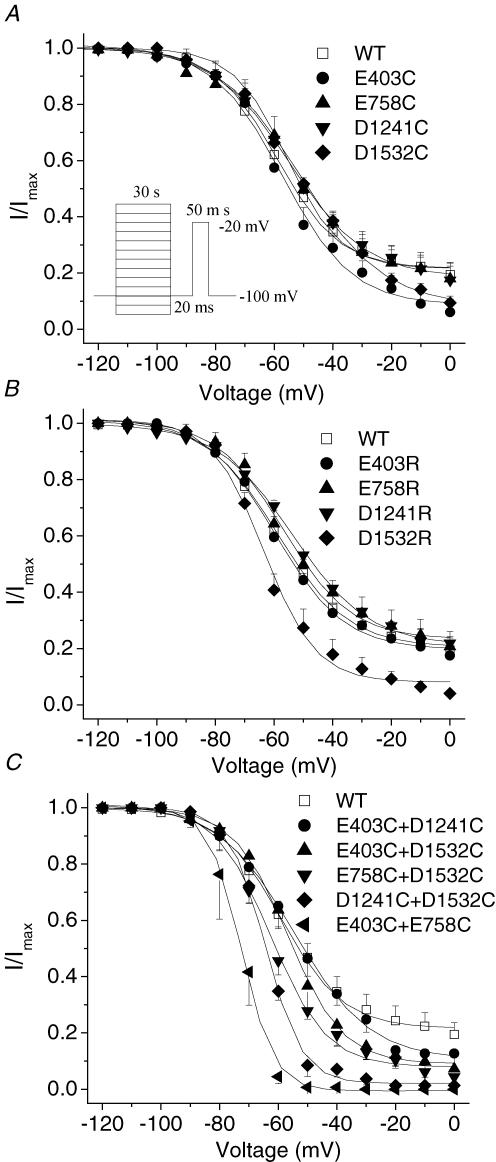
Figure 7. Voltage dependence of steady-state slow inactivation of single-mutant and double-cysteine-mutant channels.
Voltage-dependent slow-inactivation channel availability using the pulse protocol shown in the inset was fitted with a Boltzmann equation. The interval between each episode is 30 s with a holding potential of −100 mV. A–C, the midpoints, slope factors and components of non-inactivated channels of Boltzmann curves are listed in Table 2. D1532R was the only single mutant showing significant changes in voltage-dependent slow-inactivation channel availability (B), whereas E403C + D1421C was the only double mutant that did not show any significant changes in voltage dependence of steady-state slow inactivation compared with wild-type channels. E403C + E758C showed the most profound changes in midpoints, slope factors and components of non-slow-inactivated channels of Boltzmann curves (C).