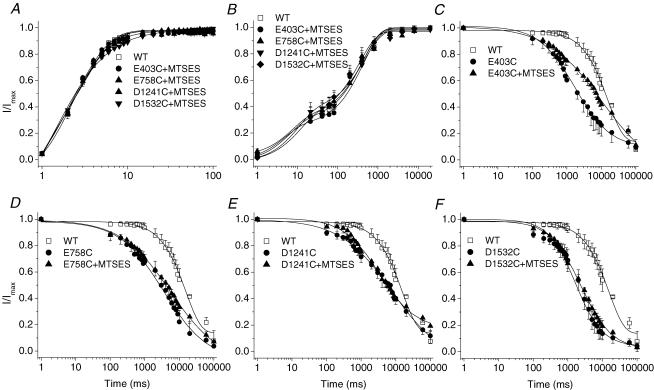
Figure 3. Effects of the negatively charged MTSES on inactivation gating of single-cysteine-mutant channels.
The voltage-clamp protocols are provided as insets in Fig. 2. A, application of MTSES (10 mm) to E403C, E758C, D1241C and D1532C had no effect on recovery from fast inactivation. B, MTSES restores the recovery from slow inactivation in these cysteine-mutant channels. Time constants and fractional weights (in parentheses) were as follows: WT (n = 5), τ1 = 48.28 ± 37.10 ms (0.34 ± 0.09), τ2 = 406.87 ± 87.52 ms (0.67 ± 0.11); E403C + MTSES: (n = 6), τ1 = 19.82 ± 15.46 ms (0.33 ± 0.06), τ2 = 608.06 ± 213.27 ms (0.62 ± 0.09); E758C + MTSES (n = 5), τ1 = 5.67 ± 2.34 ms (0.36 ± 0.07), τ2 = 561.18 ± 162.06 ms (0.66 ± 0.08); D1241C + MTSES (n = 3), τ1 = 4.13 ± 1.39 ms (0.42 ± 0.11), τ2 = 401.63 ± 53.97 ms (0.63 ± 0.05); D1532C + MTSES (n = 4), τ1 = 31.79 ± 7.41 ms (0.40 ± 0.06), τ2 = 416.86 ± 40.58 ms (0.63 ± 0.05). C–F, MTSES did not slow the kinetics of the development of slow inactivation with the exception of the partial restoration in E403C (C). The time constants were 12738 ± 1154 ms* (C, E403C + MTSES, n = 4), compared with 6846 ± 2286 ms (E403C); 7914 ± 567 ms (D, E758C + MTSES, n = 4), compared with 6587 ± 1632 ms (E758C); 8969 ± 1223 ms (E, D1241C + MTSES, n = 3), compared with 9623 ± 878 ms (D1241C); and 4058 ± 869 ms (F, D1532C + MTSES, n = 4), compared with 3970 ± 970 ms (D1532C). *P < 0.05.