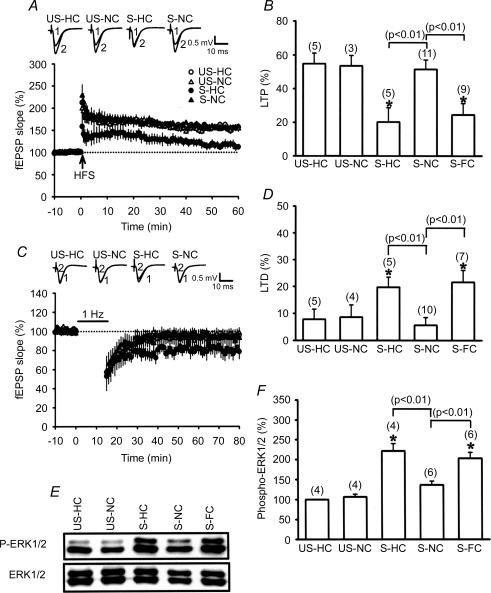
Figure 1. Novelty exploration induces a reversal of stress effects.
A, hippocampal slices obtained from stressed rats that were allowed to explore a novel cage (S-NC) immediately after the stress showed a stable LTP following HFS, whereas slices from stressed rats immediately placed into the home cage (S-HC) did not. US-HC, unstressed rats in home cage; US-NC, unstressed rats in a novel cage. B, comparison of the magnitude of LTP 50 min after HFS. C, animals that received stress plus novelty exploration were impaired in LFS-induced LTD in comparison with animals that received stress plus home cage. D, comparison of the magnitude of LTD 50 min after LFS. E, representative immunoblots show ERK1/2 phosphorylation after stress plus NC, HC or familiar cage (FC) treatment. The corresponding densitometric analysis is shown in F. The number of experiments per group is indicated by n. Asterisks indicate significant difference (P < 0.05) in comparison to the slices from US-HC rats.