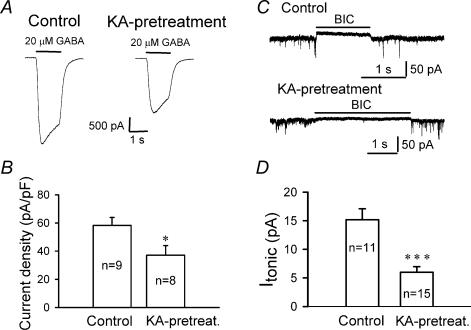
Figure 9. Chronic KA treatment significantly decreases whole-cell GABA currents.
A, representative recordings showing whole-cell currents induced by rapid application of GABA (20 μm) in control (left panel) and KA-treated (right panel) neurons in the presence of TTX (0.5 μm) and CNQX (20 μm). B, bar graphs showing a significant decrease in whole-cell GABAA receptor current density after KA treatment (37.1 ± 6.8 pA pF−1), compared to the control (58.3 ± 5.5 pA pF−1; *P < 0.03). C, typical traces illustrating GABA tonic currents induced by BIC (20 μm) in control and KA-pretreated neurons. D, bar graphs showing a significant decrease of the GABA tonic currents after KA pretreatment (***P < 0.001).