 applications, mean ±s.d.: 10 ± 3 applications per patch). Note that during the full protocol, nucleated patches were continuously voltage clamped at −70 mV to prevent activation of voltage dependent calcium channels. C, average of NMDA-induced currents, capacitance changes and membrane conductance traces from one particular nucleated patch, which lacked NMDA induced capacitance changes (n = 8). D, same as C, but in this example on average, the NMDA applications resulted in increased membrane capacitance, being indicative of vesicle release. E, cumulative all-point histograms of the recording in C, showing the lack of capacitance changes when comparing the blue and red regions. F, cumulative all-point capacitance histograms of the blue and red regions of the recording shown in D, indicating exocytosis. G, cumulative all-point histograms of capacitance changes of all pooled recordings and analysing the black, blue and red regions of the average as shown in B. H, probability histogram of capacitance changes when pooling all trials from all recordings. In five out of six recordings, on average 40% of the trials gave capacitance changes > 3 fF. In addition, an average of 40%‘failures’ (i.e. changes between −3 and +3 fF) occurred, where in a minority of the trials negative events occurred, which may imply that in addition endocytosis may occur. As indicated in text, in one recording (shown in C and E) only failures were observed. Moreover, three very negative events, referred to in text, shown in H (i.e. < −10 fF) were all from one recording also showing failures and exocytotic events.